Abstract
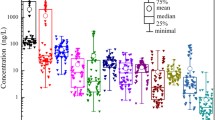
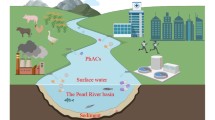
Antidepressants are gaining public attention because of increasing reports of their occurrence in environment and their potential impact on ecosystems and human health. Continuous input of pharmaceuticals into rivers, through psychiatric hospital or wastewater treatment plant (WWTPs) effluent, may cause adverse effects on the aquatic ecosystems of the receiving water bodies. This work investigates the occurrence and sources of 8 antidepressants in main stream and tributaries of Huangpu River in Shanghai. The detected concentrations of the selected antidepressants ranged from low nanogram per liter to 42.9 ng L−1 (fluoxetine) in main stream and ranged from low nanogram per liter to 33.7 ng L−1 (fluoxetine) in tributaries. To study the effect of hospital or wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) on environment, the upstream and downstream samples were analyzed. Generally, antidepressants had greater concentrations in downstream than that in upstream of the WWTPs or hospitals. It is suggesting that WWTPs and hospitals may introduce pollution into water environment. A preliminary risk assessment was conducted: none of the eight target compounds yielded risk quotient (RQ) values more than 0.1, thus indicating that no adverse effect is expected in water environment. These results will provide background data for future antidepressants pollution control and management in Shanghai, China.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboulfadl K, De Potter C, Prevost M, Sauve S (2010) Time-dependent integrity during storage of natural surface water samples for the trace analysis of pharmaceutical products, feminizing hormones and pesticides. Chem Cent J 4
Barclay VKH, Tyrefors NL, Johansson IM, Pettersson CE (2011) Trace analysis of fluoxetine and its metabolite norfluoxetine. Part I: development of a chiral liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for wastewater samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:5587–5596
Batt AL, Kostich MS, Lazorchak JM (2008) Analysis of ecologically relevant pharmaceuticals in wastewater and surface water using selective solid-phase extraction and UPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem 80:5021–5030
Besse JP, Kausch-Barreto C, Garric J (2008) Exposure assessment of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in the aquatic environment: application to the French situation and preliminary prioritization. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 14:665–695
Besse J, Latour J, Garric J (2012) Anticancer drugs in surface waters what can we say about the occurrence and environmental significance of cytotoxic, cytostatic and endocrine therapy drugs? Environ Int 39:73–86
Dai G, Wang B, Huang J, Dong R, Deng S, Yu G (2015) Occurrence and source apportionment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the Beiyun River of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 119:1033–1039
de Castro A, Femandez MDMR, Laloup M, Samyn N, De Boeck G, Wood M, Maes V, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2007) High-throughput on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous analysis of 14 antidepressants and their metabolites in plasma. J Chromatogr A 1160:3–12
Di Poi C, Evariste L, Serpentini A, Halm-Lemeille MP, Lebel JM, Costil K (2014) Toxicity of five antidepressant drugs on embryo-larval development and metamorphosis success in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:13302–13314
Fang Y, Zhu D-q, Shen X-y (2016) Analysis on usage of antidepressants in outpatient of shanghai Tongji hospital in 2015. Drugs Clinic 11:1852–1855 In Chinese with English abstract
Fedorova G, Randak T, Golovko O, Kodes V, Grabicova K, Grabic R (2014) A passive sampling method for detecting analgesics, psycholeptics, antidepressants and illicit drugs in aquatic environments in the Czech Republic. Sci Total Environ 487:681–687
Ferrer I, Thurman EM (2010) Identification of a new antidepressant and its glucuronide metabolite in water samples using liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 82:8161–8168
Fong PP, Hoy CM (2012) Antidepressants (venlafaxine and citalopram) cause foot detachment from the substrate in freshwater snails at environmentally relevant concentrations. Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 45:145–153
Ge D, Lee HK (2013) Ionic liquid based dispersive liquid liquid microextraction coupled with micro-solid phase extraction of antidepressant drugs from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1317:217–222
Gu J, Li W, Huang J, Han B (2012) Numerical study on the impact of the sewage drainage on water quality of Shanghai water sources. Adv Mater Res 1020–1026
Henry TB, Kwon JW, Armbrust KL, Black MC (2004) Acute and chronic toxicity of five selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2229–2233
Himmelsbach M, Buchberger W, Klampfl CW (2006) Determination of antidepressants in surface and waste water samples by capillary electrophoresis with electrospray ionization mass spectrometric detection after preconcentration using off-line solid-phase extraction. Electrophoresis 27:1220–1226
Hird CM, Urbina MA, Lewis CN, Snape JR, Galloway TS (2016) Fluoxetine exhibits pharmacological effects and trait-based sensitivity in a marine worm. Environ Sci Technol 50:8344–8352
Johnson DJ, Sanderson H, Brain RA, Wilson CJ, Solomon KR (2007) Toxicity and hazard of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, and sertraline to algae. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67:128–139
Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Dinsdale RM, Guwy AJ (2007) Multi-residue method for the determination of basic/neutral pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in surface water by solid-phase extraction and ultra performance liquid chromatography-positive electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1161:132–145
Kirchherr H, Kuehn-Velten WN (2006) Quantitative determination of forty-eight antidepressants and antipsychotics in human serum by HPLC tandem mass spectrometry: a multi-level, single-sample approach. J Chromatogr B 843:100–113
Kwon JW, Armbrust KL (2006) Laboratory persistence and fate of fluoxetine in aquatic environments. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2561–2568
Lajeunesse A, Gagnon C, Sauve S (2008) Determination of basic antidepressants and their n-desmethyl metabolites in raw sewage and wastewater using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 80:5325–5333
Lamas JP, Salgado-Petinal C, Garcia-Jares C, Llompart M, Cela R, Gomez M (2004) Solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the analysis of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in environmental water. J Chromatogr A 1046:241–247
Ma RX, Wang B, Lu SY, Zhang YZ, Yin L, Huang J, Deng SB, Wang YJ, Yu G (2016) Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Dongting Lake, China: occurrence, chiral profiling and environmental risk. Sci Total Environ 557:268–275
Mansour F, Al-Hindi M, Saad W, Salam D (2016) Environmental risk analysis and prioritization of pharmaceuticals in a developing world context. Sci Total Environ 557:31–43
Metcalfe CD, Chu S, Judt C, Li H, Oakes KD, Servos MR, Andrews DM (2010) Antidepressants and their metabolites in municipal wastewater, and downstream exposure in an urban watershed. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:79–89
Nalecz-Jawecki G, Sawicki J (2005) Influence of water hardness on the toxicity of selected pharmaceuticals and metals to the protozoa Spirostomum ambiguum and Tetrahymena termophila. Fresenius Environ Bull 14:873–877
Nevado J, Salcedo A (2002) Method development and validation for the simultaneous determination of five selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors by capillary zone electrophoresis. Chromatographia 55:369–373
Ort C, Lawrence MG, Rieckermann J, Joss A (2010) Sampling for pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and illicit drugs in wastewater systems: are your conclusions valid? A critical review. Environ Sci Technol 44:6024–6035
Paterson G, Metcalfe CD (2008) Uptake and depuration of the anti-depressant fluoxetine by the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere 74:125–130
Richmond EK, Rosi-Marshall EJ, Lee SS, Thompson RM, Grace MR (2016) Antidepressants in stream ecosystems: influence of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) on algal production and insect emergence. Freshw Sci 35:845–855
Schultz MM, Furlong ET, Kolpin DW, Werner SL, Schoenfuss HL, Barber LB, Blazer VS, Norris DO, Vajda AM (2010) Antidepressant pharmaceuticals in two US effluent-impacted streams: occurrence and fate in water and sediment, and selective uptake in fish neural tissue. Environ Sci Technol 44:1918–1925
Schultzt MM, Furlong ET (2008) Trace analysis of antidepressant pharmaceuticals and their select degradates in aquatic matrixes by LC/ESI/MS/MS. Anal Chem 80:1756–1762
Subedi B, Kannan K (2015) Occurrence and fate of select psychoactive pharmaceuticals and antihypertensives in two wastewater treatment plants in New York State, USA. Sci Total Environ 514:273–280
To SE, Zepf RA, Woods AG (2005) The symptoms, neurobiology, and current pharmacological treatment of depression. J Neurosci Nurs 37
Valcarcel Y, Gonzalez Alonso S, Rodriguez-Gil JL, Gil A, Catala M (2011) Detection of pharmaceutically active compounds in the rivers and tap water of the Madrid region (Spain) and potential ecotoxicological risk. Chemosphere 84:1336–1348
Xu R, Lee HK (2014) Application of electro-enhanced solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of tricyclic antidepressants in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1350:15–22
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41430644, 41473090, 41173120, 11175112) and by Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University No. IRT13078. Project supported by Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (13230500600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Kallenborn
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 190 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Xiang, J., Chen, F. et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of antidepressants in Huangpu River of Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 20291–20299 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9293-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9293-x