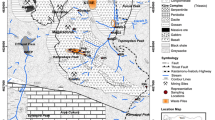
Abstract
The tools developed for acid mine drainage (AMD) prediction were proven unsuccessful to predict the geochemical behavior of mine waste rocks having a significant chemical sorption capacity, which delays the onset of contaminated neutral drainage (CND). The present work was performed in order to test a new approach of water quality prediction, by using a chelating agent solution (0.03 M EDTA, or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) in kinetic testing used for the prediction of the geochemical behavior of geologic material. The hypothesis underlying the proposed approach is that the EDTA solution should chelate the metals as soon as they are released by sulfide oxidation, inhibiting their sorption or secondary precipitation, and therefore reproduce a worst-case scenario where very low metal attenuation mechanisms are present in the drainage waters. Fresh and weathered waste rocks from the Lac Tio mine (Rio tinto, Iron and Titanium), which are known to generate Ni-CND at the field scale, were submitted to small-scale humidity cells in control tests (using deionized water) and using an EDTA solution. Results show that EDTA effectively prevents the metals to be sorbed or to precipitate as secondary minerals, therefore enabling to bypass the delay associated with metal sorption in the prediction of water quality from these materials. This work shows that the use of a chelating agent solution is a promising novel approach of water quality prediction and provides general guidelines to be used in further studies, which will help both practitioners and regulators to plan more efficient management and disposal strategies of mine wastes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade MD, Prasher SO, Hendershot WH (2007) Optimizing the molarity of a EDTA washing solution for saturated-soil remediation of trace metal contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 147:781–790
ASTM Standard D4892 (2014) Standard test method for density of solid pitch (Helium Pycnometer Method), West Conshohocken, PA, doi: 10.1520/D4892; www.astm.org
Benzaazoua M, Bussière B, Dagenais AM, Archambault M (2004) Kinetic tests comparison and interpretation for prediction of the Joutel tailings acid generation potential. Environ Geol 46:1086–1101
Blake RE, Walter LM (1999) Kinetics of feldspar and quartz dissolution at 70–80°C and near-neutral pH: effects of organic acids and NaCl. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:2043–2059
Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Jambor JL, Weisener CG (2003) The geochemistry of acid mine drainage. In: Holland H.D., Turekian K.K. (Eds), Treatise on Geochemistry, Ch 9.05. Pergamon, Oxford, pp. 149–204, ISBN: 978-0-08-043751-4
Bondietti G, Sinniger J, Stumm W (1993) The reactivity of Fe(III) (hydr)oxides: effects of ligands in inhibiting the dissolution. Colloids Surf A 79:157–167
Bouzahzah H, Benzaazoua M, Bussiere B, Plante B (2014) Prediction of acid mine drainage: importance of mineralogy and the test protocols for static and kinetic tests. Mine Water Environ 33:54–65. doi:10.1007/s10230-013-0249-1
Brantley SL (2008) Kinetics of mineral dissolution. In Kinetics of water-rock interaction. Brantley SL, Kubicki JD, White AF (eds) Springer Science + Business Media, ISBN 978-0-387-73562-7, 834p
Bridge TAM, Johnson DB (1998) Reduction of soluble iron and reductive dissolution of ferric iron- containing minerals by moderately thermophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2181–2186
Bussière B, Demers I, Dawood I, Plante B, Aubertin M, Peregoedova A, Pepin G, Lessard G, Intissar R, Benzaazoua M, Molson JW, Chouteau M, Zagury GJ, Monzon M, Laflamme D (2011) Comportement géochimique et hydrogéologique des stériles de la mine Lac Tio. Paper presented at the Symposium sur l'environnement et les mines. Rouyn-Noranda, QC, Canada
Cravotta CA III (2008) Dissolved metals and associated constituents in abandoned coal-mine discharges, Pennsylvania, USA. Part 2: geochemical controls on constituent concentrations. Appl Geochem 23:203–226
Cruz R, Bertrand V, Monroy M, González I (2001) Effect of sulfide impurities on the reactivity of pyrite and pyritic concentrates: A multi-tool approach. Appl Geochem 16:803–819
Demers I, Bussière B, Plante B (2011) Field retention tests to evaluate nickel retention on mine waste rock. Pan-Am CGS Geotechnical Conference, Toronto, Canada
Demers I, Molson J, Bussière B, Laflamme D (2013) Numerical modeling of contaminated neutral drainage from a waste-rock field test cell. Appl Geochem 33:346–356
Di Palma L, Ferrantelli P (2005) Copper leaching from a sandy soil: Mechanism and parameters affecting EDTA extraction. J Hazard Mater B 122:85–90
Éthier MP (2011) Évaluation du comportement géochimique en conditions normale et froides de différents stériles présent sur le site de la mine Raglan. Master’s thesis, Université du Québec en Abitibi-Témiscamingue, Québec, Canada, 207p
Éthier MP, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M, Nicholson RV, Garneau P (2010) Potential of contaminated neutral drainage generation from waste rock at Raglan. Proceedings of the Canadian Geotechnical Conference Geo 2010, Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 1145-1152
Evangelou MWH, Ebel M, Schaeffer A (2007) Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents. Chemosphere 68:989–1003
Frost MT, Grey IE, Harrowfield IR, Mason K (1983) The dependence of alumina and silica contents on the extent of alteration of weathered ilmenites from Western Australia. Mineral Mag 47:201–208
Hakkou R, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B (2008) Acid mine drainage at the abandoned kettara mine (Morocco): 2. mine waste geochemical behavior. Mine Water Environ 27:160–170
Hallberg KB, Grail BM, Plessis CAD, Johnson DB (2011) Reductive dissolution of ferric iron minerals: a new approach for bio-processing nickel laterites. Miner Eng 24:620–624
Heikkinen P, Räisänen M, Johnson R (2009) Geochemical characterisation of seepage and drainage water quality from two sulphide mine tailings impoundments: acid mine drainage versus neutral mine drainage. Mine Water Environ 28:30–49
Jagetiya B, Sharma A (2013) Optimization of chelators to enhance uranium uptake from tailings for phytoremediation. Chemosphere 91:692–696
Janßen A, Golla-Schindler U, Putnis A (2008) The mechanism of ilmenite leaching during experimental alteration in HCl-solution. EMC 2008 14th European Microscopy Congress 1–5 September 2008, Aachen, Germany, pp. 825-826
Jelusic M, Lestan D (2014) Effect of EDTA washing of metal polluted garden soils. Part I: toxicity hazards and impact on soil properties. Sci Total Environ 475:132–141
Johnson DB (2012) Reductive dissolution of minerals and selective recovery of metals using acidophilic iron- and sulfate-reducing acidophiles. Hydrometallurgy 127–128:172–177
Karlfeldt Fedje K, Ekberg C, Skarnemark G, Steenari BM (2010) Removal of hazardous metals from MSW fly ash—an evaluation of ash leaching methods. J Hazard Mater 173:310–317
Kirpichtchikova TA, Manceau A, Spadini L, Panfili F, Marcus MA, Jacquet T (2006) Speciation and solubility of heavy metals in contaminated soil using X-ray microfluorescence, EXAFS spectroscopy, chemical extraction, and thermodynamic modeling. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:2163–2190
Lawrence RW, Scheske M (1997) A method to calculate the neutralization potential of mining wastes. Environ Geol 32:100–106
Lim TT, Tay JH, Wang JY (2004) Chelating-agent-enhanced heavy metal extraction from a contaminated acidic soil. J Environ Eng 130:59–66
Lindsay MBJ, Condon PD, Jambor JL, Lear KG, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ (2009) Mineralogical, geochemical, and microbial investigation of a sulfide-rich tailings deposit characterized by neutral drainage. Appl Geochem 24:2212–2221
Merkus HG (2009) Particle size measurements: fundamentals, practice, quality. Particle Technology Series, Vol. 17. Springer, 519 p. ISBN 978-1-4020-9016-5
Nair AG, Babu DSS, Damodaran KT, Shankar R, Prabhu CN (2009) Weathering of ilmenite from Chavara deposit and its comparison with Manavalakurichi placer ilmenite, southwestern India. J Asian Earth Sci 34:115–122
Nicholson RV (2004) Overview of near neutral pH drainage and its mitigation: results of a MEND study. MEND Ontario Workshop, Sudbury, Canada
Nicholson RV, Rinker MJ (2000) Metal leaching from sulphide mine waste under neutral pH conditions, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, May 21-24. Denver, Colorado, pp 951–958
Nicholson RV, Gillham RW, Reardon EJ (1989) Pyrite oxidation in carbonate-buffered solution: 2. Rate control by oxide coatings. Reply: Geochim. Cosmochim Acta 54(395):402
Nicholson RV, Rinker MJ, Williams G, Napier W (1999) Assessment of water quality associated with underwater disposal of tailings and waste rock from the Voisey’s Bay Project, Labrador, Canada, Proceedings of the Sudbury’99 Mining and the Environment Conference, September 12-15. Sudbury, Ontario, pp 127–136
Paktunc AD (1999) Mineralogical constraints on the determination of neutralization potential and prediction of acid mine drainage. Environ Geol 39:103–112
Panias D, Taxiarchou M, Paspaliaris I, Kontopoulos A (1996) Mechanisms of dissolution of iron oxides in aqueous oxalic acid solutions. Hydrometallurgy 42:257–265
Parbhakar-Fox A, Lottermoser B, Bradshaw D (2013) Evaluating waste rock mineralogy and microtexture during kinetic testing for improved acid rock drainage prediction. Miner Eng 52:111–124
Peters RW (1999) Chelant extraction of heavy metals from contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 66:151–210
Plante B, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B, Biesinger MC, Pratt AR (2010) Study of Ni sorption onto Tio mine waste rock surfaces. Appl Geochem 25:1830–1844
Plante B, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B (2011a) Kinetic testing and sorption studies by modified weathering cells to characterize the potential to generate contaminated neutral drainage. Mine Water Environ 30:22–37
Plante B, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B (2011b) Predicting geochemical behaviour of waste rock with low acid generating potential using laboratory kinetic tests. Mine Water Environ 30:2–21
Plante B, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M (2012) Static tests response on 5 Canadian hard rock mine tailings with low net acid-generating potentials. J Geochem Explor 114:57–69
Plante B, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M (2014) Lab to field scale effects on contaminated neutral drainage prediction from the Tio mine waste rocks. J Geochem Explor 137:37–47
Price WA, Kwong YTJ (1997) Waste rock weathering, sampling and analysis: observations from the British Columbia Ministry of Employment and Investment Database. In: Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage (ICARD), Vancouver, pp. 31–45
Qiu R, Zou Z, Zhao Z, Zhang W, Zhang T, Dong H, Wei X (2009) Removal of trace and major metals by soil washing with Na2EDTA and oxalate. J Soils Sediments 10:45–53
Rietveld HM (1993) The Rietveld method. Young RA (editor), Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK. ISBN 0-19-855577-6
Ryan JN, Gschwend PM (1991) Extraction of iron oxides from sediments using reductive dissolution by titanium (III). Clays Clay Miner 39(5):509–518
Scheckel KG, Sparks DL (2001) Dissolution kinetics of nickel surface precipitates on clay mineral and oxide surfaces. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:685–694
Sobek AA, Schuller WA, Freeman JR, Smith RW (1978) Field and laboratory methods applicable to overburdens and minesoils. EPA-600/2–78-054. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., USA, pp. 47–50
Tandy S, Bossart K, Mueller R, Ritschel J, Hauser L, Schulin R, Nowack B (2004) Extraction of heavy metals from soils using biodegradable chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 38:937–944
Tsang DCW, Zhang W, Lo IMC (2007) Copper extraction effectiveness and soil dissolution issues of EDTA-flushing of artificially contaminated soils. Chemosphere 68:234–243
USEPA (1999) MINTEQA2, Metal speciation equilibrium model for surface and ground water, version 4.0. http://epa.gov/ceampubl/mmedia/minteq/index.html
Vaxevanidou K, Papassiopi N, Paspaliaris I (2008) Removal of heavy metals and arsenic from contaminated soils using bioremediation and chelant extraction techniques. Chemosphere 70:1329–1337
Villeneuve M, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M (2009) Assessment of interpretation methods for kinetic tests performed on tailings having a low acid generating potential, Paper presented at the Securing the Future and 8th ICARD. Skelleftea, Sweden
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plante, B., Benzaazoua, M., Bussière, B. et al. Use of EDTA in modified kinetic testing for contaminated drainage prediction from waste rocks: case of the Lac Tio mine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 7882–7896 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4106-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4106-6