Abstract
Introduction
Brain death (BD) is the irreversible cessation of all functions of the entire brain, including the brainstem. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a biological liquid that circulates in brain and spine. Metabolomics is able to reveal the response of biological systems to diverse factors in a specific moment or condition. Therefore, the study of this neurological condition through metabolic profiling using high resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is important for understanding biochemical events.
Objectives
The aim of the current study is to identify the metabolomics signature of BD using 1H-NMR spectroscopy in human CSF.
Methods
1H-NMR spectroscopy has been employed for metabolomic untargeted analysis in 46 CSF samples: 22 control and 24 with BD. Spectral data were further subjected to multivariate analysis.
Results
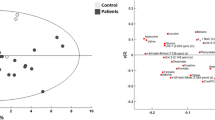
Statistically significant multivariate models separated subject’s samples with BD from controls and revealed twenty one discriminatory metabolites. The statistical analysis of control and BD subjects using Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA) model resulted in R2X of 0.733 and Q2 of 0.635. An elevation in the concentration of statistically discriminant metabolites in BD was observed.
Conclusion
This study identifies a metabolic signature associated with BD and the most relevant enriched selected metabolic pathways.
Graphic Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankarcrona, M., Dypbukt, J. M., Bonfoco, E., Zhivotovsky, B., Orrenius, S., Lipton, S. A., & Nicotera, P. (1995). Glutamate-induced neuronal death: A succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron, 15(4), 961–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(95)90186-8
Arroyo, A., Rosel, P., & Marron, T. (2005). Cerebrospinal fluid: Postmortem biochemical study. Journal of Clinical Forensic Medicine, 12(3), 153–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcfm.2004.11.001
Bak, L. K., Schousboe, A., & Waagepetersen, H. S. (2006). The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. Journal of Neurochemistry, 98(3), 641–653. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03913.x
Barklin, A. (2009). Systemic inflammation in the brain-dead organ donor. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 53(4), 425–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01879.x
Brasil, S., Bor-Seng-Shu, E., de Lima-Oliveira, M., Azevedo, M. K., Teixeira, M. J., Bernardo, L., & Bernardo, W. M. (2016). Role of computed tomography angiography and perfusion tomography in diagnosing brain death: A systematic review. Journal of Neuroradiology, 43(2), 133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2015.07.006
Brodersen, P., & Jorgensen, E. O. (1974). Cerebral blood flow and oxygen uptake, and cerebrospinal fluid biochemistry in severe coma. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 37(4), 384–391. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.37.4.384
Chamoun, R., Suki, D., Gopinath, S. P., Goodman, J. C., & Robertson, C. (2011). Role of extracellular glutamate measured by cerebral microdialysis in severe traumatic brain injury. Bone, 23(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.12.JNS09689
Chatterji, T., Singh, S., Sen, M., Singh, A. K., Agarwal, G. R., Singh, D. K., et al. (2017). Proton NMR metabolic profiling of CSF reveals distinct differentiation of meningitis from negative controls. Clinica Chimica Acta, 469, 42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2017.03.015
Chatterji, T., Singh, S., Sen, M., Singh, A. K., Maurya, P. K., Husain, N., et al. (2016). Comprehensive1H NMR metabolic profiling of body fluids for differentiation of meningitis in adults. Metabolomics, 12(8), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1073-y
Cocco, E., Murgia, F., Lorefice, L., Barberini, L., Poddighe, S., Frau, J., et al. (2016). 1H-NMR analysis provides A metabolomic profile of patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology: Neuroimmunology and NeuroInflammation, 3(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXI.0000000000000185
Condori, R. E., David, D., Encarnacion, R., & Fatteh, N. (2016). Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid from humans treated for rabies. Journal of Proteome Research, 12(1), 481–490. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr3009176
Cooper, A. J. L., & Jeitner, T. M. (2016). Central role of glutamate metabolism in the maintenance of nitrogen homeostasis in normal and hyperammonemic brain. Biomolecules, 6(2), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6020016
Cooper, A. J. L., & Lai, J. C. K. (1987). Cerebral ammonia metabolism in normal and hyperammonemic rats. Neurochemical Pathology, 6(1–2), 67–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02833601
Cooper, A. J. L., Mora, S. N., Cruz, N. F., & Gelbard, A. S. (1985). Cerebral ammonia metabolism in hyperammonemic rats. Journal of Neurochemistry, 44(6), 1716–1723. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07159.x
Cruz, T., Balayssac, S., Gilard, V., Martino, R., Vincent, C., Pariente, J., & Malet-Martino, M. (2014). 1H NMR analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from Alzheimer’s disease patients: An example of a possible misinterpretation due to non-adjustment of pH. Metabolites, 4(1), 115–128. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4010115
DeSalles, A. A. F., Kontos, H. A., Becker, D. P., Yang, M. S., Ward, J. D., Moulton, R., et al. (1986). Prognostic significance of ventricular CSF lactic acidosis in severe head injury. Journal of Neurosurgery, 65(5), 615–624. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1986.65.5.0615
Di Meo, S., Reed, T. T., Venditti, P., & Victor, V. M. (2016). Role of ROS and RNS sources in physiological and pathological conditions. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1245049
Dickens, A. M., Larkin, J. R., Griffin, J. L., Cavey, A., Matthews, L., Turner, M. R., et al. (2014). A type 2 biomarker separates relapsing-remitting from secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 83(17), 1492–1499. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000905
Ellinger, J. J., Chylla, R. A., Ulrich, E. L., & Markley, J. L. (2011). Databases and software for NMR-based metabolomics James. Bone, 72(2), 132–135. https://doi.org/10.2174/2213235x11301010028
Emwas, A. H., Roy, R., McKay, R. T., Tenori, L., Saccenti, E., Nagana Gowda, G. A., et al. (2019). Nmr spectroscopy for metabolomics research. Metabolites, 9(7), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9070123
Emwas, A. H., Saccenti, E., Gao, X., McKay, R. T., dos Santos, V. A. P. M., Roy, R., & Wishart, D. S. (2018). Recommended strategies for spectral processing and post-processing of 1D 1 H-NMR data of biofluids with a particular focus on urine. Metabolomics, 14(3), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1321-4
Emwas, A. H. M., Salek, R. M., Griffin, J. L., & Merzaban, J. (2013). NMR-based metabolomics in human disease diagnosis: Applications, limitations, and recommendations. Metabolomics, 9(5), 1048–1072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0524-y
Engelke, U. F. H., Kremer, B., Kluijtmans, L. A. J., van der Graaf, M., Morava, E., Loupatty, F. J., et al. (2006). NMR spectroscopic studies on the late onset form of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type I and other defects in leucine metabolism. NMR in Biomedicine, 19(2), 271–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1018
Eriksson, L., Antti, H., Gottfries, J., Holmes, E., Johansson, E., Lindgren, F., et al. (2004). Using chemometrics for navigating in the large data sets of genomics, proteomics, and metabonomics (gpm). Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 380, 419–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2783-y
Floerchinger, B., Oberhuber, R., & Tullius, S. G. (2012). Effects of brain death on organ quality and transplant outcome. Transplantation Reviews, 26(2), 54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trre.2011.10.001
French, C. D., Willoughby, R. E., Pan, A., Wong, S. J., Foley, J. F., Wheat, L. J., et al. (2018). NMR metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid differentiates inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 12(12), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0007045
Girela, E., Villanueva, E., Irigoyen, P., Girela, V., Hernández-Cueto, C., & Peinado, J. M. (2008). Free amino acid concentrations in vitreous humor and cerebrospinal fluid in relation to the cause of death and postmortem interval. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 53(3), 730–733. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2008.00726.x
Gonzalez-Riano, C., Tapia-González, S., García, A., Muñoz, A., DeFelipe, J., & Barbas, C. (2017). Metabolomics and neuroanatomical evaluation of post-mortem changes in the hippocampus. Brain Structure and Function, 222(6), 2831–2853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1375-5
Govindaraju, V., Young, K., & Maudsley, A. A. (2000). Proton NMR chemical shifts and coupling constants for brain metabolites. NMR in Biomedicine, 13(3), 129–153. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-1492(200005)13:3%3c129::AID-NBM619%3e3.0.CO;2-V
Graça, G., Desterro, J., Sousa, J., Fonseca, C., Silveira, M., Serpa, J., et al. (2017). Identification of putative biomarkers for leptomeningeal invasion in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma by NMR metabolomics. Metabolomics, 13(11), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1269-9
Griffin, J. L. (2003). Metabonomics: NMR spectroscopy and pattern recognition analysis of body fluids and tissues for characterisation of xenobiotic toxicity and disease diagnosis. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 7(5), 648–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.08.008
Güzel, Y., Koç, Z. P., Mitil, H. A., Köm, M., Belin Özer, A., Ibrahim Özercan, H., & Balci, T. A. (2014). Brain death scintigraphy and pathology results in a rat model. Experimental and Clinical Transplantation, 12(2), 143–147. https://doi.org/10.6002/ect.2013.0026
Häberle, J. (2011). Clinical practice: The management of hyperammonemia. European Journal of Pediatrics, 170(1), 21–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-010-1369-2
Harker, M., Coulson, H., Fairweather, I., Taylor, D., & Daykin, C. A. (2006). Study of metabolite composition of eccrine sweat from healthy male and female human subjects by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Metabolomics, 2(3), 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-006-0024-4
Holmes, E., & Antti, H. (2002). Chemometric contributions to the evolution of metabonomics: Mathematical solutions to characterising and interpreting complex biological NMR spectra. The Analyst, 127(12), 1549–1557. https://doi.org/10.1039/b208254n
Ith, M., Bigler, P., Scheurer, E., Kreis, R., Hofmann, L., Dirnhofer, R., & Boesch, C. (2002). Observation and identification of metabolites emerging during postmortem decomposition of brain tissue by means of in situ 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 48(5), 915–920. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.10294
Jeon, J. P., Yun, T., Jin, X., Cho, W. S., Son, Y. J., Bang, J. S., et al. (2015). 1H-NMR-based metabolomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from adult bilateral moyamoya disease: Comparison with unilateral moyamoya disease and atherosclerotic stenosis. Medicine (United States), 94(17), e629. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000000629
Kim, H. H., Jeong, I. H., Hyun, J. S., Kong, B. S., Kim, H. J., & Park, S. J. (2017). Metabolomic profiling of CSF in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder by nuclear magnetic resonance. PLoS ONE, 12(7), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181758
Koura, S. S., Doppenberg, E. M. R., Marmarou, A., Choi, S., Young, H. F., & Bullock, R. (1998). Relationship between excitatory amino acid release and outcome after severe human head injury. Acta Neurochirurgica, Supplement, 1998(SUPPL. 71), 244–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6475-4_70
Lebon, V., Petersen, K. F., Cline, G. W., Shen, J., Mason, G. F., Dufour, S., et al. (2002). Astroglial contribution to brain energy metabolism in humans revealed by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Elucidation of the dominant pathway for neurotransmitter glutamate repletion and measurement of astrocytic oxidative metabolism. Journal of Neuroscience, 22(5), 1523–1531. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-05-01523.2002
Li, Z., Du, B., Zheng, X., Jia, H., Xing, A., Sun, Q., et al. (2017). Cerebrospinal fluid metabolomic profiling in tuberculous and viral meningitis: Screening potential markers for differential diagnosis. Clinica Chimica Acta, 466, 38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2017.01.002
Long, F. H. (2013). Multivariate analysis for metabolomics and proteomics data. Proteomic and Metabolomic Approaches to Biomarker Discovery. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394446-7.00019-4
Lu, C., & Malenka, R. C. (2012). NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation and long-term depression (LTP/LTD). Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 4(6), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a005710
Maciejewski, P. K., & Rothman, D. L. (2008). Proposed cycles for functional glutamate trafficking in synaptic neurotransmission. Neurochemistry International, 52(4–5), 809–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2007.09.015
Madeira, C., Vargas-Lopes, C., Otávio Brandão, C., Reis, T., Laks, J., Panizzutti, R., & Ferreira, S. T. (2018). Elevated glutamate and glutamine levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease and depression. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00561
Maillet, S., Vion-Dury, J., Confort-Gouny, S., Nicoli, F., Lutz, N. W., Viout, P., & Cozzone, P. J. (1998). Experimental protocol for clinical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid by high resolution proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Brain Research Protocols, 3(2), 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-299X(98)00033-6
Mandal, R., Guo, A. C., Chaudhary, K. K., Liu, P., Yallou, F. S., Dong, E., et al. (2012). Multi-platform characterization of the human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome: A comprehensive and quantitative update. Genome Medicine, 4(4), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/gm337
Mochel, F. (2010). Nuclear magnetic resonance of cerebrospinal fluid: The neurometabolome. Methodologies for Metabolomics: Experimental Strategies and Techniques. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511996634.016
Mora-Ortiz, M., Trichard, M., Oregioni, A., & Claus, S. P. (2019). Thanatometabolomics: Introducing NMR-based metabolomics to identify metabolic biomarkers of the time of death. Metabolomics, 15(3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1498-1
Mussap, M., Antonucci, R., Noto, A., & Fanos, V. (2013). The role of metabolomics in neonatal and pediatric laboratory medicine. Clinica Chimica Acta, 426, 127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2013.08.020
Nathan, S., & Greer, D. M. (2006). Brain death. Seminars in Anesthesia, Perioperative Medicine and Pain, 25(4), 225–231. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sane.2006.09.005
National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws. (1980). Uniform Determination of Death Act - Model Statute, 8(5), pp. 1–8. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20502147
Nicholson, J. K., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (1999). “Metabonomics”: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica, 29(11), 1181–1189. https://doi.org/10.1080/004982599238047
O’Sullivan, A., Willoughby, R. E., Mishchuk, D., Alcarraz, B., Cabezas-Sanchez, C., Condori, R. E., et al. (2013). Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid from humans treated for rabies. Journal of Proteome Research, 12(1), 481–490. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr3009176
Park, S. J., Kim, J. K., Kim, H. H., Yoon, B. A., Ji, D. Y., Lee, C. W., et al. (2019). Integrative metabolomics reveals unique metabolic traits in Guillain-Barré Syndrome and its variants. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37572-w
Patel, A. B., De Graaf, R. A., Mason, G. F., Rothman, D. L., Shulman, R. G., & Behar, K. L. (2005). The contribution of GABA to glutamate/glutamine cycling and energy metabolism in the rat cortex in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(15), 5588–5593. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0501703102
Pellerin, L., & Magistretti, P. J. (1994). Glutamate uptake into astrocytes stimulates aerobic glycolysis: A mechanism coupling neuronal activity to glucose utilization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 91(22), 10625–10629. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.22.10625
Pesko, B. K., Weidt, S., McLaughlin, M., Wescott, D. J., Torrance, H., Burgess, K., & Burchmore, R. (2020). Postmortomics: The potential of untargeted metabolomics to highlight markers for time since death. OMICS A Journal of Integrative Biology, 24(11), 649–659. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2020.0084
Ramadan, S., Lin, A., & Stanwell, P. (2013). Glutamate and glutamine: A review of in vivo MRS in the human brain. NMR in Biomedicine, 26(12), 1630–1646. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.3045
Reinke, S. N., Broadhurst, D. I., Sykes, B. D., Baker, G. B., Catz, I., Warren, K. G., & Power, C. (2014). Metabolomic profiling in multiple sclerosis: Insights into biomarkers and pathogenesis. Multiple Sclerosis, 20(10), 1396–1400. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458513516528
Ren, S., Hinzman, A. A., Kang, E. L., Szczesniak, R. D., & Lu, L. J. (2015). Computational and statistical analysis of metabolomics data. Metabolomics, 11(6), 1492–1513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0823-6
Romeo, M. J., Espina, V., Lowenthal, M., Espina, B. H., Petricoin, E. F., & Liotta, L. A. (2005). CSF proteome: A protein repository for potential biomarker identification. Expert Review of Proteomics, 2(1), 57–70. https://doi.org/10.1586/14789450.2.1.57
Rosst, B. D. (1990). Biochemical considerations in 1H spectroscopy. Glutamate and glutamine; myo-inositol and related metabolites. NMR in Biomedicine, 4, 59–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1940040205
Rothman, D. L., de Graaf, R. A., Hyder, F., Mason, G. F., Behar, K. L., & De Feyter, H. M. (2019). In vivo 13C and 1H-[13C] MRS studies of neuroenergetics and neurotransmitter cycling, applications to neurological and psychiatric disease and brain cancer. NMR in Biomedicine, 32(10), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4172
Rubtsov, D. V., Jenkins, H., Ludwig, C., Easton, J., Viant, M. R., Günther, U., et al. (2007). Proposed reporting requirements for the description of NMR-based metabolomics experiments. Metabolomics, 3(3), 223–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-006-0040-4
(1996). special article Practice parameters for determining brain death in adults, pp. 1012–1014
Spector, R., Robert Snodgrass, S., & Johanson, C. E. (2015). A balanced view of the cerebrospinal fluid composition and functions: Focus on adult humans. Experimental Neurology, 273, 57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.07.027
Spinello, I. M. (2015). Brain death determination. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine, 30(6), 326–337. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066613511053
Stefani, M. A., Modkovski, R., Hansel, G., Zimmer, E. R., Kopczynski, A., Muller, A. P., et al. (2017). Elevated glutamate and lactate predict brain death after severe head trauma. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, 4(6), 392–402. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.416
Stoop, M. P., Coulier, L., Rosenling, T., Shi, S., Smolinska, A. M., Buydens, L., et al. (2010). Quantitative proteomics and metabolomics analysis of normal human cerebrospinal fluid samples. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 9(9), 2063–2075. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M110.000877
Swain, R., Kumar, A., Sahoo, J., Lakshmy, R., Gupta, S. K., Bhardwaj, D. N., & Pandey, R. M. (2015). Estimation of post-mortem interval: A comparison between cerebrospinal fluid and vitreous humour chemistry. Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine, 36, 144–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jflm.2015.09.017
Takata, T., Kitao, T., & Miyaishi, S. (2014). Relationship between post-mortem interval and creatine concentration in vitreous humour and cerebrospinal fluid. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences, 46(2), 160–165. https://doi.org/10.1080/00450618.2013.824027
Weljie, A. M., Newton, J., Mercier, P., Carlson, E., & Slupsky, C. M. (2006). Targeted pofiling: Quantitative analysis of1H NMR metabolomics data. Analytical Chemistry, 78(13), 4430–4442. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac060209g
Wevers, R. A., Engelke, U., Wendel, U., De Jong, J. G. N., Gabreels, F. J. M., & Heerschap, A. (1995). Standardized method for high-resolution 1H-NMR of cerebrospinal fluid. Clinical Chemistry, 41(5), 744–751. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/41.5.744
Wijdicks, E. F. M., Varelas, P. N., Gronseth, G. S., & Greer, D. M. (2011). Evidence-based guideline update: Determining brain death in adults: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology, 76(3), 1911–1918. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e242a8
Wishart, D. S. (2008). Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27(3), 228–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2007.12.001
Wishart, D. S., Lewis, M. J., Morrissey, J. A., Flegel, M. D., Jeroncic, K., Xiong, Y., et al. (2008). The human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome. Journal of Chromatography B, 871(2), 164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.05.001
Worley, B., & Powers, R. (2012). Multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Current Metabolomics, 1(1), 92–107. https://doi.org/10.2174/2213235x130108
Wu, J., Wuolikainen, A., Trupp, M., Jonsson, P., Marklund, S. L., Andersen, P. M., et al. (2016). NMR analysis of the CSF and plasma metabolome of rigorously matched amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. Metabolomics, 12(6), 101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1041-6
Xia, J., & Wishart, D. S. (2011). Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nature Protocols, 6(6), 743–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.319
Xia, J., & Wishart, D. S. (2016). Using metaboanalyst 3.0 for comprehensive metabolomics data analysis. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.11
Xia, J., Wishart, D. S., & Valencia, A. (2011). MetPA: A web-based metabolomics tool for pathway analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics, 27(13), 2342–2344. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq418
Zhang, S., Gowda, G. A. N., Ye, T., & Raftery, D. (2016). Advances in NMR-based biofluid analysis and metabolite profiling. Physiology & Behavior, 176(1), 100–106. https://doi.org/10.1039/c000091d.Advances
Zielman, R., Postma, R., Verhoeven, A., Bakels, F., Van Oosterhout, W. P. J., Meissner, A., et al. (2016). Metabolomic changes in CSF of migraine patients measured with 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Molecular BioSystems, 12(12), 3674–3682. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00424e
Acknowledgements
This work is dedicated to the memory of our late coworkers Dra. Sandra Porcayo-Liborio and Dr. Rolando Antonio Arguedas Camacho. MEGA gratefully acknowledges CONACYT for the PhD scholarship 295848. This study was developed at LURMN at IQ-UNAM, which is funded by CONACYT—Mexico (Project 0224747), and UNAM. The authors thank for the sample collection to the residents of INNyN Gonzalo Flores Chagolla, Francisco Bejarano Rodríguez, Emma Ortiz Islas, Elizabeth Mendoza Portillo, Fernando Jose Roosemberg Ordonez and Julissa Abreu Ramirez.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NEE and MLLA conceived the research. SPL, CMRA and JCP selected the subjects, supervised the patient’s care and the sample collection. MEGA and NEE design and perform NMR analysis. MEGA, NEE and ERSM perform chemometric analysis. MEGA and NEE wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed with the data interpretation, read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was reviewed and approved by the ethical committee of the Instituto Nacional de Neurología y Neurocirugía Manuel Velasco Suárez (Approval Number: 68/17 and 60/18).
Informed consent
CSF samples were collected for routine clinical procedures and analyzed retrospectively. Informed consent for participating in this study was obtained from patients’ family members and directly from individuals.
Research involving human and animal rights
All procedures performed directly from individuals were according to the ethical standards of the Instituto Nacional de Neurología y Neurocirugía Manuel Velasco Suárez (Approval Number: 68/17 and 60/18) and performed in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Aguilera, M.E., de San Miguel, E.R., Cruz-Pérez, J. et al. NMR-based metabolomics of human cerebrospinal fluid identifies signature of brain death. Metabolomics 17, 40 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01794-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01794-3