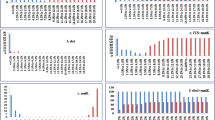
Abstract
In systematic botany, species delimitations are addressed most frequently. The desert date Balanites is a plant with the controversial membership in the Balanitaceae and Zygophyllaceae families. The morphological characters of Balanites showed close relationship with the members of Zygophyllaceae while barcode genes showed relatedness with the members of Celastraceae. On the other hand, Gymnosporia montana, a Celastraceae plant, showed close relatedness with Zygophyllaceae. In this study, cpDNAs (plastomes) of Balanites aegyptiaca and G. montana were extracted, sequenced, and annotated for the detailed analysis. These plastomes were compared and contrasted with plastomes of other members of allied groups from the NCBI databases. The comparative genomics study revealed that B. aegyptiaca related more with family Zygophyllaceae than Celastraceae. Detailed studies performed for molecular marker analysis showed distinction in marker patterns. It is concluded that B. aegyptiaca, assigned in a separate family, may be justifiable at genomic level, and screened markers can be used for identification and authentication. The nucleotide probes identified can be used for identification and authentication of these medicinally important plants.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouelhoda MI, Kurtz S, Ohlebusch E (2004) Replacing suffix trees with enhanced suffix arrays. J Discrete Algorithms 2(1):53–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1570-8667(03)00065-0
Alzahrani DA, Yaradua SS, Albokhari EJ, Abba A (2020) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Barleria prionitis, comparative chloroplast genomics and phylogenetic relationships among Acanthoideae. BMC Genomics 21(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-06798-2
Amer WM, Soliman MM, Sheded MM (2002) Biosystematic studies for Balanites aegyptiaca (Balanitaceae) populations in Egypt. Flora Mediterr 12:353–367
APGIII (Angiosperm Phylogeny Group) (2009) An update of the angiosperm phylogeny group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Bot J Linn Soc 161(2):105–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.2009.00996.x
Asaf S, Khan AL, Khan A, Khan G, Lee IJ, Al-Harrasi A (2020) Expanded inverted repeat region with large scale inversion in the first complete plastid genome sequence of Plantago ovata. Sci Rep 10:3881. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60803-y
Asaf S, Khan AL, Numan M, Al-Harrasi A (2021) Mangrove tree (Avicennia marina): insight into chloroplast genome evolutionary divergence and its comparison with related species from family Acanthaceae. Sci Rep 11(1):3586. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83060-z
Bhatt PP, Thaker VS (2018) The complete chloroplast genome of Cenchrus ciliaris (Poaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour 3(2):674–675. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2018.1481795
Chandrasekara CB, Naranpanawa DNU, Bandusekara BS, Pushpakumara DKNG, Wijesundera DSA, Bandaranayake PC (2021) Universal barcoding regions, rbcL, matK and trnH-psbA do not discriminate Cinnamomum species in Sri Lanka. PLoS One 16(2):e0245592. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245592
Chen Y, Hu N, Wu H (2019) Analyzing and characterizing the chloroplast genome of Salix wilsonii. BioMed Res Int 2019:5190425. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5190425
Chen Y, Wu Y (1994) Progress in research and manufacturing of steroidal sapogenins in China. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 2(3):59–70. https://doi.org/10.1300/J044v02n03_08
Curci PL, De Paola D, Danzi D, Vendramin GG, Sonnante G (2015) Complete chloroplast genome of the multifunctional crop globe artichoke and comparison with other Asteraceae. PLoS One 10(3):0120589. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120589
Dahlgren G (1989) The last Dahlgrenogram. System of classification of the dicotyledons. In: Kit Tan (ed) Plant taxonomy. The Davis & Hedge Festschrift. Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh, p 249–260
Dangi R, Misar A, Tamhankar S, Rao S (2014) Diosgenin content in some Trigonella species. Indian J Adv Plant Res 1(2):47–51
de Vere N, Rich TC, Ford CR, Trinder SA, Long C, Moore CW, Satterthwaite D, Davies H, Allainguillaume J, Ronca S, Tatarinova T (2012) DNA barcoding the native flowering plants and conifers of Wales. PLoS One 7(6):37945. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037945
Deng Y, Luo Y, He Y, Qin X, Li C, Deng X (2020) Complete chloroplast genome of Michelia shiluensis and a comparative analysis with four Magnoliaceae species. Forests 11:267. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030267
Dhru B, Patel B, Lakshmi B, Zaveri M (2011) Pharmacognostical and phytochemical study of leaf of Gymnosporia montana (Vikalo). J Glob Pharma Technol 3(1):23–27
Dhuru B, Jayswal P, Sharma M, Zaveri M, Lakshmi B (2012) In vitro antibacterial activity of Gymnosporia montana against some bacterial strains. Int J Univers Pharm Life Sci 2(1):12–20
Edwards D, Horn A, Taylor D, Savolainen V, Hawkins J (2008) DNA barcoding of a large genus, Aspalathus L. (Fabaceae). Taxon 57:1317–1327. https://doi.org/10.1002/tax.574021
Ennos RA, French GC, Hollingsworth PM (2005) Conserving taxonomic complexity. Trends Ecol Evol 20(4):164–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2005.01.012
Fahn A, Werker E, Baas P (1986) Wood anatomy and identification of trees and shrubs from Israel and adjacent regions. Israel Academy of Science and Humanities, Jerusalem
Feng LY, Liu J, Gao CW, Wu HB, Li GH, Gao LZ (2020) Higher genomic variation in wild than cultivated rubber trees, Hevea brasiliensis, revealed by comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes. Front Ecol Evol 8:237. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2020.00237
Figueiredo E, Smith GF (2008) Plants of Angola/Plantas de Angola. Strelitzia 22. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria
Gruenstaeudl M, Nauheimer L, Borsch T (2017) Plastid genome structure and phylogenomics of Nymphaeales: conserved gene order and new insights into relationships. Plant Syst Evol 303(9):1251–1270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-017-1436-5
Hina F, Jin Z, Yang Z, Li P, Fu C (2018) The complete chloroplast genome of Menispermum dauricum (Menispermaceae, Ranunculales). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour 3(2):913–914. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2018.1501306
Ho VT, Tran TKP, Vu TTT, Widiarsih S (2021) Comparison of matK and rbcL DNA barcodes for genetic classification of jewel orchid accessions in Vietnam. J Gen Eng Biotechnol 19(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00188-1
Hollingsworth PM, Graham SW, Little DP (2011) Choosing and using a plant DNA barcode. PLoS One 6(5):19254. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019254
Hu Y, Woeste KE, Zhao P (2017) Completion of the chloroplast genomes of five Chinese Juglans and their contribution to chloroplast phylogeny. Front Plant Sci 7:1955. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01955
Jansen RK, Saski C, Lee SB, Hansen AK, Daniell H (2011) Complete plastid genome sequences of three rosids (Castanea, Prunus, Theobroma): evidence for at least two independent transfers of rpl22 to the nucleus. Mol Biol Evol 28(1):835–847. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msq261
Jiang KW, Zhang R, Zhang ZF, Pan B, Tian B (2020) DNA barcoding and molecular phylogeny of Dumasia (Fabaceae: Phaseoleae) reveals a cryptic lineage. Plant Divers 42(5):376–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2020.07.007
Khan A, Asaf S, Khan AL, Al-Harrasi A, Al-Sudairy O, Abdul Kareem NM, Khan A, Shehzad T, Alsaady N, Al-Lawati A, Al-Rawahi A (2019) First complete chloroplast genomics and comparative phylogenetic analysis of Commiphora gileadensis and C. foliacea: Myrrh producing trees. PLoS One 14(1):e0208511. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208511
Kim KJ, Lee HL (2004) Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Res 11:247–261. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/11.4.247
Kress WJ, Wurdack KJ, Zimmer EA, Weigt LA, Janzen DH (2005) Use of DNA barcodes to identify flowering plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(23):8369–8374. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0503123102
Lahaye R, Van der Bank M, Bogarin D, Warner J, Pupulin F, Gigot G, Maurin O, Duthoit S, Barraclough TG, Savolainen V (2008) DNA barcoding the floras of biodiversity hotspots. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(8):2923–2928. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709936105
Leaché AD, Oaks JR (2017) The utility of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data in phylogenetics. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 48:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110316-022645
Lee W, Yang JY, Kim SC, Pak JH (2019) Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Ulleung-do Island endemic, Zabelia insularis (Caprifoliaceae), in Korea. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 4(2):4134–4135. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2019.1692730
Li B, Lin F, Huang P, Guo W, Zheng Y (2020) Development of nuclear SSR and chloroplast genome markers in diverse Liriodendron chinense germplasm based on low-coverage whole genome sequencing. Biol Res 53(21):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-020-00289-0
Liu C, Shi L, Zhu Y, Chen H, Zhang J, Lin X, Guan X (2012) CpGAVAS, an integrated web server for the annotation, visualization, analysis, and GenBank submission of completely sequenced chloroplast genome sequences. BMC Genomics 13(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-715
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucl Acids Res 25(5):955–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.955
Magallon S, Crane PR, Herendeen PS (1999) Phylogenetic pattern, diversity, and diversification of eudicots. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 1:297–372. https://doi.org/10.2307/2666180
Masood MS, Nishikawa T, Fukuoka SI, Njenga PK, Tsudzuki T, Kadowaki KI (2004) The complete nucleotide sequence of wild rice (Oryza nivara) chloroplast genome: first genome wide comparative sequence analysis of wild and cultivated rice. Gene 340(1):133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.008
Matthews ML, Endress PK (2004) Comparative floral structure and systematics in Cucurbitales (Corynocarpaceae, Coriariaceae, Tetramelaceae, Datiscaceae, Begoniaceae, Cucurbitaceae, Anisophylleaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 145(2):129–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.2003.00281.x
Mo Z, Lou W, Chen Y, Jia X, Zhai M, Guo Z, Xuan J (2020) The chloroplast genome of Carya illinoinensis: genome structure, adaptive evolution, and phylogenetic analysis. Forests 11(2):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11020207
Monpara J, Thaker V (2021) Phylogenic position and marker studies using cpDNA of C. wightii: a critically endangered and medicinally important plant in India. Vegetos 34(2):300–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-021-00199-w
Mower JP, Vickrey TL (2018) Structural diversity among plastid genomes of land plants. Adv Bot Res 85:263–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.abr.2017.11.013
Narayana L, Satyanarayana P, Radhakrishnaiah H, Bilgrami K, Dogra J (1990) Systematic position of Balanitaceae. Phytochemistry and plant taxonomy. CBS Publications, Delhi, p 157–164
Nour AOB, Salah AAE (2017) Variation in the levels of steroidal sapogenins within the mature fruit of Balanites aegyptiaca and among kernels of Balanites fruit accessions collected from different geographical localities in Sudan. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 8(1):768–780
Pullaih T (2006) Celastraceae. In: Encyclopedia of world medicinal plants, 1st edn. Regency Publications, New Delhi, pp 1316
Qian J, Song J, Gao H, Zhu Y, Xu J, Pang X, Yao H, Sun C, Li XE, Li C, Liu J (2013) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS One 8(2):e57607. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057607
Rono PC, Dong X, Yang JX, Mutie FM, Oulo MA, Malombe I, Kirika PM, Hu GW, Wang QF (2020) Initial complete chloroplast genomes of Alchemilla (Rosaceae): comparative analysis and phylogenetic relationships. Front Genet 11:560368. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.560368
Roy S, Tyagi A, Shukla V, Kumar A, Singh UM, Chaudhary LB, Datt B, Bag SK, Singh PK, Nair NK, Husain T (2010) Universal plant DNA barcode loci may not work in complex groups: a case study with Indian Berberis species. PLoS One 5(10):13674. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013674
Ruggiero F, Bedini G (2020) Phylogenetic and morphologic survey of orbicules in angiosperms. Taxon 69(3):543–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/tax.12281
Sands MJ (1989) Balanitaceae. In: Hedberg I, Edwards S (eds) Flora of Ethiopia 3. Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, pp 433–436
Saski C, Lee SB, Fjellheim S, Guda C, Jansen RK, Luo H, Tomkins J, Rognli OA, Daniell H, Clarke JL (2007) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Hordeum vulgare, Sorghum bicolor and Agrostis stolonifera, and comparative analyses with other grass genomes. Theor Appl Genet 115(4):571–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0567-4
Savolainen V, Fay MF, Albach DC, Backlund A, van der Bank M, Cameron KM, Johnson SA, Lledó MD, Pintaud JC, Powell M, Sheahan MC, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Weston P, Whitten WM, Wurdack KJ, Chase MW (2000) Phylogeny of the eudicots: a nearly complete familial analysis based on rbcL gene sequences. Kew Bull 55(2):257–309. https://doi.org/10.2307/4115644
Schaefer H, Renner SS (2011) Phylogenetic relationships in the order Cucurbitales and a new classification of the gourd family (Cucurbitaceae). Taxon 60(1):122–138. https://doi.org/10.1002/tax.601011
Sheahan MC (2007) Zygophyllaceae. In: Kubitzki K (ed) The families and genera of vascular plants: flowering plants Eudicots. Springer, Berlin, p 488
Sheahan MC, Chase MW (1996) A phylogenetic analysis of Zygophyllaceae R.Br. based on morphological, anatomical and rbcL DNA sequence data. Bot J Linn Soc 122:279–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.1996.tb02077.x
Shipunov AB (2012) Systema angiospermarum. Version 5.7. http://herba.msu.ru/shipunov/ang/current/syang.pdf. Accessed 21 Feb 2022
Singh BP, Kaur I, Gauchan DP (2002) Floral anatomy and systematic position of the genus Balanites. Acta Bot Hung 44(1–2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1556/abot.44.2002.1-2.10
Singh HK, Parveen I, Raghuvanshi S, Babbar SB (2012) The loci recommended as universal barcodes for plants on the basis of floristic studies may not work with congeneric species as exemplified by DNA barcoding of Dendrobium species. BMC Res Notes 5:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-42
Singh AP, Das S, Mazumder A, Kumar M, Gautam N (2017) A perspective review on a novel plant Balanites aegyptiaca (linn.). J Pharm Biol Sci 5(6):273–277
Takhtajan A (2009) Flowering plants. In: Takhatajan A (ed). Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht p 2
Urgamal M, Sanchir C (2016) An update of the family-Level taxonomy of vascular plants in Mongolia. Erforsch biol Ress Mongolei (Halle/Saale) (13):75–81
Vieira MLC, Santini L, Diniz AL, Munhoz CDF (2016) Microsatellite markers: what they mean and why they are so useful. Genet Mol Biol 39:312–328. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2016-0027
Wang C, Liu J, Su Y, Li M, Xie X, Su J (2021) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Sonchus brachyotus helps to elucidate evolutionary relationships with related species of Asteraceae. BioMed Res Int 2021:9410496. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9410496
Wang X, Zhou T, Bai G, Zhao Y (2018) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Fagopyrum dibotrys: genome features, comparative analysis and phylogenetic relationships. Sci Rep 8:12379. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30398-6
Wicke S, Schneeweiss GM, Depamphilis CW, Müller KF, Quandt D (2011) The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol Biol 76(3):273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9762-4
Wiens JJ (2007) Species delimitation: new approaches for discovering diversity. Syst Biol 56(6):875–878. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150701748506
Wu J, Xiao J, Wang L, Zhong J, Yin H, Wu S, Zhang Z, Yu J (2013) Systematic analysis of intron size and abundance parameters in diverse lineages. Sci China Life Sci 56(10):968–974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-013-4540-y
Wyman SK, Jansen RK, Boore JL (2004) Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. J Bioinform 20(17):3252–3255. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth352
Xu J, Feng D, Song G, Wei X, Chen L, Wu X, Li X, Zhu Z (2003) The first intron of rice EPSP synthase enhances expression of foreign gene. Sci China Life Sci 46(6):561–569. https://doi.org/10.1360/02yc0120
Yadav JP, Panghal M (2010) Balanites aegyptiaca (L.) Del. (Hingot): a review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties. Int J Green Pharm 4(3):https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-8258.69158
Yan C, Du J, Gao L, Li Y, Hou X (2019) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of watercress (Nasturtium officinale R. Br.): genome organization, adaptive evolution and phylogenetic relationships in Cardamineae. Gene 699:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.075
Yancai S, Bingbing L (2020) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Stephania kwangsiensis (Menispermaceae), a rare and critically endangered species endemic to China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 5(1):188–189. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2019.1698984
Yang Z, Zhao T, Ma Q, Liang L, Wang G (2018) Comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis revealed the chloroplast genome variation and interspecific relationships of Corylus (Betulaceae) species. Front Plant Sci 9:927. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00927
You FM, Huo N, Gu YQ, Luo MC, Ma Y, Hane D, Lazo GR, Dvorak J, Anderson OD (2008) BatchPrimer3: a high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design. BMC Bioinform 9(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-253
Yu XQ, Drew BT, Yang JB, Gao LM, Li DZ (2017) Comparative chloroplast genomes of eleven Schima (Theaceae) species: insights into DNA barcoding and phylogeny. PLoS One 12(6):e0178026. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178026
Yuan J, Zhang X, Wang M, Sun Y, Liu C, Li S, Yu Y, Gao Y, Liu F, Zhang X, Kong J, Fan G, Zhang C, Feng L, Xiang J, Li F (2021) Simple sequence repeats drive genome plasticity and promote adaptive evolution in penaeid shrimp. Commun Biol 4:186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-01716-y
Zhang L, Wang S, Su C, Harris AJ, Zhao L, Su N, Wang JR, Duan L, Chang ZY (2021) Comparative chloroplast genomics and phylogenetic analysis of Zygophyllum (Zygophyllaceae) of China. Front Plant Sci 12:723622. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.723622
Zhang LB, Simmons MP, Kocyan A, Renner SS (2006) Phylogeny of the Cucurbitales based on DNA sequences of nine loci from three genomes: implications for morphological and sexual system evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39(2):305–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2005.10.002
Zhou H, Gao X, Woeste K, Zhao P, Zhang S (2021) Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of four chestnut species (Castanea). Forests 12(7):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070861
Zhou J, Chen X, Cui Y, Sun W, Li Y, Wang Y, Song J, Yao H (2017) Molecular structure and phylogenetic analyses of complete chloroplast genomes of two Aristolochia medicinal species. Int J Mol Sci 18(9):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091839
Acknowledgements
The first author is thankful to Vimal Research Society for Agro-Biotech & Cosmic Powers, Rajkot for the financial support, and Department of Biosciences, Saurashtra University, Rajkot, Gujarat, India, for providing lab facilities.
Data archiving statement
This study presents cpDNA sequence data of two plants: Balanites aegyptiaca, and Gymnosporia montana. Both the genomic sequences are deposited in the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) with accession nos: MT981173 (Balanites aegyptiaca) and MW557311 (Gymnosporia montana).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by E. Dirlewanger
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Monpara, J.K., Chudasama, K.S., Vekaria, M.L. et al. Molecular marker studies on Balanites aegyptiaca and allied species for species delimitation, identification, and authentication. Tree Genetics & Genomes 19, 17 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-023-01593-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-023-01593-y