Abstract
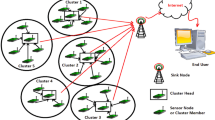
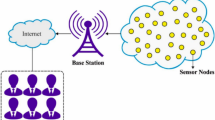
In recent years, WSNs are acquiring popularity due to small-sized and flexible implementation; many applications require quick data transfer with minimal energy consumption of nodes in the midst of the ubiquitous use of WSNs. These sensor nodes cover large regions according to application needs and choose the best optimal path. The main issue with WSN is how to cover the neighborhood correctly and send data to sink without falling into the trap of a single node and single route. Therefore, a recently researched approach namely the swarm-based dragonfly, which has been effectively used in miscellany applications is exploited for this work. The dragonfly method is based on the exploration phase using global search and exploitation phase using local search. The implicit swarming behaviors are thought to be the fundamental drive for routing algorithms. This paper introduce a Meta-heuristic based Optimized Opportunistic Routing Protocol for WSNs (MOORP) based upon the best optimal forwarder node selection and dragonfly route optimization. The forwarder node selection is optimized by residual energy and eucledian distance of the node. The path between forwarder and destination is identified by using the Dragon-fly algorithm. MOORP employs a route searching algorithm (RSA) and a Energy Level Matrix (ELM) update is used to enhancing the routing decision. The RSA finds an optimal path and selects the optimal forwarder node with the help of a heuristic update or ELM. MOORP performance is compared with other opportunistic routing protocols on important parameters such as the number of alive nodes, throughput, packet delivery ratio, message success rate, and average energy consumption,and also compare with pre-existing cluster based routing protocol. The simulation results show that the MOORP considerably outperforms its competitive techniques in terms of energy efficiency.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Available on request.
References
Bhuiyan, M. Z., Wang, G., Wu, J., Cao, J., Liu, X., & Wang, T. (2015). Dependable structural health monitoring using wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing., 14(4), 363–76.
Ota, K., Dong, M., Gui, J., & Liu, A. (2018). QUOIN: Incentive mechanisms for crowd sensing networks. IEEE Network, 32(2), 114–119.
Liu, Q., & Liu, A. (2018). On the hybrid using of unicast-broadcast in wireless sensor networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 1(71), 714–732.
Laouid, A., Dahmani, A., Bounceur, A., Euler, R., Lalem, F., & Tari, A. (2017). A distributed multi-path routing algorithm to balance energy consumption in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 1(64), 53–64.
Zin, S. M., Anuar, N. B., Kiah, M. L., & Pathan, A. S. (2014). Routing protocol design for secure WSN: Review and open research issues. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 1(41), 517–530.
Fadel, E., Gungor, V. C., Nassef, L., Akkari, N., Malik, M. A., Almasri, S., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2015). A survey on wireless sensor networks for smart grid. Computer Communications, 1(71), 22–33.
Tennina, S., Santos, M., Mesodiakaki, A., Mekikis, P. V., Kartsakli, E., Antonopoulos, A., Di Renzo, M., Stavridis, A., Graziosi, F., Alonso, L., & Verikoukis, C. (2016). WSN4QoL: WSNs for remote patient monitoring in e-Health applications. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) 2016 May 22 (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Mikhaylov, K., Tervonen, J., Heikkilä, J., & Känsäkoski, J. (2012). Wireless sensor networks in industrial environment: Real-life evaluation results. In 2012 2nd Baltic Congress on Future Internet Communications 2012 Apr 25 (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Hodge, V. J., O’Keefe, S., Weeks, M., & Moulds, A. (2014). Wireless sensor networks for condition monitoring in the railway industry: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 16(3), 1088–1106.
Pantazis, N. A., Nikolidakis, S. A., & Vergados, D. D. (2012). Energy-efficient routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 15(2), 551–591.
Ahmad, A., Javaid, N., Khan, Z. A., Qasim, U., & Alghamdi, T. A. (2014). \((ACH)^ 2\): Routing scheme to maximize lifetime and throughput of Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(10), 3516–3532.
Liu, X., Zhao, S., Liu, A., Xiong, N., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2019). Knowledge-aware proactive nodes selection approach for energy management in Internet of Things. Future Generation Computer Systems, 1(92), 1142–1156.
Hintsch, T. (2021). Large multiple neighborhood search for the soft-clustered vehicle-routing problem. Computers & Operations Research, 1(129), 105132.
Alghamdi, T. A. (2018). Secure and energy efficient path optimization technique in wireless sensor networks using DH method. IEEE Access, 17(6), 53576–82.
Qayyum, A., Viennot, L., & Laouiti, A. (2002). Multipoint relaying for flooding broadcast messages in mobile wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 35th annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences 2002 Jan 10 (pp. 3866-3875). IEEE.
Chithaluru, P., Tiwari, R., & Kumar, K. (2021). Performance analysis of energy efficient opportunistic routing protocols in wireless sensor network. International Journal of Sensors Wireless Communications and Control, 11(1), 24–41.
Bagirathan, K., & Palanisamy, A. (2021). Opportunistic routing protocol based EPO–BES in MANET for optimal path selection. Wireless Personal Communications, 1–22.
Elshrkawey, M., Al-Mahdi, H., & Atwa, W. (2022). An enhanced routing algorithm based on a re-position particle swarm optimization (RA-RPSO) for wireless sensor network. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 34(10), 10304–10318.
Latiff, N. A., Tsimenidis, C. C., & Sharif, B. S. (2007). Energy-aware clustering for wireless sensor networks using particle swarm optimization. In 2007 IEEE 18th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications 2007 Sep 3 (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Li, X., Keegan, B., Mtenzi, F., Weise, T., & Tan, M. (2019). Energy-efficient load balancing ant based routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 12(7), 113182–11396.
Kanthimathi, N. (2017). Balanced and multi-objective optimized opportunistic routing for underwater sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 94, 2417–2440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3495-2
Mirjalili, S. (2016). Dragonfly algorithm: A new meta-heuristic optimization technique for solving single-objective, discrete, and multi-objective problems. Neural Computing And Applications, 27, 1053–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1920-1
Debnath, S., Baishya, S., Sen, D., & Arif, W. (2021). A hybrid memory-based dragonfly algorithm with differential evolution for engineering application. Engineering with Computers, 37, 2775–2802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-00958-4
Daely, P. T., & Shin, S. Y. (2016). Range based wireless node localization using dragonfly algorithm. In 2016 eighth international conference on ubiquitous and future networks (ICUFN) 2016 Jul 5 (pp. 1012–1015). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/icufn.2016.7536950.
Hema, C., & Sankar, S. (2016). Energy efficient cluster based protocol to extend the RFID network lifetime using dragonfly algorithm. In 2016 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP) 2016 Apr 6 (pp. 0530–0534). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccsp.2016.7754194.
Reddy, A. S. (2016). Optimization of distribution network reconfiguration using dragonfly algorithm. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 16(4), 10–10.
Aadil, F., Ahsan, W., Rehman, Z. U., Shah, P. A., Rho, S., & Mehmood, I. (2018). Clustering algorithm for internet of vehicles (IoV) based on dragonfly optimizer (CAVDO). The Journal of Supercomputing, 74, 4542–4567.
Kumar, C. A., & Vimala, R. (2019). C-FDLA: Crow search with integrated fractional dragonfly algorithm for load balancing in cloud computing environments. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 28(07), 1950115. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126619501159
Ashok Kumar, C., Vimala, R., Aravind Britto, K. R., & Sathya, Devi S. (2019). FDLA: fractional dragonfly based load balancing algorithm in cluster cloud model. Cluster Computing, 16(22), 1401–1414.
Mahseur, M., Boukra, A., & Meraihi, Y. (2018). QoS multicast routing based on a quantum chaotic dragonfly algorithm. InModelling and Implementation of Complex Systems: Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium, MISC 2018, December 16–18, 2018, Laghouat, Algeria 2018 Nov 30 (pp. 47–59). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05481-6-4
Shafiq, M., Ashraf, H., Ullah, A., & Tahira, S. (2020). Systematic literature review on energy efficient routing schemes in WSN—A survey. Mobile Networks and Applications, 25, 882–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-020-01523-5
Xiaohua, X., Xiang-Yang, L., & Huadong, M. (2011). Energy-efficient opportunistic routing in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Transaction on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22(11).
Luo, J., Hu, J., Wu, D., & Li, R. (2014). Opportunistic routing algorithm for relay node selection in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 11(1), 112–121.
Biswas, S., & Morris, R. (2005). ExOR: Opportunistic multi-hop routing for wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2005 conference on Applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications 2005 Aug 22 (pp. 133–144).
Chachulski, S., Jennings, M., Katti, S., & Katabi, D. (2007). Trading structure for randomness in wireless opportunistic routing. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 37(4), 169–180.
Boukerche, A., & Darehshoorzadeh, A. (2014). Opportunistic routing in wireless networks: Models, algorithms, and classifications. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 47(2), 1–36.
Rozner, E., Seshadri, J., Mehta, Y., & Qiu, L. (2009). SOAR: Simple opportunistic adaptive routing protocol for wireless mesh networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 8(12), 1622–1635.
Rahman, Z., Hashim, F., Rasid, M. F., Othman, M., & Alezabi, K. A. (2020). Normalized advancement based totally opportunistic routing algorithm with void detection and avoiding mechanism for underwater wireless sensor network. IEEE Access, 31(8), 67484–67500. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2984652
Chithaluru, P., Tiwari, R., & Kumar, K. (2019). AREOR-Adaptive ranking based energy efficient opportunistic routing scheme in Wireless Sensor Network. Computer Networks, 24(162), 106863.
Eberhart, R., & Kennedy, J. (1995). A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In MHS’95. Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science 1995 Oct 4 (pp. 39–43). IEEE.
Song, Y., Liu, Z., & He, X. (2020). Hybrid PSO and evolutionary game theory protocol for clustering and routing in wireless sensor network. Journal of Sensors, 30(2020), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8817815
Dorigo, M., & Di Caro, G. (1990). Ant colony optimization: a new meta-heuristic. InProceedings of the 1999 congress on evolutionary computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406) 1999 Jul 6 (Vol. 2, pp. 1470–1477). IEEE.
Li, X., Keegan, B., & Mtenzi, F. (2015). Ant colony clustering routing protocol for optimization of large-scale Wireless Sensor Networks, in Proceedings 14th Inf. Technol. Telecommun. Conf. (ITT), C. Muntean and P. Pathak, Eds. Dublin, Ireland: National College of Ireland, pp. 2–9.
Yang, X. S. (2009). Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In: International symposium on stochastic algorithms. Springer. pp. 169–178.
Fister, I., Yang, X. S., & Fister, D. (2014). Firefly Algorithm: A brief review of the expanding literature. book In Cuckoo Search and Firefly Algorithm, Springer, pp. 347–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02141-6-17
Fister, I., Fister, I., Jr., Yang, X. S., & Brest, J. (2013). A comprehensive review of firefly algorithms. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 13, 34–46.
Yang, X. S. (2010). A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. In: Nature inspired cooperative strategies for optimization (NICSO 2010). Springer, pp 65–74.
Yang, X. S. (2013). Bat algorithm: Literature review and applications. International Journal of Bio-inspired Computation, 5(3), 141–149.
Alshinwan, M., Abualigah, L., Shehab, M., Elaziz, M. A., Khasawneh, A. M., Alabool, H., & Hamad, H. A. (2021). Dragonfly algorithm: A comprehensive survey of its results, variants, and applications. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80, 14979–15016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10255-3
Jang, Kil-Woong. (2012). A tabu search algorithm for routing optimization in mobile ad-hoc networks. Telecommunication Systems, 51, 177–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9428-1
Yue, Yinggao, Cao, Li., & Luo, Zhongqiang. (2019). Hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm for improving the coverage and connectivity of Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 108, 1719–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06492-x
Rao, P. C. S., Jana, P. K., & Banka, H. (2017). A particle swarm optimization-based energy efficient cluster head selection algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 23, 2005–2020.
Kaur, S., & Mahajan, R. (2018). Hybrid meta-heuristic optimization-based energy efficient protocol for wireless sensor networks. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 19(3), 145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2018.01.002
Pitchaimanickam, B., & Murugaboopathi, G. (2020). A hybrid firefly algorithm with particle swarm optimization for energy efficient optimal cluster head selection in wireless sensor networks. Neural Computing and Applications, 32, 7709–7723.
Shanmugam, R., & Kaliaperumal, B. (2021). An energy-efficient clustering and cross-layer-based opportunistic routing protocol (CORP) for wireless sensor network. International Journal of Communication Systems, 34(7), e4752.
Alghamdi, T. A. (2020). Energy efficient protocol in wireless sensor network: Optimized cluster head selection model. Telecommunication Systems, 74, 331–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-020-00659-9
Singh, Harmanpreet, & Singh, Damanpreet. (2019). An energy efficient scalable clustering protocol for dynamic wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 109, 2637–2662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06701-7
Valentini, G., Abbas, C. J. B., Villalba, J. J. G., & Astorga, L. (2010). Dynamic multi-objective routing algorithm: a multi-objective routing algorithm for the simple hybrid routing protocol on wireless sensor networks. IET Commun., 4(14), 1732–1741.
Funding
No funding received to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Equally contributed.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
As per journal policy.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaurasia, S., Kumar, K. MOORP: Metaheuristic Based Optimized Opportunistic Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Network. Wireless Pers Commun 132, 1241–1272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10659-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10659-y