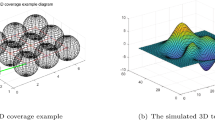
Abstract
Wireless Sensor Networks are booming with the development of computer technology, network communication technology, and sensor technology. However, the question of how to use fewer nodes to achieve maximum coverage still exists. In this paper, a two-layer Surrogate-Assisted Phasmatodea Population Evolution (SAPPE) is proposed for 3D coverage of wireless sensors by combining the characteristics of meta-heuristic algorithms and surrogate models. In this algorithm, Radial Basis Function Networks are used to construct the surrogate model, and the two surrogate models are global surrogate-assisted and local surrogate-assisted, respectively. The global-surrogate model is used to smooth the fitness function, and the local surrogate-assisted model is used to find the optimal value accurately. They use the same archive DataBase (DB) to store particle positions and true fitness values. However, the number of particles involved in the creation of the surrogate-assisted model is different. Seven benchmark functions are used to test and analyze the algorithm, and the results show that the algorithm has good performance. Also, the algorithm verified the significance of the algorithm using Wilcoxon rank test. The result shows that the proposed algorithm is effective compared with PPE, PSO, PPSO, FMO, and BA. This paper compares the number of nodes and coverage radius using different algorithms to ensure maximum coverage. The result shows that the SAPPE algorithm has better performance in terms of 3D coverage.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The document has no associated data.
References
Huang, C. F., Tseng, Y. C., & Lo, L. C. (2004). The coverage problem in three-dimensional wireless sensor networks. In IEEE global telecommunications conference, 2004. GLOBECOM’04 (pp. 3182–3186).
Watfa, M. K., & Commuri, S. (2006). A coverage algorithm in 3D wireless sensor networks. In 2006 1st international symposium on wireless pervasive computing (p. 6).
Alrabea, A., Alzubi, O., & Alzubi, J. (2020). An enhanced Mac protocol design prolong sensor network lifetime. International Journal on Communications Antenna and Propagation (IRECAP), 10(1), 37–43.
Poduri, S., Pattem, S., Krishnamachari, B., & Sukhatme, G. S. (2006). Sensor network configuration and the curse of dimensionality. In Proceedings of third workshop on embedded networked sensors (EmNets 2006), Cambridge, MA, USA
Nickabadi, A., Ebadzadeh, M. M., & Safabakhsh, R. (2011). A novel particle swarm optimization algorithm with adaptive inertia weight. Applied Soft Computing, 11(4), 3658–3670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2011.01.037.
Lim, W. H., & Isa, N. A. M. (2014). Teaching and peer-learning particle swarm optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 18, 39–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.01.009.
Poli, R., Kennedy, J., & Blackwell, T. (2007). Particle swarm optimization. Swarm Intelligence, 1(1), 33–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11721-007-0002-0.
Schutte, J. F., Reinbolt, J. A., Fregly, B. J., Haftka, R. T., & George, A. D. (2004). Parallel global optimization with the particle swarm algorithm. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 61(13), 2296–2315.
Deng, W., Shang, S., Cai, X., Zhao, H., Song, Y., & Xu, J. (2021). An improved differential evolution algorithm and its application in optimization problem. Soft Computing, 25(7), 5277–5298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05527-x.
Yang, X. S., & Gandomi, A. H. (2012). Bat algorithm: A novel approach for global engineering optimization. Engineering Computations, 29(5), 464–483. https://doi.org/10.1108/02644401211235834.
Jayabarathi, T., Raghunathan, T., & Gandomi, A. H. (2018). The bat algorithm, variants and some practical engineering applications: A review. Nature-Inspired Algorithms and Applied Optimization, 744, 313–330.
Katoch, S., Chauhan, S. S., & Kumar, V. (2021). A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80(5), 8091–8126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10139-6.
Grierson, D. E., & Pak, W. H. (1993). Optimal sizing, geometrical and topological design using a genetic algorithm. Structural Optimization, 6(3), 151–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01743506.
Pan, J. S., Dao, T. K., Pan, T. S., Nguyen, T.-T., Chu, S. C., & Roddick, J. F. (2017). An improvement of flower pollination algorithm for node localization optimization in WSN. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 8(2), 486–499.
Chu, S. C., Du, Z. G., & Pan, J. S. (2020). Symbiotic organism search algorithm with multi-group quantum-behavior communication scheme applied in wireless sensor networks. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030930.
Gao, K., Cao, Z., Zhang, L., Chen, Z., Han, Y., & Pan, Q. (2019). A review on swarm intelligence and evolutionary algorithms for solving flexible job shop scheduling problems. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 6(4), 904–916.
Xyngi, I., & Popov, M. (2013). An intelligent algorithm for the protection of smart power systems. IEEE Transactions on smart grid, 4(3), 1541–1548.
Qi, C., Fourie, A., & Chen, Q. (2018). Neural network and particle swarm optimization for predicting the unconfined compressive strength of cemented paste backfill. Construction and Building Materials, 159, 473–478.
Zhou, Y., Wu, H., Luo, Q., & Abdel-Baset, M. (2019). Automatic data clustering using nature-inspired symbiotic organism search algorithm. Knowledge-Based Systems, 163, 546–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.09.013.
Du, Z. G., Pan, J. S., Chu, S. C., Luo, H. J., & Hu, P. (2020). Quasi-affine transformation evolutionary algorithm with communication schemes for application of RSSI in wireless sensor networks. In IEEE Access, 8(8583–8594), 2020.
Pan, J. S., Hu, P., & Chu, S. C. (2021). Binary fish migration optimization for solving unit commitment. Energy, 226, 120329.
Pan, J. S., Sun, X. X., Chu, S. C., Abraham, A., & Yan, B. (2021). Digital watermarking with improved SMS applied for QR code. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 97, 104049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2020.104049.
Movassagh, A. A., Alzubi, J. A., Gheisari, M., Rahimi, M., Mohan, S., Abbasi, A. A., & Nabipour, N. (2021). Artificial neural networks training algorithm integrating invasive weed optimization with differential evolutionary model. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02623-6.
Alzubi, J. A., Jain, R., Nagrath, P., Satapathy, S., Taneja, S., & Gupta, P. (2021). Deep image captioning using an ensemble of CNN and LSTM based deep neural networks. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 40(4), 5761–5769.
Alzubi, O. A., Alzubi, J. A., Alweshah, M., Qiqieh, I., Al-Shami, S., & Ramachandran, M. (2020). An optimal pruning algorithm of classifier ensembles: Dynamic programming approach. Neural Computing and Applications, 32(20), 16091–16107.
Forrester, A. I., & Keane, A. J. (2009). Recent advances in surrogate-based optimization. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 45(1–3), 50–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2008.11.001.
Cheng, K., Lu, Z., Ling, C., & Zhou, S. (2020). Surrogate-assisted global sensitivity analysis: An overview. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 61(3), 1187–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02413-5.
Sun, X. Y., Gong, D. W., & Ma, X. P. (2009). Directed fuzzy graph-based surrogate model-assisted interactive genetic algorithms with uncertain individual’s fitness. In 2009 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (pp. 2395–2402).
Regis, R. G. (2014). Particle swarm with radial basis function surrogates for expensive black-box optimization. Journal of Computational Science, 5(1), 12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2013.07.004.
Li, F., Shen, W., Cai, X., Gao, L., & Wang, G. G. (2020). A fast surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization algorithm for computationally expensive problems. Applied Soft Computing, 92, 106303.
Chu, S. C., Du, Z. G., Peng, Y. J., & Pan, J. S. (2021). Fuzzy hierarchical surrogate assists probabilistic particle swarm optimization for expensive high dimensional problem. Knowledge-Based Systems, 220, 106939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106939.
Zhou, Z., Ong, Y. S., Nguyen, M. H., & Lim, D. (2005). A study on polynomial regression and gaussian process global surrogate model in hierarchical surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithm. In 2005 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (pp. 2832–2839).
Goel, T., Hafkta, R. T., & Shyy, W. (2009). Comparing error estimation measures for polynomial and kriging approximation of noise-free functions. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 38(5), 429–442.
Hearst, M. A., Dumais, S. T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., & Scholkopf, B. (1998). Support vector machines. IEEE Intelligent Systems and their applications, 13(4), 18–28.
Gutmann, H. M. (2001). A radial basis function method for global optimization. Journal of Global Optimization, 19(3), 201–227.
Sun, C., Jin, Y., Zeng, J., & Yu, Y. (2015). A two-layer surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization algorithm. Soft Computing, 19(6), 1461–1475.
Jin, R., Chen, W., & Simpson, T. W. (2001). Comparative studies of metamodelling techniques under multiple modelling criteria. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 23(1), 1–13.
Díaz-Manríquez, A., Toscano, G., & Coello Coello, C. A. (2017). Comparison of metamodeling techniques in evolutionary algorithms. Soft Computing, 21(19), 5647–5663.
Liu, N., Pan, J. S., Sun, C., & Chu, S. C. (2020). An efficient surrogate-assisted quasi-affine transformation evolutionary algorithm for expensive optimization problems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 209, 106418.
Yu, H., Tan, Y., Zeng, J., Sun, C., & Jin, Y. (2018). Surrogate-assisted hierarchical particle swarm optimization. Information Sciences, 454, 59–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.04.062.
Kaveh, A., & Nasrolahi, A. (2014). A new probabilistic particle swarm optimization algorithm for size optimization of spatial truss structures. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 12(1), 1–13.
Hou, Y., Hao, G. S., Zhang, Y., Gu, F., Wang, X., & Zhang, T. T. (2020). A molecular interactions-based social learning particle swarm optimization algorithm. IEEE Access, 8, 135661–135674.
Song, P. C., Chu, S. C., Pan, J. S., & Yang, H. (2020). Phasmatodea population evolution algorithm and its application in length-changeable incremental extreme learning machine. In 2020 2nd international conference on industrial artificial intelligence (IAI) (pp. 1–5).
Rather, S. A., & Bala, P. S. (2020). Swarm-based chaotic gravitational search algorithm for solving mechanical engineering design problems. World Journal of Engineering, 17(1), 97–114. https://doi.org/10.1108/WJE-09-2019-0254.
Coello Coello, C. A. (2000). Constraint-handling using an evolutionary multiobjective optimization technique. Civil Engineering Systems, 17(4), 319–346.
Kandris, D., Nakas, C., Vomvas, D., & Koulouras, G. (2020). Applications of wireless sensor networks: An up-to-date survey. Applied System Innovation, 3(1), 14.
Zhang, J., Nian, H., Ye, X., Ji, X., & He, Y. (2020). A spatial correlation based partial coverage scheduling scheme in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network Intelligence, 5(2), 34–43.
Li, J., & Lu, G. (2018). Dynamic cooperative localization algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 9(4), 949–958.
Wu, J., Xu, M., Liu, F. F., Huang, M., Ma, L., & Lu, Z. M. (2021). Solar wireless sensor network routing algorithm based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 12(1), 1–11.
Babu, M. V., Alzubi, J. A., Sekaran, R., Patan, R., Ramachandran, M., & Gupta, D. (2021). An improved IDAF-FIT clustering based ASLPP-RR routing with secure data aggregation in wireless sensor network. Mobile Networks and Applications, 26(3), 1059–1067.
Temel, S., Unaldi, N., & Kaynak, O. (2013). On deployment of wireless sensors on 3-D terrains to maximize sensing coverage by utilizing cat swarm optimization with wavelet transform. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 44(1), 111–120.
Herrera, L. J., Pomares, H., Rojas, I., Guillén, A., Rubio, G., & Urquiza, J. (2011). Global and local modelling in RBF networks. Neurocomputing, 74(16), 2594–2602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2011.03.027.
Suganthan, P. N., Hansen, N., Liang, J. J., Deb, K., Chen, Y. P., Auger, A., & Tiwari, S. (2005). Problem definitions and evaluation criteria for the CEC 2005 special session on real-parameter optimization. KanGAL Report, 2005005(2005), 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. No funding was received for conducting this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, LL., Chu, SC., Du, ZG. et al. Surrogate-assisted Phasmatodea population evolution algorithm applied to wireless sensor networks. Wireless Netw 29, 637–655 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-03168-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-03168-6