Abstract
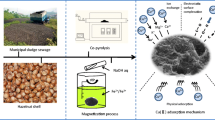
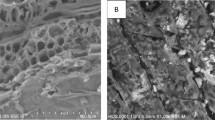
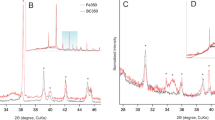
The contamination of chromium (Cr(VI)) in groundwater threatens public health because of the industrial development being historically less supervised. To remove Cr(VI) from groundwater and other surface waters, a new FeCl3-modified magnetic biochar (MBPH550) was prepared from a waste peanut hull. The magnetic potential was to facilitate the separation of absorbent from the water phase. The removal efficiency, adsorption kinetics and isotherm models, and adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) on MBPH550 were investigated. MBPH550 had a large specific surface of 243.23 m2/g and saturation magnetization of 5.65 emu/g. MBPH550 achieved a removal efficiency of Cr(VI) up to 92.2% ± 2.0%. Low pH favored the adsorption of Cr(VI). At pH 6.0, the adsorption of Cr(VI) on MBPH550 fits the Elovich kinetic model and Freundlich isothermal adsorption model, with an equilibrium adsorption capacity of 6.64 mg/g. In addition to the direct functional group coordination and precipitation on the surface of MBPH550, Cr(VI) was also reduced to Cr3+, Cr(OH)3, Cr2O3, and FeCr2O4, which were all deposited on the surface of MBPH550. MBPH550 could be a widely applied efficient adsorbent for removing Cr(VI) from wastewater, groundwater, and leachate of Cr-contaminated soil.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abul, H., Sofia, P., Sadia, M., Anik, H., Shahruk, N., Aminur, R., & Majher, I. (2022). Chromium adsorption on surface activated biochar made from tannery liming sludge: A waste-to-wealth approach. Water Science and Engineering, 15(4), 328–336.
Adeyinka, S., Lekan, T., & Anselm, I. (2022). Response surface modeling and optimization of hexavalent chromium adsorption onto eucalyptus tree bark-derived pristine and chemically-modified biochar. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 182, 592–603.
Al-Ghouti, M., & Da'ana, D. (2020). Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 393, 122383.
Cao, W., Zhou, X., Hao, M., & Mei, X. (2021). Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using montmorillonite-biochar composites. Desalination and Water Treatment, 215, 98–107.
Chen, G., Han, J., Mu, Y., Yu, H., & Qin, L. (2019). Two-stage chromium isotope fractionation during microbial Cr(VI) reduction. Water Research, 148, 10–18.
Değermenci, G., Değermenci, N., Ayvaoğlu, V., Durmaz, E., Çakır, D., & Akan, E. (2019). Adsorption of reactive dyes on lignocellulosic waste; characterization, equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 225, 1220–1229.
Değermenci, G., Değermenci, N., Emin, N., & Aşıkuzun, E. (2022). Characterization of Mg-rich natural serpentine clay mineral and removal of reactive blue 19 from aqueous solutions. EQA - International Journal of Environmental Quality, 47, 40–55.
Diao, Z., Xu, X., Chen, H., Jiang, D., Yang, Y., Kong, L., Sun, Y., Hu, Q., Hao, Q., & Liu, L. (2016a). Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and phenol by persulfate activated with bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: Reactivity and mechanism. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 316, 186–193.
Diao, Z., Xu, X., Jiang, D., Kong, L., Sun, Y., Hu, Y., Hao, Q., & Chen, H. (2016b). Bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron/persulfate system for the simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and phenol from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016(302), 213–222.
Di Natale, F., Erto, A., Lancia, A., & Musmarra, D. (2015). Equilibrium and dynamic study on hexavalent chromium adsorption onto activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 281, 47–55.
Dong, X., Ma, L. Q., & Li, Y. (2011). Characteristics and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium removal by biochar from sugar beet tailing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190(1), 909–915.
Fasina, O. (2008). Physical properties of peanut hull pellets. Bioresource Technology, 99(5), 1259–1266.
Feng, Z., Gao, X., Zhou, B., Li, H., Liu, H., Yuan, R., Wang, X., Chen, Z., Luo, S., & Chen, H. (2023). Influence mechanisms of different stalks on iron species type of magnetic biochar prepared from Fe2O3. Science of the Total Environment, 903, 166790.
Gong, Y., Gai, L., Tang, J., Fu, J., Wang, Q., & Zeng, E. Y. (2017). Reduction of Cr(VI) in simulated groundwater by FeS-coated iron magnetic nanoparticles. Science of The Total Environment, 595, 743–751.
Gurav, R., Bhatia, S., Choi, T., Park, Y., Park, J., Han, Y., Vyavahare, G., Jadhav, J., Song, H., Yang, P., Yoon, J., Bhatnagar, A., Choi, Y., & Yang, Y. (2020). Treatment of furazolidone contaminated water using banana pseudostem biochar engineered with facile synthesized magnetic nanocomposites. Bioresource Technology, 297, 122472.
Hage, D., & Carr, J. (2010). Analytical chemistry and quantitative analysis. China Machine Press.
Han, Y., Cao, X., Ouyang, X., Sohi, S., & Chen, J. (2016). Adsorption kinetics of magnetic biochar derived from peanut hull on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Effects of production conditions and particle size. Chemosphere, 145, 336–341.
Huang, M., Mishra, S., & Liu, S. (2017). Waste glass fiber fabric as a support for facile synthesis of microporous carbon to adsorb Cr(VI) from wastewater. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5(9), 8127–8136.
Huang, X., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Tan, X., Ding, Y., Zeng, G., Zhou, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, S., & Zheng, B. (2016). Effective removal of Cr (VI) using β-cyclodextrin–chitosan modified biochars with adsorption/reduction bifuctional roles. Rsc Advances, 6(1), 94–104.
Inyang, M. I., Gao, B., Yao, Y., Xue, Y., Zimmerman, A., Mosa, A., Pullammanappallil, P., Ok, Y. S., & Cao, X. (2016). A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 46(4), 406–433.
Jiang, B., Gong, Y., Gao, J., Sun, T., Liu, Y., Oturan, N., & Oturan, M. (2019). The reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) mediated by environmentally relevant carboxylic acids: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 365, 205–226.
Kim, K., Kim, J., Cho, T., & Choi, J. (2012). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on physicochemical properties of biochar obtained from the fast pyrolysis of pitch pine (Pinus rigida). Bioresource Technology, 118, 158–162.
Korkmaz, C., Değermenci, G. D., & Değermenci, N. (2023). Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution using anion exchange resin: Equilibrium isotherms and kinetics. Fibers and Polymers, 24, 3753–3760.
Krea, N., Bhaumik, M., Pillay, K., Ray, S., & Maity, A. (2017). Selective removal of toxic Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption combined with reduction at a magnetic nanocomposite surface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 503, 214–228.
Li, H., Dong, X., da Silva, E., de Oliveira, L., Chen, Y., & Ma, L. (2017). Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere, 178, 466–478.
Li, N., Yue, Q., Gao, B., Xu, X., Su, R., & Yu, B. (2019). One-step synthesis of peanut hull/graphene aerogel for highly efficient oil-water separation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 207, 764–771.
Liu, N., Zhang, Y., Xu, C., Liu, P., Lv, J., Liu, Y., & Wang, Q. (2020a). Removal mechanisms of aqueous Cr(VI) using apple wood biochar: A spectroscopic study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 384, 121371.
Liu, L., Liu, X., Wang, D., Lin, H., & Huang, L. (2020b). Removal and reduction of Cr(VI) in simulated wastewater using magnetic biochar prepared by co-pyrolysis of nano-zero-valent iron and sewage sludge. Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, 120562.
Liu, Q., Liu, F., & Chen, H. (2017). Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by low-temperature biochars from crop residues: Role of redox reactions. Desalination and Water Treatment, 75, 94–106.
Lu, A., Zhong, S., Chen, J., Shi, J., Tang, J., & Lu, X. (2006). Removal of Cr (VI) and Cr (III) from aqueous solutions and industrial wastewaters by natural clino-pyrrhotite. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(9), 3064–3069.
Luo, L., Xu, C., Chen, Z., & Zhang, S. (2015). Properties of biomass-derived biochars: Combined effects of operating conditions and biomass types. Bioresource Technology, 192, 83–89.
Lyu, H., Tang, J., Huang, Y., Gai, L., Zeng, E. Y., Liber, K., & Gong, Y. (2017). Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 322, 516–524.
Ma, F., Bakunzibake, P., Zhao, B., Diao, J., & Li, J. (2020). Simultaneous adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium on biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in aqueous solution. Water Science & Technology, 82(7), 1339–1349.
Ma, J., & Chen, K. (2020). Designing porous nickel architectures for adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) to achieve drinking water standard. Separation and Purification Technology, 241, 116705.
Mao, Y., Tao, Y., Zhang, X., Chu, Z., Zhang, X., & Huang, H. (2023). Removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by tea stalk biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: Performance and mechanism. Water, Air, Soil Pollution, 234, 149.
Mohan, D., Rajput, S., Singh, V., Steele, P., & Pittman, C. (2011). Modeling and evaluation of chromium remediation from water using low cost bio-char, a green adsorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 188(1), 319–333.
Morsy, F. (2011). Hydrogen production from acid hydrolyzed molasses by the hydrogen overproducing Escherichia coli strain HD701 and subsequent use of the waste bacterial biomass for biosorption of Cd(II) and Zn(II). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36(22), 14381–14390.
Picard, M., Thakur, S., Misra, M., Mielewski, D., & Mohanty, A. (2020). Biocarbon from peanut hulls and their green composites with biobased poly(trimethylene terephthalate) (PTT). Scientific Reports, 10(1), 3310.
Polti, M., Aparicio, J., Benimeli, C., & Amoroso, M. (2014). Simultaneous bioremediation of Cr(VI) and lindane in soil by actinobacteria. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 88, 48–55.
Qu, J., Zhang, X., Liu, S., Li, X., Wang, S., Feng, Z., Wu, Z., Wang, L., Jiang, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2022). One-step preparation of Fe/N co-doped porous biochar for chromium(VI) and bisphenol a decontamination in water: Insights to co-activation and adsorption mechanisms. Bioresource Technology, 361, 127718.
Rajapaksha, A., Alam, M., Chen, N., Alessi, D., Igalavithana, A., Tsang, D., & Ok, Y. (2018). Removal of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solutions using biochar: Chemical and spectroscopic investigations. Science of The Total Environment, 625, 1567–1573.
Rama, S., Rakesh, K., Prabhakar, S., Nishi, K., Shang, J., & Tejraj, M. (2022a). Removal of hexavalent chromium via biochar-based adsorbents: State-of-the-art, challenges, and future perspectives. Journal of Environmental Management, 317, 115356.
Rama, S., Rakesh, K., Kumar, A., Shang, J., Sayan, B., Shubhalakshmi, S., Nishant, K., Jyotirekha, M., Manoranjan, K., & Prabhakar, S. (2022b). Single-step synthesis of activated magnetic biochar derived from rice husk for hexavalent chromium adsorption: Equilibrium mechanism, kinetics, and thermodynamics analysis. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 18, 100796.
Tumolo, M., Ancona, V., De Paola, D., Losacco, D., Campanale, C., Massarelli, C., & Uricchio, V. F. (2020). Chromium pollution in European water, sources, health risk, and remediation strategies: An overview. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 5438.
Wang, K., Sun, Y., Tang, J., He, J., & Sun, H. (2020). Aqueous Cr(VI) removal by a novel ball milled Fe0-biochar composite: Role of biochar electron transfer capacity under high pyrolysis temperature. Chemosphere, 241, 125044.
Wang, S., Tang, Y., Li, K., Mo, Y., Li, H., & Gu, Z. (2014). Combined performance of biochar sorption and magnetic separation processes for treatment of chromium-contained electroplating wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 174, 67–73.
Wang, S., Gao, B., Zimmerman, A., Li, Y., Ma, L., Harris, W., & Migliaccio, K. (2015). Physicochemical and sorptive properties of biochars derived from woody and herbaceous biomass. Chemosphere, 134, 257–262.
Wang, S., Zhong, D., Xu, Y., & Zhong, N. (2022). Removal of hexavalent chromium from simulated wastewater by polyethylene glycol–modified D201 resin-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water, Air, Soil Pollution, 233, 446.
Wei, Y., Zhang, K., Cheng, T., & Zhou, G. (2023). Characteristics and mechanisms of Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution by FeSm/BC composite. Water, Air, Soil Pollution, 234, 68.
Wu, F., Tseng, R., & Juang, R. (2009). Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150(2), 366–373.
Wu, H., Wei, W., Xu, C., Meng, Y., Bai, W., Yang, W., & Lin, A. (2020). Polyethylene glycol-stabilized nano zero-valent iron supported by biochar for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 188, 109902.
Xia, S., Song, Z., Jeyakumar, P., Bolan, N., & Wang, H. (2019). Characteristics and applications of biochar for remediating Cr(VI)-contaminated soils and wastewater. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42, 1543–1567.
Xu, S., Yu, W., Liu, S., Xu, C., Li, J., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium using banana pseudostem biochar and its mechanism. Sustainability, 10(11), 4250.
Ye, Z., Yin, X., Chen, L., He, X., Lin, Z., Liu, C., Ning, S., Wang, X., & Wei, Y. (2019). An integrated process for removal and recovery of Cr (VI) from electroplating wastewater by ion exchange and reduction–precipitation based on a silica-supported pyridine resin. Journal of Cleaner Production, 236, 117631.
Yi, Y., Huang, Z., Lu, B., Xian, J., Tsang, E. P., Cheng, W., Fang, J., & Fang, Z. (2020). Magnetic biochar for environmental remediation: A review. Bioresource Technology, 298, 122468.
Yi, Y., Tu, G., Zhao, D., Tsang, P., & Fang, Z. (2019). Biomass waste components significantly influence the removal of Cr(VI) using magnetic biochar derived from four types of feedstocks and steel pickling waste liquor. Chemical Engineering Journal, 360, 212–220.
Yin, Z., Xu, S., Liu, S., Xu, S., Li, J., & Zhang, Y. (2020). A novel magnetic biochar prepared by K2FeO4-promoted oxidative pyrolysis of pomelo peel for adsorption of hexavalent chromium. Bioresource Technology, 300, 122680.
Yu, Y., An, Q., Jin, L., Luo, N., Li, Z., & Jiang, J. (2020). Unraveling sorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by FeCl3 and ZnCl2-modified corn stalks biochar: Implicit mechanism and application. Bioresource Technology, 297, 122466.
Zhang, X., Lv, L., Qin, Y., Xu, M., Jia, X., & Chen, Z. (2018). Removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a magnetic biochar derived from Melia azedarach wood. Bioresource Technology, 256, 1–10.
Zhang, T., Tian, G., Hu, X., Xie, Y., Zhang, L., & Bian, B. (2021). Intensity analysis of chromium cycling in south Jiangsu region of China. Chemosphere, 263, 128138.
Zhu, S., Huang, X., Wang, D., Wang, L., & Ma, F. (2018). Enhanced hexavalent chromium removal performance and stabilization by magnetic iron nanoparticles assisted biochar in aqueous solution: Mechanisms and application potential. Chemosphere, 207, 50–59.
Funding
This work was supported by a Science and Technology Major Special Project of Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (No.19ZXSZSN00080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare Nno competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 391 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liang, Y., Cui, W. et al. Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Magnetic Biochar Derived from Peanut Hull. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 100 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06912-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06912-0