Abstract
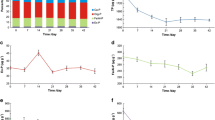
Algal bloom in eutrophication water, which can cause various risks, are closely related to phosphorus concentration of water environment, especially endogenous phosphorus. In this study, the relationship between algal bloom and phosphorus in water environment was investigated by collecting water and sediment in three different time in 2019 in Zhushan Bay, Taihu Lake. The result showed that algal bloom occurred during 27 June to 28 September in 2019. A large amount of phosphorus in overlying water was absorbed at the initial stage of algal bloom and sediment played as “source” to supplement AAP for bloom forming, which was mainly NAIP. Large phosphorus released at the decay period of algal bloom was largely OP and adsorbed by sediment, which played as “sink” of phosphorus. Moreover, the main phosphorus form of TP in the sediments of Zhushan Bay was IP, in which main component was NAIP. The main component of AAP was NAIP that phosphorus combined with iron, aluminum, and other metals. Furthermore, phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in the sediments of Zhushan Bay were mainly Alcaligenes, which could release phosphorus in sediment into overlying water to supplement phosphorus source required for algae bloom outbreak. The results of this study showed that endogenous phosphorus played an important role in the outbreak of algal blooms, and the control of endogenous phosphorus should be the key step of algal bloom control.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files. Should any raw data files be needed in another format they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Azevedo, S. M., et al. (2002). Human intoxication bymicrocystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru-Brazil. Toxicology, 181–182, 441–446.
Behera, B. C., et al. (2014). Diversity, mechanism and biotechnology of phosphate solubilising microorganism in mangrove-A review. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 3(2), 97–110.
Cao, X. (2017). Study on relationship between algal blooms and phosphorus release from sediment in eutrophic lakes. Shanghai, China: Fudan University.
Cao, X., et al. (2016). Phosphorus mobility among sediments, water and cyanobacteria enhanced by cyanobacteria blooms in eutrophic Lake Dianchi. Environmental Pollution, 219, 580–587.
Chen, W., et al. (2008). Reduction in microcystin concentrations in large and shallow lakes: Water and sediment-interface contributions. Water Research, 42(3), 763–773.
Dang, F. H., Wu, Q., & Ke, L. L. (2018). Study on the relationship between cyanobacteria bloom and 10 factors such as pH valuein Lake Chaohu. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 44(8), 210–211.
Ding, Y., et al. (2023). Quantifying phosphorus levels in water columns equilibrated with sediment particles in shallow lakes: From algae/cyanobacteria-available phosphorus pools to pH response. Science of the Total Environment, 868, 161694.
Duan, H. T., et al. (2009). Two-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environmental Science Technology, 43, 3522–3528.
Dugopolski, R. A., Rydin, E., & Brett, M. T. (2008). Short-term effects of a buffered alum treatment on Green Lake sediment phosphorus speciation. Lake and Reservoir Management, 24(2), 181–189.
Gunnars, A., & Blomqvist, S. (1997). Phosphate exchange across the sediment-water interface when shifting from anoxic to oxic conditions an experimental comparison of freshwater and brackish-marine systems. Biogeochemistry, 37, 203–226.
Hecky, R. E., & Kilham, P. (1988). Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: A review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography, 33(4, part 2), 796–822.
Howard, P. J. A., & Howard, D. M. (1990). Use of organic carbon and loss-on-ignition to estimate soil organic matter in different soil types and horizons. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 9, 306–310.
Huang, W., et al. (2015). Identification of inorganic and organic species of phosphorus and its bio-availability in nitrifying aerobic granular sludge. Water Research, 68, 423–431.
Huisman, J., et al. (2018). Cyanobacterial blooms. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(8), 471–483.
Kour, D., et al. (2021). Biodiversity, current developments and potential biotechnological applications of phosphorus-solubilizing and- mobilizing microbes: A review. Pedosphere, 31(1), 43–75.
Li, J., et al. (2012). Carbon mineralization and oxygen dynamics in sediments with deep oxygen penetration. Lake Superior. Limnology and Oceanography, 57(6), 1634–1650.
Lin, Y., et al. (2017). Research progress in phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 29(2), 99–103.
Liu, Z., et al. (2023). Enrichment of geogenic phosphorus in a coastal groundwater system: New insights from dissolved organic matter characterization. Chemosphere, 322, 138214.
Long, Z., Ji, Z., & Pei, Y. (2023). Characteristics and distribution of phosphorus in surface sediments of a shallow lake. Journal of Environmental Sciences (china), 124, 50–60.
López-Archilla, A. I., et al. (2004). Phytoplankton diversity and cyanobacterial dominance in a hypereutrophic shallow lake with biologically produced alkaline pH. Extremophiles, 8(8), 109–115.
Lu, D., et al. (2016). Evaluation of phosphorus distribution and bioavailability in sediments of a subtropical wetland reserve in southeast China. Ecological Indicators, 66, 556–563.
Lu, X., et al. (2020). Long-term application of fertilizer and manures affect P fractions in Mollisol. Science and Reports, 10(1), 14793.
Paerl, H. W., & Paul, V. J. (2012). Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Research, 46, 1349–1363.
Penn, M. R., et al. (1995). Phosphorus diagenesis in lake sediments- Investigations using fractionation techniques. Marine and Freshwater Research, 46(1), 89–99.
Plaas, H. E., & Paerl, H. W. (2021). Toxic cyanobacteria: A growing threat to water and air quality. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(1), 44–64.
Prescott, L. M., Harley, J. P., & Klein, D. A., (1997). Microbiology. WCB/McGraw-Hill.
Qin, B., et al. (2006). Estimation of internal nutrient release in large shallow Lake Taihu China. Science in China Series D, 49(S1), 38–50.
Qin, B., et al. (2010). A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environmental Management, 45(1), 105–112.
Qiu, Z., et al. (2022). Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of phosphorus forms, TOC, and TN in the sediments of Daye Lake, Central China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 23(2), 1023–1036.
Ruban, V., et al. (2001). Development of a harmonised phosphorus extraction procedure and certification of a sediment reference material. Journal of Environment Monitoring, 3(1), 121–125.
Schindler, D. W., et al. (2016). Reducing phosphorus to curb lake eutrophication is a success. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(17), 8923–8929.
Schreckinger, J., Mutz, M., & Mendoza-Lera, C. (2022). When water returns: Drying history shapes respiration and nutrients release of intermittent river sediment. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 155950.
Soliman, N. F., El Zokm, G. M., & Okbah, M. A. (2017). Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in El Mex Bay and Lake Mariut sediments. International Journal of Sediment Research, 32(3), 432–441.
Wang, Q., et al. (2006). Distribution of phosphorus fractions and bio-available phosphorus forms and their relationship in the sediments from different regions of Lake Taihu. Journal of Lake Sciences, 18(2), 120–126.
Wang, D. Y., Feng, X. Z., & Zhou, L. G. (2008). Relationship between blue algal bloom and water temperature in Lake Taihu based on MODIS. Journal of Lake Sciences, 20(2), 173–178.
Wang, K., Razzano, M., & Mou, X. (2020a). Cyanobacterial blooms alter the relative importance of neutral and selective processes in assembling freshwater bacterioplankton community. Science of the Total Environment, 706, 135724.
Wang, L., et al. (2020b). Migration and transformation of phosphorus in waste activated sludge during ozonation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 27(24), 30315–30322.
Wauer, G., et al. (2005). Sediment treatment with a nitrate-storing compound to reduce phosphorus release. Water Research, 39, 494–500.
Wong, Y. J., et al. (2020). Comparison among different ASEAN water quality indices for the assessment of the spatial variation of surface water quality in the Selangor river basin, Malaysia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(10), 644.
Xu, H., et al. (2010). Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu. China. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(1), 420–432.
Xu, W. L., et al. (2011). Assessment the influence of P avaliability of sediments in Lake Taihu to Microystis aeruginosa using different methods. China Environmental Science, 31(9), 1486–1491.
Xu, X. G., et al. (2015). Predominance of terrestrial organic matter in sediments from a cyanobacteria- blooming hypereutrophic lake. Ecological Indicators, 50, 35–43.
Xue, Y., et al. (2009). Study process of phosphorus absorption and release at sediments. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (natural Science), 28, 146–148.
Yang, Y., et al. (2017). Nitrogen and phosphorus in sediments in China: A national-scale assessment and review. Science of the Total Environment, 576, 840–849.
Yin, H., Yin, P., & Yang, Z. (2023). Seasonal sediment phosphorus release across sediment-water interface and its potential role in supporting algal blooms in a large shallow eutrophic Lake (Lake Taihu, China). Science of the Total Environment, 896, 165252.
Younis, A. M., et al. (2022). Distribution and ecological risk evaluation of bioavailable phosphorus in sediments of El Temsah Lake. Suez Canal. Oceanologia, 64(2), 287–298.
Yu, J. Q., et al. (2010). The regularity of early-warning during bIue green algae outbreak in taihu lake with automatic monitoring. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 22(2), 7–10.
Zhang, W. Z. (2019). Cyanobacteria bloom and decomposing impact on water environment and its prevention & control. Shanghai, China: Fudan University.
Zhou, Q. X., Gibson, C. E., & Zhu, Y. (2001). Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK. Chemosphere, 42, 221–225.
Zhu, M., et al. (2013). Influence of algal bloom degradation on nutrient release at the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu. China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 20(3), 1803–1811.
Funding
This work was supported by ABA Chemicals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Q., Huang, S., Yang, S. et al. Relationship Between Algal Bloom and Phosphorus in Water Environment in Zhushan Bay, Taihu Lake. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 69 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06866-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06866-9