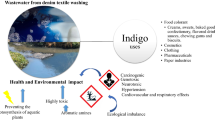
Abstract
Effluent discharged from textile industries, particularly the denim dyeing units containing indigo carmine/crystal violet/highly dimethyl-aminated crystal violet, is a huge threat to flora and fauna in that area. These effluents are highly toxic, mutagenic, and linked to prevalence of cancer in these areas. Since no single enzyme is capable of breaking down these different chemical moieties, this study involved production of complex oxidoreductases on thermally extracted aqueous extract of wheat bran. The extracellular filtrate was rich in several oxidoreductases, particularly laccase (88.64 U g−1 wheat bran) and manganese peroxidase (20.13 U g−1 wheat bran). Addition of 2,6-dimethyl aniline further increased the laccase production to 153.76 U g−1 wheat bran. The culture filtrate produced on wheat bran alone could marginally (< 20%) decolorize (except reactive orange 16 or RO16 which was not acted upon) the tested dyes at dosage of 500 U L−1. Addition of 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) or ABTS during the decolorization process increased decolorization to more than 70% for Kiton blue A, acid violet 17, and reactive black 5. Nearly 60% decolorization was achieved for RO16 by culture filtrate produced on induced medium in the presence of ABTS. Treatment of the combined effluent, containing derivatives of crystal violet, resulted in nearly 90% decolorization with concomitant removal of dimethyl-amino units and accumulation of o-dimethyl-amino dimethyl aniline (m/z 164) indicating an oxidative breakdown pathway which is reverse of the chemical synthetic route of these dyes. The phyto-detoxification and reduction of mutagenicity accompanied the degradation process.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data used and/or analyzed in this study are available with the corresponding author and can be supplied on reasonable request.
References
Ayed, L., Bakir, K., Mansour, H. B., Hammami, S., Cheref, A., & Bakhrouf, A. (2017). In vitro mutagenicity, NMR metabolite characterization of azo and triphenylmethanes dyes by adherents bacteria and the role of the “cna” adhesion gene in activated sludge. Microbial Pathogenesis, 103, 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.12.016
Banerjee, S., & Mazumdar, S. (2012). Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: A technique to access the information beyond the molecular weight of the analyte. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 282574. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/282574
Bedekar, P. A., Saratale, R. G., Saratale, G. D., & Govindwar, S. P. (2014). Oxidative stress response in dye degrading bacterium Lysinibacillus sp. RGS exposed to reactive orange 16, degradation of RO16 and evaluation of toxicity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 21, 11075–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-014-3041-2
Bhatia, D., Sharma, N. R., Singh, J., & Kanwar, R. S. (2017). Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 47, 1836–1876. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1393263
Bilal, M., Rasheed, T., Nabeel, F., Iqbal, H. M. N., & Zhao, Y. (2019). Hazardous contaminants in the environment and their laccase-assisted degradation - a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 234, 253–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.Jenvman.2019.01.001
Brusick, D. (1980). Principles of genetic toxicology. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7661-7
Camarero, S., Sarkar, S., Ruiz-Dueñas, F. J., Martínez, M. J., & Martínez, Á. T. (1999). Description of a versatile peroxidase involved in the natural degradation of lignin that has both manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase substrate interaction sites. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 10324–30. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.274.15.1032
Chhabra, M., Mishra, S., & Sreekrishnan, T. R. (2009). Laccase/mediator assisted degradation of triarylmethane dyes in a continuous membrane reactor. Journal of Biotechnology, 143, 69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.06.011
Chung, K. T. (2016). Azo dyes and human health: A review. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part C, 34(4), 233–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2016.1236602
Di Salvatore, M., Carafa, A. M., & Carratù, G. (2008). Assessment of heavy metals phytotoxicity using seed germination and root elongation tests: A comparison of two growth substrates. Chemosphere, 73, 1461–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.061
Eggert, C., Temp, U., & Eriksson, K. E. L. (1996). The ligninolytic system of the white rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: Purification and characterization of the laccase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 1151–8. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.62.4
Elwakeel, K. Z., Elgarahy, A. M., Elshoubaky, G. A., et al. (2020). Microwave assist sorption of crystal violet and Congo red dyes onto amphoteric sorbent based on upcycled sepia shells. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 18, 35–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00435-1
Fernandes, F. H., Bustos-Obregon, E., & Salvadori, D. M. F. (2015). Disperse red 1 (textile dye) induces cytotoxic and genotoxic effects in mouse germ cells. Reproductive Toxicology, 53, 75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2015.04.002
Gessner, T., & Mayer, U. (2000). Triarylmethane and diarylmethane dyes. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1002/14356007.A27_179
Hernández-Ortega, A., Ferreira, P., & Martínez, A. T. (2012). Fungal aryl-alcohol oxidase: A peroxide-producing flavoenzyme involved in lignin degradation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 1395–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00253-011-3836-8
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/delhi/dye-another-day/articleshow/84251466.cms
Kenzom, T., Srivastava, P., & Mishra, S. (2014). Structural insights into 2,2′-azino-Bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS)-mediated degradation of reactive blue 21 by engineered Cyathus bulleri laccase and characterization of degradation products. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80, 7484–95. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02665-14
Ledakowicz, S., & Paździor, K. (2021). Recent achievements in dyes removal focused on advanced oxidation processes integrated with biological methods. Molecules, 26, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040870
Maila, M. P., & Cloete, T. E. (2005). The use of biological activities to monitor the removal of fuel contaminants—perspective for monitoring hydrocarbon contamination: A review. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 55(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2004.10.003
Malarczyk, E., Kochmanska-Rdest, J., & Jarosz-Wilkolazka, A. (2009). Influence of very low doses of mediators on fungal laccase activity - nonlinearity beyond imagination. Nonlinear Biomedical Physics, 3, 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1753-4631-3-10
Mazzeo, D. E., Roberto, M. M., Sommaggio, L. R., Marin-Morales, M. A. (2018). Bioassays used to assess the efficacy of biodegradation. In Toxicity and biodegradation testing (pp. 215-239). Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7425-2_11
Mittal, S., Roy, A. (2021). Fungus and plant-mediated synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their application in degradation of dyes. In Photocatalytic degradation of dyes, 287-308. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-823876-9.00009-3
Okamoto, K., & Yanase, H. (2002). Aryl alcohol oxidases from the white-rot basidiomycete Pleurotus ostreatus. Mycoscience, 43, 391–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/S102670200057
Paras, N. A., Simmons, B., & MacMillan, D. W. C. (2009). A process for the rapid removal of dialkylamino-substituents from aromatic rings. Application to the expedient synthesis of (R)-tolterodine. Tetrahedron, 65, 3232–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2008.12.054
US Patent EP1309662B1 - Triarylmethane dyes .
US Patent EP3429900-Stable triphenyl-methane dye Leucos.
Pawlik, A., Stefanek, S., & Janusz, G. (2022). Properties, physiological functions and involvement of basidiomycetous alcohol oxidase in wood degradation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 13808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232213808
Prival, M. J., Bell, S. J., Mitchell, V. D., Peiperl, M. D., & Vaughan, V. L. (1984). Mutagenicity of benzidine and benzidine-congener dyes and selected monoazo dyes in a modified Salmonella assay. Mutation Research, 136, 33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(84)90132-0
Przystas, W., Zablocka-Godlewska, E., & Grabinska-Sota, E. (2012). Biological removal of azo and triphenylmethane dyes and toxicity of process by-products. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 223, 1581. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11270-011-0966-7
Puneetha, J., Kottam, N., & Rathna, A. (2021). Investigation of photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet and its correlation with bandgap in ZnO and ZnO/GO nanohybrid. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 125, 108460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108460
Rehman, F., Sayed, M., Khan, J. A., & Khan, H. M. (2017). Removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution by gamma irradiation. Journal of Chilean Chemical Society, 62, 3359–64. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-97072017000100011
Rehman, F., Sayed, M., Khan, J. A., Shah, L. A., Shah, N. S., Khan, H. M., et al. (2018). Degradation of crystal violet dye by Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation processes. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 232, 1771–86. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2017-1099
Rice, E. W., Baird, R. B., Eaton, A. D., & Clesceri, L. S. (2012). Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater (22nd ed.). American Public Health Association WWA.
Salony, Mishra, & S., Bisaria, V.S. (2006). Production and characterization of laccase from Cyathus bulleri and its use in decolourization of recalcitrant textile dyes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 71, 646–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0206-4
Svobodová, K., Senholdt, M., Novotný, Č, & Rehorek, A. (2007). Mechanism of reactive orange 16 degradation with the white rot fungus Irpex lacteus. Process Biochemistry, 42, 1279–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2007.06.002
Telke, A. A., Kalyani, D. C., Dawkar, V. V., & Govindwar, S. P. (2009). Influence of organic and inorganic compounds on oxidoreductive decolorization of sulfonated azo dye C.I. reactive orange 16. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 298–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.Jhazmat.2009.07.008
Valle, J. S., Vandenberghe, L. P. S., Oliveira, A. C. C., Tavares, M. F., Linde, G. A., Colauto, N. B., & Soccol, C. R. (2015). Effect of different compounds on the induction of laccase production by Agaricus blazei. Genetics and Molecular Research, 14, 15882–15891. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.December.1.40
Vats, A., & Mishra, S. (2017). Decolorization of complex dyes and textile effluent by extracellular enzymes of Cyathus bulleri cultivated on agro-residues/domestic wastes and proposed pathway of degradation of Kiton blue A and reactive orange 16. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 11650–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8802-2
Vats, A., & Mishra, S. (2018). Identification and evaluation of bioremediation potential of laccase isoforms produced by Cyathus bulleri on wheat bran. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 344, 466–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.043
Vats, A., & Mishra, S. (2021). An insight into transcriptome of Cyathus bulleri for lignocellulase expression on wheat bran. Archives of Microbiology, 203, 3727–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00203-021-02326-2
Wang, D., Li, J., Wong, A. C. Y., Aachmann, F. L., & Hsieh, Y. S. Y. (2018). A colorimetric assay to rapidly determine the activities of lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases. Biotechnology and Biofuels, 11, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13068-018-1211-Z
Wariishi, H., Valli, K., & Gold, M. H. (1992). Manganese(II) oxidation by manganese peroxidase from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Kinetic mechanism and role of chelators. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 23688–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)35893-9
Wiberth, C. C., Casandra, A. Z. C., Zhiliang, F., et al. (2019). Oxidative enzymes activity and hydrogen peroxide production in white-rot fungi and soil-borne micromycetes co-cultures. Annals of Microbiology, 69, 171–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1413-4
Wu, M.-H., Lee, C.-C., Hsiao, A.-S., Yu, S.-M., Wang, A.H.-J., & Ho, T.-H.D. (2018). Kinetic analysis and structural studies of a high-efficiency laccase from Cerrena sp. RSD1. FEBS Open Bio, 8, 1230–1246. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12459
Yang, X., Wang, L., Shao, X., Tong, J., Zhou, J., Feng, Y., Chen, R., Yang, Q., Han, Y., Yang, X., Ding, F., Meng, Q., Yu, J., Zimmerman, A. R., & Bin Gao, B. (2022). Characteristics and aqueous dye removal ability of novel biosorbents derived from acidic and alkaline one-step ball milling of hickory wood. Chemosphere, 309, 136610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136610
Acknowledgements
AA acknowledges the award of SRF from Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Govt. of India.
Funding
SM gratefully acknowledges the Department of Biotechnology (Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India) for providing financial (BT/PR28676/BCE/8/1508/2019) support to perform a part of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aakanksha Ahlawat: conceptualization, experimental work, data analysis, mass spectrometry, and first draft. Saroj Mishra: conceptualization, planning, resources, data analysis, and editing and preparation of the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable
Consent for Publication
All authors have agreed to submit the paper.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahlawat, A., Mishra, S. Complex Laccase-Oxidoreductase Mixture: Effective for Oxidative Decolorization and Detoxification of Dyes and Complex Effluent from Textile Mill. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 135 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06163-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06163-5