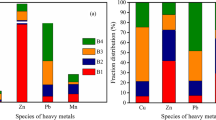
Abstract
This study investigated several pre-treatments as strategies to increase the efficacy of the removal of metals when using exopolymeric substances (EPS) produced by Bacillus cereus. The pre-treatments used include heat (autoclaving, boiling) and chemical agents (sulphuric acid, sodium hydroxide, and methanol). Pre-treated EPS was subsequently used for metal removal in single-metal systems (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cr) and characterized for functional groups via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Results revealed that pre-treatment significantly improved metal removal efficacy of EPS compared to EPS without pre-treatment (removal of Cu: 29.48%, Pb: 73.44%, Zn: 39.27%, Cd: 35.64%, Cr: 56.13%). Pre-treatment using autoclaving (removal of Cu: 40.29%, Pb: 91.18%, Zn: 52.65%, Cd: 45.41%, Cr: 73.33%) and methanol (removal of Cu: 48.41%, Pb: 93.31%, Zn: 58.15%, Cd: 56.49%, Cr: 84.95%) was the most effective heat and chemical pre-treatment, respectively. The combination of autoclaving + methanol further improved metal removal efficacy of the treated EPS with removal of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, and Cr at 60.86%, 98.44%, 70.56%, 64.46%, and 91.85%, respectively. The improved biosorption by pre-treated EPS was attributed to the effect of pre-treatments liberating and increasing the number of functional groups present. EPS pre-treated by autoclaving + methanol were detected with a significantly higher number of hydroxyl groups compared to non-treated EPS. This study suggests that pre-treatment using a combination of autoclaving + methanol successfully improved the quality of EPS as a more superior biosorbent for feasible adoption in wastewater treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahluwalia, S. S., & Goyal, D. (2007). Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 98(12), 2243–2257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.12.006
Ahmad, T., & Danish, M. (2018). Prospects of banana waste utilization in wastewater treatment: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 206(1), 330–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.10.061
Azimi, A., Azari, A., Rezakazemi, M., & Ansarpour, M. (2017). Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: A review. ChemBioEng Reviews, 4(1), 37–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201600010
Bentley, M. J., & Summers, R. S. (2020). Ash pretreatment of pine and biosolids produces biochars with enhanced capacity for organic micropollutant removal from surface water, wastewater, and stormwater. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 6(3), 635–644. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EW00862D
Camacho-Chab, J. C., Castañeda-Chávez, M. D. R., Chan-Bacab, M. J., Aguila-Ramírez, R. N., Galaviz-Villa, I., Bartolo-Pérez, P., Lango-Reynoso, F., Tabasco-Novelo, C., Gaylarde, C., & Ortega-Morales, B. O. (2018). Biosorption of cadmium by non-toxic extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) synthesized by bacteria from marine intertidal biofilms. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(2), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020314
Cheah, C., Cheow, Y. L., & Ting, A. S. Y. (2022a). Comparative analysis on metal removal potential of exopolymeric substances with live and dead cells of bacteria. International Journal of Environmental Research, 16(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-021-00386-2
Cheah, C., Cheow, Y. L., & Ting, A. S. Y. (2022b). Co-cultivation, metal stress and molasses: Strategies to improving exopolymeric yield and metal removal efficacy. Sustainable Environment Research, 32(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42834-022-00121-2
Cheah, C., & Ting, A.S.Y. (2020). Microbial exopolymeric substances for metal removal. In: Inamuddin, M.I. Ahamed, E. Lichtfouse, & A.M. Asiri (Eds.), Methods for Bioremediation of Water and Wastewater Pollution, 225–251. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48985-4_10
Cheah, C., Yue, C. S., & Ting, A. S. Y. (2021). Effects of heat and chemical pretreatments of banana peels for metal removal in single and multimetal systems. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 232(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04945-9
Chug, R., Gour, V. S., Mathur, S., & Kothari, S. L. (2016). Optimization of extracellular polymeric substances production using Azotobacter beijreinckii and Bacillus subtilis and its application in chromium (VI) removal. Bioresource Technology, 214, 604–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.010
Crini, G., & Lichtfouse, E. (2018). Green adsorbents for pollutant removal: Innovative materials. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92162-4
Das, N., Charumathi, D., & Vimala, R. (2007). Effect of pretreatment on Cd2+ biosorption by mycelial biomass of Pleurotus florida. African Journal of Biotechnology, 6(22), 2555–2558. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2007.000-2407
Eccles, H. (1995). Removal of heavy metals from effluent streams—Why select a biological process? International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 35(1), 5–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0964-8305(95)00044-6
Farooq, U., Kozinski, J. A., Khan, M. A., & Athar, M. (2010). Biosorption of heavy metal ions using wheat based biosorbents–A review of the recent literature. Bioresource Technology, 101(14), 5043–5053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.030
Feng, N. C., & Guo, X. Y. (2012). Characterization of adsorptive capacity and mechanisms on adsorption of copper, lead and zinc by modified orange peel. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 22(5), 1224–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61309-5
García-Mendieta, A., Olguín, M. T., & Solache-Ríos, M. (2012). Biosorption properties of green tomato husk (Physalis philadelphica Lam) for iron, manganese and iron–manganese from aqueous systems. Desalination, 284, 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.08.052
Gupta, P., & Diwan, B. (2017). Bacterial exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: A review on biosynthesis, mechanism and remediation strategies. Biotechnology Reports, 13, 58–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.12.006
Hokkanen, S., Bhatnagar, A., & Sillanpää, M. (2016). A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Research, 91, 156–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.008
Hossain, M. A., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W. S., & Nguyen, T. V. (2012). Removal of copper from water by adsorption onto banana peel as bioadsorbent. Geomate Journal, 2(4), 227–234.
Ilhan, S., Cabuk, A., Filik, C., & Caliskan, F. (2004). Effect of pretreatment on biosorption of heavy metals by fungal biomass. Trakya University Journal of Natural Sciences, 5(1), 11–17.
Iqbal, M., Saeed, A., & Zafar, S. I. (2009). FTIR spectrophotometry, kinetics and adsorption isotherms modeling, ion exchange, and EDX analysis for understanding the mechanism of Cd2+ and Pb2+ removal by mango peel waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(1), 161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.141
Javaid, A., Bajwa, R., & Manzoor, T. (2011). Biosorption of heavy metals by pretreated biomass of Aspergillus niger. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 43(1), 419–425.
Kalpana, R., Angelaalincy, M. J., Kamatchirajan, B. V., Vasantha, V. S., Ashokkumar, B., Ganesh, V., & Varalakshmi, P. (2018). Exopolysaccharide from Bacillus cereus VK1: Enhancement, characterization and its potential application in heavy metal removal. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 171, 327–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.07.043
Khan, A., Naqvi, H.J., Afzal, S., Jabeen, S., Iqbal, M., & Riaz, I. (2017). Efficiency enhancement of banana peel for waste water treatment through chemical adsorption: Efficiency of banana peel for waste water treatment. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: A. Physical and Computational Sciences, 54(3), 329–335
Krishnamurthy, M., Uthaya, C. J., Thangavel, M., Annadurai, V., Rajendran, R., & Gurusamy, A. (2020). Optimization, compositional analysis, and characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by multi-metal resistant Bacillus cereus KMS3–1. Carbohydrate Polymers, 227, 115369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115369
Li, F., Wang, W., Li, C., Zhu, R., Ge, F., Zheng, Y., & Tang, Y. (2018). Self-mediated pH changes in culture medium affecting biosorption and biomineralization of Cd2+ by Bacillus cereus Cd01. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 358, 178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.06.066
Mane, P. C., Bhosle, A. B., Jangam, C. M., & Vishwakarma, C. V. (2011). Bioadsorption of selenium by pretreated algal biomass. Advances in Applied Science Research, 2(2), 202–207.
Manzoor, Q., Nadeem, R., Iqbal, M., Saeed, R., & Ansari, T. M. (2013). Organic acids pretreatment effect on Rosa bourbonia phyto-biomass for removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) from aqueous media. Bioresource Technology, 132, 446–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.156
Min, S. H., Han, J. S., Shin, E. W., & Park, J. K. (2004). Improvement of cadmium ion removal by base treatment of juniper fiber. Water Research, 38(5), 1289–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.11.016
More, T. T., Yadav, J. S. S., Yan, S., Tyagi, R. D., & Surampalli, R. Y. (2014). Extracellular polymeric substances of bacteria and their potential environmental applications. Journal of Environmental Management, 144, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.05.010
Ngah, W. W., & Hanafiah, M. M. (2008). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review. Bioresource Technology, 99(10), 3935–3948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.011
Nguyen, T. A. H., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W. S., Zhang, J., Liang, S., Yue, Q. Y., Li, Q., & Nguyen, T. V. (2013). Applicability of agricultural waste and by-products for adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 148, 574–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.124
Ochman, H., Lawrence, J. G., & Groisman, E. A. (2000). Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature, 405(6784), 299–304. https://doi.org/10.1038/35012500
Özgenç, Ö., Durmaz, S., Boyaci, I. H., & Eksi-Kocak, H. (2017). Determination of chemical changes in heat-treated wood using ATR-FTIR and FT Raman spectrometry. Spectrochimica Acta Part a: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 171, 395–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.08.026
Parmar, M., & Thakur, L. S. (2013). Heavy metal Cu, Ni and Zn: Toxicity, health hazards and their removal techniques by low cost adsorbents: A short overview. International Journal of Plant, Animal and Environmental Sciences, 3(3), 143–157.
Rafiu, A. O., Okechukwu, O. J., Badenhorst, J., & Jordaan, E. (2006). A new approach to chemical modification protocols of Aspergillus niger and sorption of lead ion by fungal species. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 9(4), 340–348. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol9-issue4-fulltext-1
Sheng, G. P., Yu, H. Q., & Li, X. Y. (2010). Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnology Advances, 28(6), 882–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.08.001
Shroff, K. A., & Vaidya, V. K. (2011). Effect of pre-treatments on biosorption of Ni (II) by dead biomass of Mucor hiemalis. Engineering in Life Sciences, 11(6), 588–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201000205
Shroff, K. A., & Vaidya, V. K. (2012). Effect of pre-treatments on the biosorption of Chromium (VI) ions by the dead biomass of Rhizopus arrhizus. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 87(2), 294–304. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2715
Sim, S. F., & Ting, A. S. Y. (2017). FTIR and kinetic modelling of fungal biosorbent Trichoderma asperellum for the removal of Pb (II), Cu (II), Zn (II) and Cd (II) from multi-metal solutions. Desalination and Water Treatment, 63, 167–171.
Sivakumar, T., Narayani, S. S., Shankar, T., & Dhinakaran, D. I. (2012). Applications of exopolysaccharide producing bacterium Frateuria aurentia. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 1(3), 1–7.
Tan, W. S., & Ting, A. S. Y. (2014). Kinetic and equilibrium modelling on copper (II) removal by live and dead cells of Trichoderma asperellum and the impact of pre-treatments on biosorption. Separation Science and Technology, 49(13), 2025–2030. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.907808
Tyagi, B., Gupta, B., & Thakur, I. S. (2020). Biosorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) produced by Parapedobacter sp. ISTM3 strain isolated from Mawsmai cave, Meghalaya. India. Environmental Research, 191, 110064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110064
Yazici, H., Kiliç, M., & Solak, M. (2008). Biosorption of copper (II) by Marrubium globosum subsp. globosum leaves powder: Effect of chemical pretreatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 151(2–3), 669–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.042
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Malaysian Ministry of Education (MOE) for the funding under the FRGS grant scheme (FRGS/1/2018/STG03/MUSM/02/1). The authors also thank Monash University Malaysia for providing the resources and facilities to conduct the project.
Funding
This project was funded by the Malaysian Ministry of Education (MOE) under the FRGS grant scheme (FRGS/1/2018/STG03/MUSM/02/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Caleb Cheah, Yuen Lin Cheow, and Adeline Su Yien Ting contributed to the conception and design of the study. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Caleb Cheah and Adeline Su Yien Ting. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Caleb Cheah, and all authors commented on the subsequent versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheah, C., Cheow, Y.L. & Ting, A.S.Y. Pre-Treatment of Exopolymeric Substances from Bacillus cereus for Metal Removal as a Novel Strategy to Enhance Metal Biosorption. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06150-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06150-w