Abstract
Purpose
Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) is reported to be widely used in the surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which consists of two procedures: enucleation and morcellation. This study is to examine the efficiency and safety of two different morcellator systems within a cohort of men undergoing HoLEP for BPH.
Methods
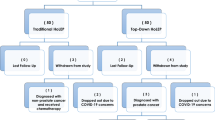
A total of 210 consecutive patients undergoing HoLEP and morcellation procedures were enrolled. Individuals were randomly divided into 2 separated groups: the first group (105 patients) was performed with a nephroscope using a mechanical Versacut morcellator and the second (105 patients) was performed with the new morcellation system, nephroscopes and Piranha morcellator. Perioperative characteristics were studied and analyzed.
Results
The morcellation time and the morcellation rate was similar when the prostate volume (PV) ≤ 60 mL while the morcellation time was significantly shorter and the morcellation rate was higher in the Piranha group with PV > 60 mL. No significant difference was observed according to the bladder irrigation time, indwelling catheter time, and discharge time.
Conclusion
Piranha morcellator presents a higher efficiency for the prostate over 60 mL.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All of the data included in this research are available if needed.
References
Vincent MW, Gilling PJ (2015) HoLEP has come of age. World J Urol 33(4):487–493
Rieken M, Bachmann A (2014) Laser treatment of benign prostate enlargement–which laser for which prostate? Nat Rev Urol 11(3):142–152
Zhang X et al (2016) Different lasers in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a network meta-analysis. Sci Rep 6:23503
Werneburg GT, Shoskes DA, De S (2021) Rapid prostatic regrowth and a free-floating necrotic bladder mass serving as a nidus for infection following ThuLEP: management with morcellation and HoLEP. Urology 148:e9–e10
Rijo E et al (2018) Recommendations for safe and efficient morcellation after endoscopic enucleation of the prostate. Urology 121:197
Chen Q et al (2012) An improved morcellation procedure for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. J Endourol 26(12):1625–1628
Chen YB et al (2013) A prospective, randomized clinical trial comparing plasmakinetic resection of the prostate with holmium laser enucleation of the prostate based on a 2-year followup. J Urol 189(1):217–222
Gilling PJ et al (1998) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) combined with transurethral tissue morcellation: an update on the early clinical experience. J Endourol 12(5):457–459
Xu H et al (2018) Benign prostatic hyperplasia surgical scoring (BPHSS): an novel scoring system for the perioperative outcomes of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Lasers Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2425-1
Wei Z et al (2021) Plasma kinetic enucleation vs holmium laser enucleation for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized controlled trial with a 3-year follow-up. J Endourol. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2021.0086
Fraundorfer MR, Gilling PJ (1998) Holmium:YAG laser enucleation of the prostate combined with mechanical morcellation: preliminary results. Eur Urol 33(1):69–72
Das AK, Teplitsky S, Humphreys MR (2019) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP): a review and update. Can J Urol 26(4 Suppl 1):13–19
Chen Q et al (2010) Bipolar transurethral resection in saline vs traditional monopolar resection of the prostate: results of a randomized trial with a 2-year follow-up. BJU Int 106(9):1339–1343
Xu H et al (2016) Modified morcellation procedure in holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 22(11):991–995
Funding
This study is sponsored by Shanghai Sailing Program (21YF1423300); Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (21ZR1437800); Cross-disciplinary Research Fund of Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine (YG2021QN75), grants from the Multi-center clinical research project of Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine (DLY201809), Shanghai Huangpu District Industry Support Fund (XK2020011) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81902616).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: YC, HX, DG; administrative support: ZW, QC, MZ; provision of study materials or patients: MG, CL, ZC; collection and assembly of data: YC; data analysis and interpretation: HX, DG; manuscript writing: all authors; final approval of manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Consent for publication
Informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This project was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Shanghai ninth people’s Hospital associated with Shanghai Jiaotong University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Xu, H., Gao, D. et al. A prospective randomized controlled trial comparing the effect and safety of Piranha and VersaCut morcellation devices in transurethral holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 2977–2981 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03218-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03218-0