Abstract
Purpose
A network meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the renal protective effect and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science were searched by two authors using the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool.
Results
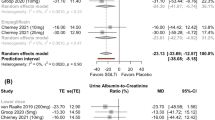
Compared with controls, luseogliflozin 2.5 mg (MD = − 3.50, 95% CI − 6.65 to − 0.35), bexagliflozin 20 mg (MD = − 3.48, 95% CI − 6.57 to − 0.39), and dapagliflozin 10 mg (MD = − 3.08, 95% CI − 5.09 to − 1.06) reduced the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Empagliflozin 25 mg (MD = − 240.43, 95% CI − 414.13 to − 66.73), dapagliflozin 10 mg (MD = − 94.15, 95% CI − 111.72 to − 76.59), and canagliflozin 100 mg (MD = − 193.25, 95% CI − 279.16 to − 107.34) reduced urine albumin-creatinine ratio levels compared with controls. Empagliflozin 25 mg, canagliflozin 100 mg and dapagliflozin 10 mg induced a significant decline in urine albumin-creatinine ratio compared to dapagliflozin 5 mg. In terms of safety, ertugliflozin 5 mg reduced the risk of urinary tract infection. Compared with controls, empagliflozin 10 mg and 25 mg, and canagliflozin 100 mg reduced the risk of any adverse events while canagliflozin 100 mg reduced the risk of serious adverse events. Dapagliflozin 10 mg had a lower risk of treatment discontinuation.
Conclusions
Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors have favourable renal protective effect and safety; however, additional randomised clinical trials are needed to validate these findings.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ene-Iordache B, Perico N, Bikbov B et al (2016) Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk in six regions of the world (ISN-KDDC): a cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob Health 4:e307–e319
Chantrel F, Ott J, Dimitrov Y et al (2020) Blood pressure control in patients with chronic kidney disease according to office and home blood pressures. Blood Press Monit 25:246–251
Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ (2011) The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus–present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8:228–236
Wu L, Liu C, Chang D et al (2021) Annexin A1 alleviates kidney injury by promoting the resolution of inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 100:107–121
Ambarsari CG, Tambunan T, Pardede SO et al (2021) Role of dipstick albuminuria in progression of paediatric chronic kidney disease. J Pak Med Assoc S103-S106.
Yamada T, Wakabayashi M, Bhalla A et al (2021) Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with SGLT-2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol 20:14
Lee YJ, Han HJ (2007) Regulatory mechanisms of Na(+)/glucose cotransporters in renal proximal tubule cells. Kidney Int Suppl S27–35.
Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 16:1016–1027
Wanner C, Lachin JM, Inzucchi SE et al (2018) Empagliflozin and clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, established cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease. Circulation 137:119–129
Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Pitt B et al (2021) Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 384:129–139
Haneda M, Seino Y, Inagaki N et al (2016) Influence of renal function on the 52-week efficacy and safety of the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor luseogliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther 38:66-88.e20
Takashima H, Yoshida Y, Nagura C et al (2018) Renoprotective effects of canagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized open-label prospective trial. Diab Vasc Dis Res 15:469–472
Pollock C, Stefánsson B, Reyner D et al (2019) Albuminuria-lowering effect of dapagliflozin alone and in combination with saxagliptin and effect of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (DELIGHT): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 7:429–441
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B et al (2019) Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 380:2295–2306
Kashiwagi A, Takahashi H, Ishikawa H et al (2015) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on long-term efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment: results of the long-term ASP1941 safety evaluation in patients with type 2 diabetes with renal impairment (LANTERN) study. Diabetes Obes Metab 17:152–160
Fioretto P, Del PSt, Buse JB, et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (chronic kidney disease stage 3A): The DERIVE Study. Diabetes Obes Metab 20:2532–2540
Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2:369–384
Allegretti AS, Zhang W, Zhou W et al (2019) Safety and effectiveness of bexagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and stage 3a/3b CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 74:328–337
Grunberger G, Camp S, Johnson J et al (2018) Ertugliflozin in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the vertis renal randomized study. Diabetes Ther 9:49–66
Zambrowicz B, Lapuerta P, Strumph P et al (2015) LX4211 therapy reduces postprandial glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment despite low urinary glucose excretion. Clin Ther 37:71-82.e12
Petrykiv SI, Laverman GD, de Zeeuw D et al (2017) The albuminuria-lowering response to dapagliflozin is variable and reproducible among individual patients. Diabetes Obes Metab 19:1363–1370
Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Tang W et al (2014) Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int 85:962–971
Sen T, Heerspink HJL (2021) A kidney perspective on the mechanism of action of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Cell Metab 33:732–739
Seidu S, Kunutsor SK, Cos X et al (2018) SGLT2 inhibitors and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes with or without renal impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim CareDiabetes 12(3):265–283
Zinman B, WannerC LJM et al (2015) EMPAREG OUTCOME Investigators: Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 373:2117–2128
Ji L, Liu Y, Miao H et al (2019) Safety and efficacy of ertugliflozin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy: VERTIS Asia. Diabetes Obes Metab 21:1474–1482
Zhang L, Zhang M, Lv Q et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal function impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 140:295–303
Lega IC, Bronskill SE, Campitelli MA et al (2019) Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and risk of genital mycotic and urinary tract infection: a population-based study of older women and men with diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 21:2394–2404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, J., Wang, S., Wen, T. et al. Renal protective effect and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis and systematic review. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 2305–2316 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03117-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03117-4