Abstract
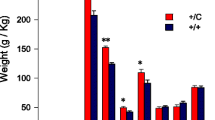
Follistatin (FST), which was first found in the follicles of cattle and pigs, has been shown to be an essential regulator for muscle development. Mice that were genetically engineered to overexpress Fst specifically in muscle had at least twice the amount of skeletal muscle mass as controls; these findings are similar to earlier results obtained in myostatin-knockout mice. However, the role of follistatin in skeletal muscle development has yet to be clarified in livestock. Here, we describe transgenic Duroc pigs that exogenously express Fst specifically in muscle tissue. The transgenic pigs exhibited an increased proportion of skeletal muscle and a reduced proportion of body fat that were similar to those reported in myostatin-null cattle. The lean percentage of lean meat was significantly higher in the F1 generation of TG pigs (72.95 ± 1.0 %) than in WT pigs (69.18 ± 0.97 %) (N = 16, P < 0.05). Myofiber hypertrophy was also observed in the longissimus dorsi of transgenic pigs, possibly contributing to the increased skeletal muscle mass. Western blot analysis showed a significantly reduced level of Smad2 phosphorylation and an increased level of AktS473 phosphorylation in the skeletal muscle tissue of the transgenic pigs. Moreover, no cardiac muscle hypertrophy or reproductive abnormality was observed. These findings indicate that muscle-specific Fst overexpression in pigs enhances skeletal muscle growth, at least partly due to myofiber hypertrophy and providing a promising approach to increase muscle mass in pigs and other livestock.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y, Abe T, Aida Y, Hara Y, Maeda K (2004) Follistatin restricts bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 action on the differentiation of osteoblasts in fetal rat mandibular cells. J Bone Min Res 19:1302–1307. doi:10.1359/JBMR.040408
Amthor H, Christ B, Rashid-Doubell F, Kemp CF, Lang E, Patel K (2002) Follistatin regulates bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP-7) activity to stimulate embryonic muscle growth. Dev Biol 243:115–127. doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0555
Amthor H, Nicholas G, McKinnell I, Kemp CF, Sharma M, Kambadur R, Patel K (2004) Follistatin complexes myostatin and antagonises myostatin-mediated inhibition of myogenesis. Dev Biol 270:19–30. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.01.046
Bellinge RH, Liberles DA, Iaschi SP, O’Brien PA, Tay GK (2005) Myostatin and its implications on animal breeding: a review. Anim Genet 36:1–6. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2004.01229.x
Cash JN, Rejon CA, McPherron AC, Bernard DJ, Thompson TB (2009) The structure of myostatin:follistatin 288: insights into receptor utilization and heparin binding. EMBO J 28:2662–2676. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.205
Forbes D, Jackman M, Bishop A, Thomas M, Kambadur R, Sharma M (2006) Myostatin auto-regulates its expression by feedback loop through Smad7 dependent mechanism. J Cell Physiol 206(1):264–272
Gilson H, Schakman O, Kalista S, Lause P, Tsuchida K, Thissen JP (2009) Follistatin induces muscle hypertrophy through satellite cell proliferation and inhibition of both myostatin and activin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297:E157–E164. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00193.2009
Haidet AM et al (2008) Long-term enhancement of skeletal muscle mass and strength by single gene administration of myostatin inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:4318–4322. doi:10.1073/pnas.0709144105
Iemura S et al (1998) Direct binding of follistatin to a complex of bone-morphogenetic protein and its receptor inhibits ventral and epidermal cell fates in early Xenopus embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9337–9342
Iezzi S et al (2004) Deacetylase inhibitors increase muscle cell size by promoting myoblast recruitment and fusion through induction of follistatin. Dev Cell 6:673–684
Joulia-Ekaza D, Cabello G (2006) Myostatin regulation of muscle development: molecular basis, natural mutations, physiopathological aspects. Exp Cell Res 312:2401–2414. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.04.012
Kambadur R, Sharma M, Smith TP, Bass JJ (1997) Mutations in myostatin (GDF8) in double-muscled Belgian Blue and Piedmontese cattle. Genome Res 7:910–916
Kollias HD, McDermott JC (2008) Transforming growth factor-beta and myostatin signaling in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 104:579–587. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01091.2007
Kota J et al (2009) Follistatin gene delivery enhances muscle growth and strength in nonhuman primates. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3000112
Langley B, Thomas M, Bishop A, Sharma M, Gilmour S, Kambadur R (2002) Myostatin inhibits myoblast differentiation by down-regulating MyoD expression. J Biol Chem 277:49831–49840. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204291200
Lee SJ (2007) Quadrupling muscle mass in mice by targeting TGF-beta signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2:e789. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000789
Lee SJ, McPherron AC (2001) Regulation of myostatin activity and muscle growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9306–9311. doi:10.1073/pnas.151270098
Lee SJ et al (2010) Regulation of muscle mass by follistatin and activins. Mol Endocrinol 24:1998–2008. doi:10.1210/me.2010-0127
Liu S, Li X, Lu D, Shang S, Wang M, Zheng M, Zhang R, Tang B, Li Q, Dai Y, Li N (2012) High-level expression of bioactive recombinant human lysozyme in the milk of transgenic mice using a modified human lactoferrin BAC. Transgenic Res 21(2):407–414
Matzuk MM, Lu N, Vogel H, Sellheyer K, Roop DR, Bradley A (1995) Multiple defects and perinatal death in mice deficient in follistatin. Nature 374:360–363. doi:10.1038/374360a0
McPherron AC, Lee SJ (1997) Double muscling in cattle due to mutations in the myostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12457–12461
McPherron AC, Lawler AM, Lee SJ (1997) Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-beta superfamily member. Nature 387:83–90. doi:10.1038/387083a0
Medeiros EF, Phelps MP, Fuentes FD, Bradley TM (2009) Overexpression of follistatin in trout stimulates increased muscling. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R235–R242. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.91020.2008
Mosher DS, Quignon P, Bustamante CD, Sutter NB, Mellersh CS, Parker HG, Ostrander EA (2007) A mutation in the myostatin gene increases muscle mass and enhances racing performance in heterozygote dogs. PLoS Genet 3:e79. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030079
Patel K (1998) Follistatin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 30:1087–1093
Schneyer AL, Wang Q, Sidis Y, Sluss PM (2004a) Differential distribution of follistatin isoforms: application of a new FS315-specific immunoassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5067–5075. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0162
Schneyer AL, Wang QF, Sidis Y, Sluss PM (2004b) Differential distribution of follistatin isoforms: application of a new FS315-specific immunoassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5067–5075. doi:10.1210/Jc.2004-0162
Sugino K et al (1993) Molecular heterogeneity of follistatin, an activin-binding protein—higher affinity of the carboxyl-terminal truncated forms for heparan-sulfate proteoglycans on the ovarian granulosa-cell. J Biol Chem 268:15579–15587
Thompson TB, Lerch TF, Cook RW, Woodruff TK, Jardetzky TS (2005a) The structure of the follistatin: activin complex reveals antagonism of both type I and type II receptor binding. Dev Cell 9:535–543. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2005.09.008
Thompson TB, Lerch TF, Cook RW, Woodruff TK, Jardetzky TS (2005b) The structure of the follistatin:activin complex reveals antagonism of both type I and type II receptor binding. Dev Cell 9:535–543. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2005.09.008
Trendelenburg AU, Meyer A, Rohner D, Boyle J, Hatakeyama S, Glass DJ (2009) Myostatin reduces Akt/TORC1/p70S6 K signaling, inhibiting myoblast differentiation and myotube size. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C1258–C1270. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00105.2009
Vandekerckhove J, Bugaisky G, Buckingham M (1986) Simultaneous expression of skeletal muscle and heart actin proteins in various striated muscle tissues and cells. A quantitative determination of the two actin isoforms. J Biol Chem 261:1838–1843
Wang Q, Keutmann HT, Schneyer AL, Sluss PM (2000) Analysis of human follistatin structure: identification of two discontinuous N-terminal sequences coding for activin A binding and structural consequences of activin binding to native proteins. Endocrinology 141:3183–3193
Welle SL (2009) Myostatin and muscle fiber size. Focus on “Smad2 and 3 transcription factors control muscle mass in adulthood” and “Myostatin reduces Akt/TORC1/p70S6 K signaling, inhibiting myoblast differentiation and myotube size”. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C1245–C1247. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00154.2009
Williams MS (2004) Myostatin mutation associated with gross muscle hypertrophy in a child. N Engl J Med 351:1030–1031 (author reply 1030–1031)
Winbanks CE et al (2012) Follistatin-mediated skeletal muscle hypertrophy is regulated by Smad3 and mTOR independently of myostatin. J Cell Biol 197:997–1008. doi:10.1083/jcb.201109091
Zhang Y, Li J, Villemoes K, Pedersen AM, Purup S, Vajta G (2007) An epigenetic modifier results in improved in vitro blastocyst production after somatic cell nuclear transfer. Cloning Stem Cells 9:357–363. doi:10.1089/clo.2006.0090
Acknowledgments
We thank Qiuyan Li for technical assistance. This work was supported by funding from the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB943103), National Transgenic Breeding Program (2014ZX08006 and 2013ZX08006-002) and National Scientific Foundation of China (81370840).
Author contributions
Rui Fang conceived and designed the experiments; Fei Chang, Meng Wang, Xin Zhao, Rui Fang and Wen Chang performed the experimental work; Zaihu Zhang managed the breeding and feeding of transgenic pigs; Rui Fang, Fei Chang, Meng Wang, Ning Li and Qingyong Meng wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Fei Chang, Rui Fang and Meng Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, F., Fang, R., Wang, M. et al. The transgenic expression of human follistatin-344 increases skeletal muscle mass in pigs. Transgenic Res 26, 25–36 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-016-9985-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-016-9985-x