Abstract
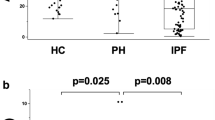
Limited data exist on changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) collagen biomarkers levels during chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) development. This study aimed to investigate ECM collagen biomarkers levels in stable patients with CTEPH. Patients with CTEPH and healthy persons were enrolled. Serum levels of procollagen III N-terminal peptide (PIIINP), carboxyterminal propeptide of type I procollagen (PICP), matrix metalloproteinases (MMP2), MMP9, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1(TIMP1) were measured by ELISA. Clinical data coincident with samples were collected. The pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA) and control pulmonary artery tissue samples were analyzed for genetic and immunohistochemical differences. The serum concentrations of PIIINP, PICP, MMP2, and MMP9 decreased significantly in CTEPH patients compared to healthy controls (P < 0.001 for each). CTEPH patients had higher serum concentrations of TIMP1 (median, 111.97 [interquartile range, 84.35–139.93]) compared to healthy controls (74.97 [44.03–108.45] ng/mL, P < 0.001). The MMP2 to TIMP1 ratio was lower in patients than in the controls (P < 0.001). After adjusting for the body mass index (BMI), the MMP2 to TIMP1 ratio correlated negatively with pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) (r = − 0.327, P = 0.025). Increased TIMP1 (P = 0.04) gene expression was identified in tissues of CTEPH patients. Immunohistochemistry results of vascular walls substantiated qRT-PCR results. This study indicates that ECM collagen biomarkers levels were significantly different in stable patients with CTEPH and healthy controls with significantly increased TIMP1 and decreased MMP2 and MMP9. Differences in TIMP1 expression should be expected not only among healthy controls and patients serum, but also across pathological tissue regions. These findings suggest that the state of vascular remodeling in pulmonary vascular bed in stable patients may be represented by ECM collagen biomarkers levels. We conclude that TIMP1 may play an important role in pulmonary vascular reconstruction in stable CTEPH patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akahane T, Akahane M, Shah A, Connor CM, Thorgeirsson UP (2004) TIMP-1 inhibits microvascular endothelial cell migration by MMP-dependent and MMP-independent mechanisms. Exp Cell Res 301:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.002
Bochenek ML, Rosinus NS, Lankeit M, Hobohm L, Bremmer F, Schutz E, Klok FA, Horke S, Wiedenroth CB, Munzel T, Lang IM, Mayer E, Konstantinides S, Schafer K (2017) From thrombosis to fibrosis in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Thromb Haemost 117:769–783. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH16-10-0790
Duprez DA, Gross MD, Ix JH, Peralta CA, Kizer JR, Shea S, Jacobs DJ (2019) Collagen biomarkers are associated with decline in renal function independently of blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Study. J Hypertens 37:2398–2403. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000002207
Fessler JH, Fessler LI (1978) Biosynthesis of procollagen. Annu Rev Biochem 47:129–162. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001021
Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery J, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Beghetti M, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Hansmann G, Klepetko W, Lancellotti P, Matucci M, McDonagh T, Pierard LA, Trindade PT, Zompatori M, Hoeper M (2015) 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 46:903–975. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01032-2015
Golob MJ, Tabima DM, Wolf GD, Johnston JL, Forouzan O, Mulchrone AM, Kellihan HB, Bates ML, Chesler NC (2017) Pulmonary arterial strain- and remodeling-induced stiffening are differentiated in a chronic model of pulmonary hypertension. J Biomech 55:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2017.02.003
Higuchi M, Yasuda O, Kawamoto H, Yotsui T, Baba Y, Ozaki T, Maeda N, Fukuo K, Rakugi H, Ogihara T (2007) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 deficiency inhibits blood pressure elevation and myocardial microvascular remodeling induced by chronic administration of Nomega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester in mice. Hypertens Res 30:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.563
Rossignol P, Iraqi W, Angioi M, Fay R, Nuée J, Ketelslegers JM, Vincent J, Pitt B, Zannad F (2009) Extracellular cardiac matrix biomarkers in patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure. Circulation 119:2471–2479. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.809194
Jujo T, Sakao S, Tsukahara M, Kantake M, Maruoka M, Tanabe N, Masuda M, Tatsumi K (2014) The role of matrix metalloproteinase in the intimal sarcoma-like cells derived from endarterectomized tissues from a chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patient. PLoS ONE 9:e87489. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087489
Kölmel S, Hobohm L, Käberich A, Krieg VJ, Bochenek ML, Wenzel P, Wiedenroth CB, Liebetrau C, Hasenfuß G, Mayer E, Konstantinides SV, Schäfer K, Guth S, Lankeit M (2019) Potential involvement of osteopontin in inflammatory and fibrotic processes in pulmonary embolism and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Thromb Haemost 119:1332–1346. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1692174
Li K, Tay FR, Yiu C (2019) The past, present and future perspectives of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107465
Lombardi R, Betocchi S, Losi MA, Tocchetti CG, Aversa M, Miranda M, D’Alessandro G, Cacace A, Ciampi Q, Chiariello M (2003) Myocardial collagen turnover in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 108:1455–1460. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000090687.97972.10
Overall CM, Lopez-Otin C (2002) Strategies for MMP inhibition in cancer: innovations for the post-trial era. Nat Rev Cancer 2:657–672. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc884
Qi JH, Ebrahem Q, Moore N, Murphy G, Claesson-Welsh L, Bond M, Baker A, Anand-Apte B (2003) A novel function for tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP3): inhibition of angiogenesis by blockage of VEGF binding to VEGF receptor-2. Nat Med 9:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm846
Quarck R, Wynants M, Ronisz A, Sepulveda MR, Wuytack F, Van Raemdonck D, Meyns B, Delcroix M (2012) Characterization of proximal pulmonary arterial cells from chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients. Respir Res 13:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-13-27
Quarck R, Wynants M, Verbeken E, Meyns B, Delcroix M (2015) Contribution of inflammation and impaired angiogenesis to the pathobiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 46:431–443. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00009914
Quintero-Fabian S, Arreola R, Becerril-Villanueva E, Torres-Romero JC, Arana-Argaez V, Lara-Riegos J, Ramirez-Camacho MA, Alvarez-Sanchez ME (2019) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis and cancer. Front Oncol 9:1370. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01370
Safdar Z, Tamez E, Chan W, Arya B, Ge Y, Deswal A, Bozkurt B, Frost A, Entman M (2014) Circulating collagen biomarkers as indicators of disease severity in pulmonary arterial hypertension. JACC Heart Fail 2:412–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchf.2014.03.013
Safdar Z, Tamez E, Frost A, Guffey D, Minard CG, Entman ML (2015) Collagen metabolism biomarkers and health related quality of life in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int J Cardiovasc Res. https://doi.org/10.4172/2324-8602.1000198
Saleby J, Bouzina H, Lundgren J, Radegran G (2017) Angiogenic and inflammatory biomarkers in the differentiation of pulmonary hypertension. Scand Cardiovasc J 51:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/14017431.2017.1359419
Seo DW, Li H, Guedez L, Wingfield PT, Diaz T, Salloum R, Wei BY, Stetler-Stevenson WG (2003) TIMP-2 mediated inhibition of angiogenesis: an MMP-independent mechanism. Cell 114:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00551-8
Serralheiro P, Novais A, Cairrão E, Maia C, Costa Almeida C, Verde I (2018) Variability of MMP/TIMP and TGF-β1 receptors throughout the clinical progression of chronic venous disease. Int J Mol Sci 19:6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010006
Stintzing S, Heuschmann P, Barbera L, Ocker M, Jung A, Kirchner T, Neureiter D (2005) Overexpression of MMP9 and tissue factor in unstable carotid plaques associated with Chlamydia pneumoniae, inflammation, and apoptosis. Ann Vasc Surg 19:310–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10016-005-0003-7
Tiede SL, Wassenberg M, Christ K, Schermuly RT, Seeger W, Grimminger F, Ghofrani HA, Gall H (2016) Biomarkers of tissue remodeling predict survival in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Int J Cardiol 223:821–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.08.240
Vieillard-Baron A, Frisdal E, Raffestin B, Baker AH, Eddahibi S, Adnot S, D’Ortho MP (2003) Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases by lung TIMP-1 gene transfer limits monocrotaline-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats. Hum Gene Ther 14:861–869. https://doi.org/10.1089/104303403765701150
Wang XM, Shi K, Li JJ, Chen TT, Guo YH, Liu YL, Yang YF, Yang S (2015) Effects of angiotensin II intervention on MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and collagen expression in rats with pulmonary hypertension. Genet Mol Res 14:1707–1717. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.March.6.17
Wang Z, Chesler NC (2011) Pulmonary vascular wall stiffness: An important contributor to the increased right ventricular afterload with pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Circ 1:212–223. https://doi.org/10.4103/2045-8932.83453
Wetzl V, Tiede SL, Faerber L, Weissmann N, Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA, Gall H (2017) Plasma MMP2/TIMP4 ratio at follow-up assessment predicts disease progression of idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Lung 195:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-017-0014-5
Zaloudikova M, Eckhardt A, Vytasek R, Uhlik J, Novotny T, Bacakova L, Musilkova J, Hampl V (2019) Decreased collagen VI in the tunica media of pulmonary vessels during exposure to hypoxia: a novel step in pulmonary arterial remodeling. Pulm Circ 9:766686965. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045894019860747
Zhang YX, Li JF, Yang YH, Zhai ZG, Gu S, Liu Y, Miao R, Zhong PP, Wang Y, Huang XX, Wang C (2018) Renin-angiotensin system regulates pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell migration in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 314:L276–L286. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00515.2016
Funding
This study is fund by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81570049, 81970058); Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (No. 2018-I2M-1-003); Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7152062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WP: Conception and design of the study; collection, analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; final approval of the manuscript. ZZ: Analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; final approval of the manuscript. YZ and MZ: Collection the surgical specimens; final approval of the manuscript. RM: Provide technical guidance and analysis of data; final approval of the manuscript. YY, JW, WX and CW: Participate in patients clinical data acquisition and interpret of the data; final approval of the manuscript. ZZ: Conception and design of the study; collection, analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All the procedures carried out with human data and samples were approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital (Nos. 2015-S-53, 2019-121-K83) in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, W., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. Extracellular matrix collagen biomarkers levels in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J Thromb Thrombolysis 52, 48–58 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02329-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02329-8