Abstract
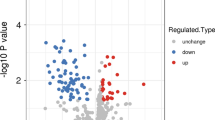
To investigate differences in the expression of plasma proteins in immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and normal control groups, bone marrow samples were collected from 20 active ITP patients and 20 healthy controls. Quantitative proteomics analysis based on mass spectrometry was used to measure the protein levels and understand the protein networks. We found differentially expressed proteins in ITP patients and healthy controls. Parallel reaction monitoring (PRM), a targeted proteome quantification technique, was used to quantitatively confirm the identified target proteins and verify the proteomics data. In this study, a total of 829 proteins were identified, and the fold-change cut-off was set at 1.5 (patients vs controls); a total of 26 proteins were upregulated, and 69 proteins were downregulated. The bioinformatics analysis indicated that some differentially expressed proteins were associated with apoptosis. KEGG enrichment analysis showed that the apoptosis-related proteins were closely related to the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway. PRM demonstrated that apoptosis-related proteins were significantly decreased in ITP patients, which further confirmed the important effect of apoptosis on ITP pathogenesis. We hypothesised that apoptosis may be closely related to ITP pathogenesis through the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swinkels M, Rijkers M, Voorberg J, Vidarsson G, Leebeek FWG, Jansen AJG (2018) Emerging concepts in immune thrombocytopenia. Front Immunol 9:880
Liu Z, Mei T (2018) Immune thrombocytopenia induces autophagy and suppresses apoptosis in megakaryocytes. Mol Med Rep 18:4016–4022
Audia S, Mahevas M, Samson M, Godeau B, Bonnotte B (2017) Pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia. Autoimmun Rev 16:620–632
Zhao C, Li XF, Zhang F, Wang L, Peng J, Hou M (2008) Increased cytotoxic T-lymphocytemediated cytotoxicity predominant in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura without platelet autoantibodies. Haematologica 93:1428–1430
Speer O, Schmugge M (2010) Investigating caspases and other markers of apoptosis in ITP. Ann Hematol 89(Suppl 1):45–46
McArthur K, Chappaz S, Kile BT (2018) Apoptosis in megakaryocytes and platelets: the life and death of a lineage. Blood 131(6):605–610
De Botton S, Sabri S, Daugas E, Zermati Y, Guidotti JE, Hermine O et al (2002) Platelet formation is the consequence of caspase activation within megakaryocytes. Blood 100(4):1310–1317
Josefsson EC, James C, Henley KJ, Debrincat MA, Rogers KL, Dowling MR et al (2011) Megakaryocytes possess a functional intrinsic apoptosis pathway that must be restrained to survive and produce platelets. J Exp Med 208(10):2017–2031
Houwerzijl EJ, Blom NR, van der Want JJL, Esselink MT, Koornstra JJ, Smit JW et al (2004) Ultrastructural study shows morphologic features of apoptosis and para-apoptosis in megakaryocytes from patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 103(2):500–506
Iraqi M, Perdomo J, Yan F, Choi PY, Chong BH (2015) Immune thrombocytopenia: antiplatelet autoantibodies inhibit proplatelet formation by megakaryocytes and impair platelet production in vitro. Haematologica 100(5):623–632
Vrbensky JR, Nazy I, Toltl LJ, Ross C, Ivetic N, Smith JW et al (2018) Megakaryocyte apoptosis in immune thrombocytopenia. Platelets 29(7):729–732
Sloan JM, Coburn JP, Bertino AM, Wood V, Kuter DJ (2007) a comparative proteomic analysis of platelets from healthy human patients and chronic ITP patients receiving AMG 531, a thrombopoiesis-stimulating protein. Blood 110(11):1313
Kamhieh-Milz J, Sterzer V, Celik H, Khorramshahi O, Fadl Hassan Moftah R, Salama A (2017) Identification of novel autoantigens via mass spectroscopy-based antibody-mediated identification of autoantigens (MS-AMIDA) using immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) as a model disease. J Proteomics 157:59–70
Zhang HW, Zhou P, Wang KZ, Liu JB, Huang YS, Tu YT et al (2016) Platelet proteomics in diagnostic differentiation of primary immune thrombocytopenia using SELDI-TOF-MS. Clin Chim Acta 455:75–79
Lambert MP, Gernsheimer TB (2017) Clinical updates in adult immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 129(21):2829–2835
Geiger T, Wehner A, Schaab C, Cox J, Mann M (2012) Comparative proteomic analysis of eleven common cell lines reveals ubiquitous but varying expression of most proteins. Molecular Cellular Proteomics. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M111.014050
Dimmer EC, Huntley RP, Alam-Faruque Y, Sawford T, O’Donovan C, Martin MJ et al (2012) The UniProt-GO annotation database in 2011. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D565–D570
de Hoon MJ, Imoto S, Nolan J, Miyano S (2004) Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 20(9):1453–1454
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P et al (2011) The STRING database in 2011: functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D561–D568
Xu X, Liu T, Yang J, Chen L, Liu B, Wang L et al (2018) The first whole-cell proteome- and lysine-acetylome-based comparison between trichophyton rubrum conidial and mycelial stages. J Proteome Res 17(4):1436–1451
Beere HM, Beni BW, Kelvin C, Dick DM, Artin M, Tomomi K et al (2000) Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol 2:469–475
Sverchinsky DV, Nikotina AD, Komarova EY, Mikhaylova ER, Aksenov ND, Lazarev VF et al (2018) Etoposide-induced apoptosis in cancer cells can be reinforced by an uncoupled link between Hsp70 and Caspase-3. Int J Mol Sci. 19(9):2519
Aitken A (2006) 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol 16(3):162–172
Park GY, Han JY, Han YK, Kim SD, Kim JS, Jo WS et al (2014) 14-3-3 eta depletion sensitizes glioblastoma cells to irradiation due to enhanced mitotic cell death. Cancer Gene Ther 21(4):158–163
Kwon Y, Vinayagam A, Sun X, Dephoure N, Gygi SP, Hong P et al (2013) The Hippo signaling pathway interactome. Science 342(6159):737–740
Bury L, Falcinelli E, Chiasserini D, Springer TA, Italiano JE Jr, Gresele P (2016) Cytoskeletal perturbation leads to platelet dysfunction and thrombocytopenia in variant forms of Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Haematologica 101(1):46–56
Marta S, Fuentes P, Esteve-Codina A, Béjar E, McGrai K, Thomas G et al (2017) Hypoxia-mediated translational activation of ITGB3 in breast cancer cells enhances TGF-β signaling and malignant features in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 8(70):114856–114876
Fisher AB (2011) Peroxiredoxin 6: a bifunctional enzyme with glutathione peroxidase and phospholipase A2 activities. Antioxid Redox Signal 15(3):831–844
Fernandez MC, Moawad YuA, AR, O’Flaherty C, (2019) Peroxiredoxin 6 regulates the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway to maintain human sperm viability. Mol Hum Reprod 25:787–796
Deng G, Yu S, Li Q, He Y, Liang W, Yu L et al (2017) Investigation of platelet apoptosis in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Hematology 22(3):155–161
Stojanovic A, Marjanovic JA, Brovkovych VM, Peng X, Hay N, Skidgel RA et al (2006) A phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT-nitric oxide-cGMP signaling pathway in stimulating platelet secretion and aggregation. J Biol Chem 281(24):16333–16339
Chen M, Yan R, Zhou K, Li X, Zhang Y, Liu C et al (2018) Akt-mediated platelet apoptosis and its therapeutic implications in immune thrombocytopenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(45):E10682–E10691
Nam GS, Lee K-S, Nam K-S (2019) Morin hydrate inhibits platelet activation and clot retraction by regulating integrin αIIbβ3, TXA2, and cAMP levels. European Journal Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172734
Schoenwaelder SM, Ono A, Nesbitt WS, Lim J, Jarman K, Jackson SP (2010) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110 beta regulates integrin alpha IIb beta 3 avidity and the cellular transmission of contractile forces. J Biol Chem 285(4):2886–2896
Chen J, De S, Damron DS, Chen WS, Hay N, Byzova TV (2004) Impaired platelet responses to thrombin and collagen in AKT-1–deficient mice. Blood 104(6):1703–1710
Tzivion G, Avruch J (2002) 14-3-3 proteins: active cofactors in cellular regulation by serine/threonine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 277(5):3061–3064
Gomez-Suarez M, Gutierrez-Martinez IZ, Hernandez-Trejo JA, Hernandez-Ruiz M, Suarez-Perez D, Candelario A et al (2016) 14-3-3 Proteins regulate Akt Thr308 phosphorylation in intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Death Differ 23(6):1060–1072
Lee KH, Jeong J, Yoo CG (2013) Positive feedback regulation of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) is mediated through Toll-like receptor 4-PI3K/Akt-glycogen synthase kinase-3beta pathway. Exp Cell Res 319(1):88–95
Chatterjee M, Andrulis M, Stuhmer T, Muller E, Hofmann C, Steinbrunn T et al (2013) The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway regulates the expression of Hsp70, which critically contributes to Hsp90-chaperone function and tumor cell survival in multiple myeloma. Haematologica 98(7):1132–1141
Walsh B, Pearl A, Suchy S, Tartaglio J, Visco K, Phelan SA (2009) Overexpression of Prdx6 and resistance to peroxide-induced death in Hepa1-6 cells: Prdx suppression increases apoptosis. Redox Rep 14(6):275–284
Nogueira V, Park Y, Chen CC, Xu PZ, Chen ML, Tonic I et al (2008) Akt determines replicative senescence and oxidative or oncogenic premature senescence and sensitizes cells to oxidative apoptosis. Cancer Cell 14(6):458–470
Song X, Wang Z, Liang H, Zhang W, Ye Y, Li H et al (2017) Dioscin induces gallbladder cancer apoptosis by inhibiting ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT signalling. Int J Biol Sci 13(6):782–793
Wang JD, Ou TT, Wang CJ, Chang TK, Lee HJ (2010) Platelet apoptosis resistance and increased CXCR4 expression in pediatric patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Res 126(4):311–318
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by grants from by Taishan Youth Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. tsqn201812140), Academic promotion programme of Shandong First Medical University (Grant No. 2019RC018), Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81570104), Key Research and Development Project of Jinan (Grant Nos. 201907021; 201907026), Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2018CXGC1213); Technology Development Projects of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2017GSF18189).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LSY contributed to experimental design and data analysis. YD contributed to data analysis. SRJ and ZJJ contributed to the statistical analysis. SNN obtained funding, experimental design and writing of the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Informed consent was obtained from each participating patient and/or legal guardian. Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Medical Ethical Committee of Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University and Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Sy., Yuan, D., Sun, RJ. et al. Significant reductions in apoptosis-related proteins (HSPA6, HSPA8, ITGB3, YWHAH, and PRDX6) are involved in immune thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Thrombolysis 51, 905–914 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02310-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02310-5