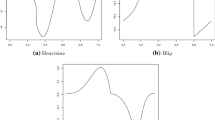
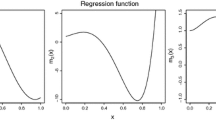
Abstract
The paper considers regression problems with univariate design points. The design points are irregular and no assumptions on their distribution are imposed. The regression function is retrieved by a wavelet based reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) technique with the penalty equal to the sum of blockwise RKHS norms. In order to simplify numerical optimization, the problem is replaced by an equivalent quadratic minimization problem with an additional penalty term. The computational algorithm is described in detail and is implemented with both the sets of simulated and real data. Comparison with existing methods showed that the technique suggested in the paper does not oversmooth the function and is superior in terms of the mean squared error. It is also demonstrated that under additional assumptions on design points the method achieves asymptotic optimality in a wide range of Besov spaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovich F., Bailey T. and Sapatinas T. 2000. Wavelet analysis and its statistical applications. The Statistician—Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Ser. D 49: 1–29.
Amato, U. and Vuza, D.T. 1997. Wavelet approximation of a function from samples affected by noise. Rev. Roumaine Math. Pures Appl. 42: 481–493.
Antoniadis, A. 1996. Smoothing noisy data with tapered coiflets series. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 23: 313–330.
Antoniadis, A., Bigot, J. and Sapatinas, T. 2001. Wavelet estimators in nonparametric regression: a comparative simulation study. Journal of Statistical Software 6.
Antoniadis, A. and Fan, J. 2001. Regularization by Wavelet Approximations. J. Amer. Statist. Assoc. 96: 939–967.
Aronszajn, N. 1950. Theory of reproducing kernels. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 68: 337–404.
Birgé, L. and Massart, P. 2000. An adaptive compression algorithm in Besov spaces, Journal of Constructive Approximation 16: 1–36.
Birman, M.S. and Solomjak, M.Z. 1967. Piecewise-polynomial approximation of functions of the classes W p. Mat. Sbornik. 73: 295–317.
Brinkman, N. 1981. Ethanol fuel - a single-cylinder engine study of efficiency and exhaust emissions. SAE Transactions 90: 1414–1424.
Cai, T. 1999. Adaptive wavelet estimation: A block thresholding and oracle inequality approach. Ann. Statist. 27: 898–924.
Cai, T. 2001. Discussion of “Regularization of Wavelets Approximations” by A. Antoniadis and J. Fan. J. American Statistical Association 96: 960–962.
Cai, T. and Brown, L. D. 1998. Wavelet Shrinkage for nonequispaced samples, The Annals of Statistics 26: 1783–1799.
Cai, T. and Silverman, B.W. 2001. Incorporating information on neighboring coefficients into wavelet estimation. Sankhya 63: 127–148.
Canu, S., Mary, X., and Rakotomamonjy, A. 2003. Functional learning through kernel, in Advances in Learning Theory: Methods, Models and Applications, NATO Science Series III: Computer and Systems Sciences, Suykens, J. et al., Eds. IOS Press, Amsterdam 90: 89–110.
Craven, P. and Wahba, G. 1979. Smoothing noisy data with spline functions. Numer. Math. 31: 377–403.
Daubechies, I. 1992. Ten Lectures on Wavelets. Philadelphia: SIAM.
Delouille, V., Franke, J. and Von Sachs, R. 2001. Nonparametric stochastic regression with design-adapted wavelets. Sankhya, Series A, Vol 63 (3), pp. 328–366.
DeVore, R.A. and Popov, V. 1988. Interpolation of Besov Spaces. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 305: 397–414.
Donoho D.L., Elad, M. and Temlyakov, V. 2004. Stable Recovery of Sparse Overcomplete Representations in the Presence of Noise. Technical report, Stanford University.
Donoho, D.L., Johnstone, I.M., Kerkyacharian, G. and Picard, D. 1995. Wavelet shrinkage: asymptopia? (with discussion). Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 57: 301–337.
Eubank, R.L. 1988 Spline Smoothing and Nonparametric Regression, New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
van de Geer, S. 2000. Empirical Processes in M-Estimation. Cambridge University Press.
Gradshtein, I.S., and Ryzhik, I.M. 1980 Tables of Integrals, Series, and Products. Academic Press, New York.
Green, P.J. and Silverman, B.W. 1994. Nonparametric Regression and Generalised Linear Models. London: Chapman and Hall.
Gunn, S.R. and Kandola, J.S. 2002. Structural modeling with sparse kernels. Mach. Learning 48: 115–136.
Hall, P., Kerkyacharian, G. and Picard, D. 1999. On the minimax optimality of block thresholded wavelet estimators. Statist. Sinica 9: 33–50.
Hall, P. and Turlach, B.A. 1997 Interpolation methods for nonlinear wavelet regression with ir- regularly spaced design. Ann. Statist. 25: 1912–1925.
Härdle, W., Kerkyacharian, G., Picard, D. and Tsybakov, A. 1998. Wavelets, Approximation, and Statistical Applications, Lecture Notes in Statistics, 129: Springer-Verlag, New-York.
Karlovitz, L.A. 1970. Construction of nearest points in the l p , p even and l 1 norms, Journal of Approximation Theory 3: 123–127.
Kerkyacharian, G. and Picard, D. 2003. Replicant compression coding in Besov spaces, ESAIM: P and S 7: 239–250.
Kimeldorf G., and Wahba, G.1971. Some results on Tchebycheffian spline functions. J. Math. Anal. Applic. 33: 82–95.
Kohler, M. 2003 Nonlinear orthogonal series estimation for random design regression. J. Stat. Plan. Infer. 115: 491–520.
Kovac, A. and Silverman, B. 2000. Extending the scope of wavelet regression methods by coefficient-dependent thresholding. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 95: 172–183.
Lin, Y. and Zhang, H.H. 2003. Component Selection and Smoothing in Smoothing Spline Analysis of Variance Models, Technical report, University of Wisconsin—Madison.
Lin, X., Wahba, G., Xiang, D., Gao, F., Klein, R. and Klein, B. 2000. Smoothing spline ANOVA models for large data sets with Bernoulli observations and the randomized GACV. Ann. Statist. 28: 1570–1600.
Loubes, J.-M. and van de Geer, S. 2002, Adaptive estimation with soft thresholding penalties, Statistica Neerlandica 56: 454–479.
Mallat, S.G. 1999. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press.
Meyer, Y. 1992. Wavelets and Operators. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Nason, G. 1998. WaveThresh3 Software. Department of Mathematics, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK.
Nason, G. 2002 Choice of wavelet smoothness, primary resolution and threshold in wavelet shrinkage. Statistics and Computing 12: 219–227.
Sardy, S., Percival, D.B., Bruce A., G., Gao, H.-Y. and Stuelzle, W. 1999. Wavelet shrinkage for unequally spaced data, Statistics and Computing 9: 65–75.
Silverman, B.W. 1985 Some aspects of the spline smoothing approach to non-parametric curve fitting. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society series B. 47: 1–52.
Tapia, R. and Thompson, J. 1978. Nonparametric Probability Density Estimation. Baltimore, MD, Johns Hopkins University Press.
Tibshirani, R. J. 1996. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. Journal of Royal Statistical Society, B 58: 267–288.
Triebel, H. 1983. Theory of Function Spaces. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel.
Vidakovic, B. 1999. Statistical Modeling by Wavelets. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Wahba, G. 1990. Spline Models for Observational Data, SIAM. CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics, 59.
Wahba, G., Wang, Y., Gu, C., Klein, R. and Klein, B. 1995 Smoothing spline ANOVA for exponential families, with application to the Wisconsin Epidemiological Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. Ann. Statist. 23: 1865–1895.
Zhang, H., Wahba, G., Lin, Y., Voelker, M., Ferris, M., Klein, R. and Klein, B. 2002. Variable selection and model building via likelihood basis pursuit. Technical report, University of Wisconsin—Madison.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amato, U., Antoniadis, A. & Pensky, M. Wavelet kernel penalized estimation for non-equispaced design regression. Stat Comput 16, 37–55 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-006-5283-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-006-5283-4