Abstract
In recent years, debates on sustainable economic development have highlighted the importance of comprehensive growth especially in developing countries. Inclusive growth is widely seen as a key ingredient for sustainable development. However, there is little empirical evidence to support this claim. The current study examines the level of inclusive growth and sustainable development and association among them in 11 selected developing countries for the year 2008 and 2018. We extract key factors on variables of interest from 7 pillars of inclusive growth level and United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals by using the Principal Components Analysis and the Multivariate Analysis. The key results highlight that Turkey and China have achieved highest while Pakistan and Indonesia represent the lowest level of inclusive growth. Similarly, Brazil and Pakistan show the lowest while Cambodia and Thailand hold the highest rank on sustainable development level. The empirical findings show high value of negative correlation coefficients between social inclusion of inclusive growth and prevalence of poverty with life-threatening factors of sustainable development. Similarly, a high positive value between unsatisfactory medical services, education and state transparency of inclusive growth; poverty and its consequences of sustainable development further confirms the robustness of association among variables of interest our. A strong recommendation on improving the inclusive growth as policy strategy is suggested in developing countries to further enhance the sustainable development.

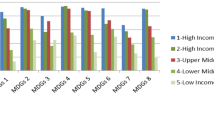
(Source: World Economic Forum)

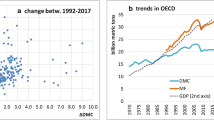
Source: Author’s framework




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, I., & Zhuang, J. (2007). Inclusive growth toward a prosperous Asia: Policy implications. ERD Working Paper Series.
Alrasheedi, M., Mardani, A., Mishra, A. R., Streimikiene, D., Liao, H., & Al-nefaie, A. H. (2021). Evaluating the green growth indicators to achieve sustainable development: A novel extended interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy-combined compromise solution approach. Sustainable Development, 29(1), 120–142. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2136
Aşici, A. A. (2013). Economic growth and its impact on environment: A panel data analysis. Ecological Indicators, 24, 324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.06.019
Assembly, G. (2019). Resolution adopted by the general assembly on 25 September 2015. Sustainable Development Goals. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119541851.app1
Bąk, I., Cheba, K., & Szczecińska, B. (2019). The statistical analysis of road traffic in cities of Poland. Transportation Research Procedia, 39, 14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2019.06.003
Brundtland, G. H., Khalid, M., Agnelli, S., Al-Athel, S., & Chidzero, B. (1987). Our common future. New York. Report of the World Council For Economic Development.
Cabeza-García, L., Del Brio, E. B., & Oscanoa-Victorio, M. L. (2018). Gender factors and inclusive economic growth: The silent revolution. Sustainability (switzerland), 10(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010121
Carmignani, F. (2010). The economics of growth. Economic record (Vol. 86). MIT Press. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4932.2010.00622.x
Cichowicz, E., & Rollnik-Sadowska, E. (2018). Inclusive growth in CEE countries as a determinant of sustainable development. Sustainability (switzerland), 10(11), 3973. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10113973
Conway, J. M., & Huffcutt, A. I. (2003). A review and evaluation of exploratory factor analysis practices in organizational research. Organizational Research Methods, 6(2), 147–168. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428103251541
Costanza, R., Kubiszewski, I., Giovannini, E., Lovins, H., McGlade, J., Pickett, K. E., et al. (2014). Development: Time to leave GDP behind. Nature News, 505(7483), 283.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16(3), 297–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02310555
Dalampira, E. S., & Nastis, S. A. (2020). Mapping Sustainable development goals: A network analysis framework. Sustainable Development, 28(1), 46–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.1964
Demirguc-Kunt, A., Klapper, L., Singer, D., Ansar, S., & Hess, J. (2018). The Global Findex Database 2017: Measuring financial inclusion and the fintech revolution. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1259-0
Demirguc-Kunt, A., Klapper, L., Singer, D., & Van Oudheusden, P. (2015). The Global Findex Database 2014. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper. The World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/1813-9450-7255
Desa, U. (2018). Transforming our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development. A New Era in Global Health. https://doi.org/10.1891/9780826190123.ap02
Diamond, P. (2010). How globalisatin is changing patterns of marginalisation and inclusion in the UK. Joseph Rowntree Foundation New York.
Divakaran, S., Shariff, M., & McGinnis, P. (2014). Private Equity and Venture Capital in Smes in Developing Countries: The Role for Technical Assistance. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper. The World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/1813-9450-6827
Dörffel, C., & Schuhmann, S. (2020). What is inclusive development? Introducing the multidimensional inclusiveness index. Social Indicators Research, 2022(September), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11205-021-02860-Y
Doumbia, D. (2019). The quest for pro-poor and inclusive growth: The role of governance. Applied Economics, 51(16), 1762–1783. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2018.1529392
Farooq, Q., Hao, J., Liu, X., Xiao, D., & Hao, Y. (2020). Social and environmental development: Fresh concepts and soft measures towards sustainable development. Sustainable Development, 28(6), 1796–1803. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2075
Georgescu, M. A., & Herman, E. (2019). Productive employment for inclusive and sustainable development in European Union countries: A multivariate analysis. Sustainability (switzerland), 11(6), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061771
Giddings, B., Hopwood, B., & O’Brien, G. (2002). Environment, economy and society: Fitting them together into sustainable development. Sustainable Development, 10(4), 187–196. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.199
Guijarro, F., & Poyatos, J. A. (2018). Designing a sustainable development goal index through a goal programming model: The case of EU-28 countries. Sustainability (switzerland), 10(9), 3167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093167
Hardi, P., & Zdan, T. (1997). Assessing sustainable development: Principles in practice. International Institute for Sustainable Development, 175. http://www.iisd.org/pdf/bellagio.pdf.
Hedlund-de Witt, A. (2014). Rethinking sustainable development: Considering how different worldviews envision “development” and “quality of life.” Sustainability (switzerland), 6(11), 8310–8328. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6118310
Holden, E., Linnerud, K., & Banister, D. (2017). The Imperatives of sustainable development. Sustainable Development, 25(3), 213–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.1647
Hopwood, B., Mellor, M., & O’Brien, G. (2005). Sustainable development: Mapping different approaches. Sustainable Development, 13(1), 38–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.244
Jain, P., & Jain, P. (2020). Are the sustainable development goals really sustainable? A policy perspective. Sustainable Development, 28(6), 1642–1651. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2112
Jingyu, W., Yuping, B., Yihzong, W., Zhihui, L., Xiangzheng, D., Islam, M., & Managi, S. (2020). Measuring inclusive wealth of China: Advances in sustainable use of resources. Journal of Environmental Management, 264, 110328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110328
Khan, M. (2020). CO2 emissions and sustainable economic development: New evidence on the role of human capital. Sustainable Development, 28(5), 1279–1288. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2083
Klikocka, H. (2019). Assumptions and implementation of smart growth and inclusive growth targets under the Europe 2020 strategy. European Research Studies Journal, XXII(2), 199–217. https://doi.org/10.35808/ersj/1433
Kouton, J. (2019). Relationship between economic freedom and inclusive growth: A dynamic panel analysis for sub-Saharan African countries. Journal of Social and Economic Development, 21(1), 143–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40847-019-00076-y
Lakner, C., & Milanovic, B. (2016). Global income distribution: From the fall of the Berlin Wall to the Great Recession. World Bank Economic Review, 30(2), 203–232. https://doi.org/10.1093/wber/lhv039
Lee, N. (2019). Inclusive Growth in cities: A sympathetic critique. Regional Studies, 53(3), 424–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2018.1476753
Lior, N., Radovanović, M., & Filipović, S. (2018). Comparing sustainable development measurement based on different priorities: Sustainable development goals, economics, and human well-being—Southeast Europe case. Sustainability Science, 13(4), 973–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-018-0557-2
Manly, B. F. J., & Alberto, J. A. N. (2005). Multivariate statistical methods: A prime (4th ed.). Chapman\& Hall.
Matthew, O., Adeniji, A., Osabohien, R., Olawande, T., & Atolagbe, T. (2020). Gender inequality, maternal mortality and inclusive growth in Nigeria. Social Indicators Research, 147(3), 763–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-019-02185-x
McKinley, T. (2010). Inclusive growth criteria and indicators: An inclusive growth index for diagnosis of country progress.
Meyer, D., & Meyer, N. (2019). Assessment of Inclusive Growth performance: A comparative analysis of the BRICS countries. Acta Universitatis Danubius. Œconomica, 15(4).
Moyer, J. D., & Hedden, S. (2020). Are we on the right path to achieve the sustainable development goals? World Development, 127, 104749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104749
Myers, J. H., & Mullet, G. M. (2003). Managerial applications of multivariate analysis in marketing (pp. 238–304). American Marketing Association.
OECD. (2018). Opportunities for All: A Framework for Policy Action on Inclusive Growth. Paris: OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264301665-en
Oyinlola, M. A., Adedeji, A. A., Bolarinwa, M. O., & Olabisi, N. (2020). Governance, domestic resource mobilization, and inclusive growth in sub-Saharan Africa. Economic Analysis and Policy, 65, 68–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2019.11.006
Panayotou, T. (2000). Economic growth and the environment. CID Working Papers. Retrieved August 1, 2021 from https://ideas.repec.org/p/cid/wpfacu/56a.html.
Paprotny, D. (2021). Convergence between developed and developing countries: A centennial perspective. Social Indicators Research, 153(1), 193–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-020-02488-4
Passaris, C. (2006). The Business of Globalization and the Globalization of Business. The Business of Globalization and the Globalization of Business, 9(1), 3. Retrieved August 1, 2021 from https://id.erudit.org/iderudit/jcim9_1art01.
Raheem, I. D., Isah, K. O., & Adedeji, A. A. (2018). Inclusive growth, human capital development and natural resource rent in SSA. Economic Change and Restructuring, 51(1), 29–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10644-016-9193-y
Rai, S. M., Brown, B. D., & Ruwanpura, K. N. (2019). SDG 8: Decent work and economic growth—A gendered analysis. World Development, 113, 368–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.09.006
Ren, X., Cheng, C., Wang, Z., & Yan, C. (2021). Spillover and dynamic effects of energy transition and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions for the European Union: A dynamic spatial panel model. Sustainable Development, 29(1), 228–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2144
Romeiro, A. R. (2012). Desenvolvimento sustentável: Uma perspectiva econômico-ecológica. Estudos Avançados, 26, 65–92.
Sabir, S. (2019). Fiscal policy, institutions and inclusive growth: Evidence from the developing Asian countries. International Journal of Social Economics, 46(6), 822–837. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSE-08-2018-0419
Samans, R., Blanke, J., Corrigan, G., & Drzeniek, M. (2015). The inclusive growth and development report 2015 (Vol. 13). World Economic Forum.
Sarwar, S., Streimikiene, D., Waheed, R., & Mighri, Z. (2021). Revisiting the empirical relationship among the main targets of sustainable development: Growth, education, health and carbon emissions. Sustainable Development, 29(2), 419–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2156
Silander, D. (2019). The European Commission and Europe 2020: smart, sustainable and inclusive growth. smart, sustainable and inclusive growth (pp. 2–35). Edward Elgar Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781788974097.00006
Stiglitz, J. E., Fitoussi, J.-P., & Durand, M. (2018). Beyond GDP. OECD. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264307292-en
Štreimikienė, D., & Kačerauskas, T. (2020). The creative economy and sustainable development: The Baltic States. Sustainable Development, 28(6), 1632–1641. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2111
Sun, C., Liu, L., & Tang, Y. (2018). Measuring the inclusive growth of China’s coastal regions. Sustainability (switzerland), 10(8), 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082863
Sun, H., Liu, Z., & Chen, Y. (2020). Foreign direct investment and manufacturing pollution emissions: A perspective from heterogeneous environmental regulation. Sustainable Development, 28(5), 1376–1387. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2091
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics. Journal of Applied Psychology (Vol. 87). Pearson Boston, MA. https://www.vlebooks.com/Vleweb/Product/Index/437320?page=0
Waheed, A., Zhang, Q., Rashid, Y., Tahir, M. S., & Zafar, M. W. (2020). Impact of green manufacturing on consumer ecological behavior: Stakeholder engagement through green production and innovation. Sustainable Development, 28(5), 1395–1403. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2093
Waite, D., & Roy, G. (2022). The promises and pitfalls of operationalizing inclusive growth. Regional Studies. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2022.2050201
Wang, Q., Xu, Z., Yuan, Q., Yuan, X., Zuo, J., Song, Y., & Wang, M. (2020). Evaluation and countermeasures of sustainable development for urban energy-economy-environment system: A case study of Jinan in China. Sustainable Development, 28(6), 1663–1677. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2115
West Midlands Round Table. (2000). Quality of Life: the Future Starts Here. West Midlands Round Table for Sustainable Development.
Whajah, J., Bokpin, G. A., & Kuttu, S. (2019). Government size, public debt and inclusive growth in Africa. Research in International Business and Finance, 49, 225–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ribaf.2019.03.008
World Bank. (2008). The growth report: Strategies for sustained growth and inclusive development. World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-0-8213-7491-7
Zafar, M. W., Saeed, A., Zaidi, S. A. H., & Waheed, A. (2021). The linkages among natural resources, renewable energy consumption, and environmental quality: A path toward sustainable development. Sustainable Development, 29(2), 353–362. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kamran, M., Rafique, M.Z., Nadeem, A.M. et al. Does Inclusive Growth Contribute Towards Sustainable Development? Evidence from Selected Developing Countries. Soc Indic Res 165, 409–429 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-022-03020-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-022-03020-6