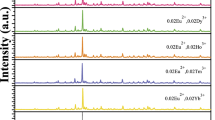
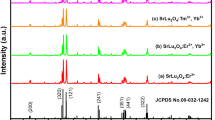
Blue aluminum silicate phosphors of Sr1Al2Si2O8, Sr0.98Al2Si2O8:0.02Eu2+ and Sr0.98–xAl2Si2O8:0.02Eu2+, xTm3+ (x = 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.04, 0.08) compositions are prepared by high temperature solid phase method. Their XRD, fluorescence emission and excitation luminescence properties, afterglow attenuation, afterglow luminescence, thermoluminescence and photostimulated luminescence properties are investigated. The results show that a high purity crystallized phosphor can be successfully prepared at 1350°C for 4 h. It is proven that Eu2+ as the luminescent center is replaced by Sr2+ with a coordination number of 12; Eu2+ and Tm3+ are substituted for Sr2+, which is the reason for a decrease in the unit cell parameter values. The sample excitation and emission spectra have peak wavelengths of 330 nm and 405 nm. Sr0.97Al2Si2O8:0.02Eu2+, 0.01Tm3+ has a minimum afterglow decay rate of 0.61389, which is suitable for use as a long-lasting luminescent blue phosphor. The pyroluminescence indicates that doping with Tm3+ significantly deepens the trap level. The photostimulated luminescence proves that the co-doped Tm3+ greatly improves the initial intensity and the optical storage performance of the photostimulated luminescence, especially the Sr0.96Al2Si2O8:0.02Eu2+; the 0.02Tm3+ sample trap level is 0.8999 eV. The initial photostimulated luminescence intensity of the co-doped sample is shown to be 1000 times that of the single doped Eu2+, and the optical storage – 1.8 times that of the single doping case.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Shao, H. Lin, Y. Dong, Y. Fu, C. Liang, and J. He, J. Solid State Chem., 72–77, 225 (2015).
X. Yu, T. Wang, X. Xu, D. Zhou, and J. Qiu, ECS Solid State Lett., R4–R6, 3 (2013).
F. Liu, W. Yan, Y.J. Chuang, Z. Zhen, J. Xie, and Z. Pan, Sci. Rep., 1554–1563, 3 (2013).
X. Liu, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, Z. Hao, J. Qiao, and X. Dong, Opt. Lett., 148–150, 38 (2013).
X. Xu, Q. He, and L. Yan, J. Alloys Compd., 22–26, 574 (2013).
A. McAulay, J. Wang, and C. Ma, Proc. SPIE, 271–276, 77 (1989).
Z. Wen, N. H. Farhat, and Z. J. Zhao, Appl. Opt., 7251–7265, 32 (1993).
H. Yu, G. Xiong, and J. Ma, J. TIT, 18–23, 17 (2001).
W. Jiang, Z. Xu, and X. Zhang, Sm. Mater. Lett., 1042–1045, 61 (2007).
A. S. Pradhan, J. I. Lee, and J. L. Kim, Med. Phys., 85–99, 33 (2008).
H. B. Liu, B. L. Feng, L. Luo, C. L. Han, and P. A. Tanner, Opt. Mater. Express, 3375–3385, 6 (2016).
Y. X. Zhuang, Y. Lv, L. Wang, W. W. Chen, T. L. Zhou, T. Takeda, N. Hirosaki, and R. J. Xie, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 1854–1864, 10 (2018).
Y. X. Zhuang, Y. Lv, Y. Li, T. L. Zhou, J. Xu, J. Ueda, S. Tanabe, and R. J. Xie, Inorg. Chem., 11890–11897, 55 (2016).
L. Xiao, J. Zhou, G. Z. Liu, and L. Wang, J. Alloys Compd., 24–29, 712 (2017).
S. Hufner and B. Judd, NY Acad. Press, 87–95, 32 (1979).
J. Wu, N. Wang, V. Yan, and H. Wang, Nano Res., 1863–1877, 14 (2021).
A. Lecointre, A. Bessiere, A. Bos, and P. Dorenbos, J. Phys. Chem. C, 4217–4227, 115 (2011).
P. Dorenbos, J. Lumin., 155–176, 91 (2000).
F. Clabau, A. Garcia, P. Bonville, D. Gonbeau, T. Le Mercier, P. Deniard, and S. Jobic. J. Solid State Chem., 1456–1461, 181 (2008).
M. Ma, D. Zhu, C. Zhao, T. Han, S. Cao, and M. Tu, Opt. Commun., 665–668, 285 (2012).
S. C. Gadam and S. Dhoble, J. Lumin., 23–26, 14 (2013).
Y. Kojima, T. Aoi, and U. Tetsuo, J. Lumin., 42–45, 146 (2014).
O. Y. Manashirov, E. M. Zvereva, V. B. Gutan, A. N. Gorgobiani, S. A. Ambrozevic, and A. N. Lobanov, Inorg. Mater., 487–491, 49 (2013).
S. Shuang, D. Kai, K. Huang, and L. Cheng, Adv. Powder Technol., 1516–1519, 25 (2014).
Z. Hua, L. Salamanca-Riba, M. Wuttig, and P. K. Soltani, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 1464–1469, 10 (1993).
M. V. Nadezhkin, D. V. Orlova, S. A. Barannikova, and N. M. Mnikh, Russ. Phys. J., 65, No. 3, 507 (2022).
Z. Zhang, X. Xu, and J. Qiu, Spectrosc. Spectral Anal., 1486–1491, 34 (2014).
X. Sun, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Luo, and Z. Hao, J. Appl. Phys., 013501, 105 (2009).
F. Wang, Y .G. Tian, and Q. Zhang, J. Optoelectron. Laser, 1520–1525, 26 (2015).
P. Li, Z. Yang, and Z. Wang, Chin. Sci. Bull., 973–977, 53 (2008).
R. Chen, Phys. J. Electrochem. Soc., 1254–1257, 116 (1969).
M. Wang, X. Zhang, and Z. Hao, Opt. Mater., 1042–1045, 32 (2010).
A. H. Krumpel and E. V. Kolk, J. Appl. Phys., 073505–073514, 104 (2008).
X. Liu, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, Z. Hao, J. Qiao, and X. Dong, Opt. Lett., 148–150, 38 (2013).
L. G. Van Uitert, J. Lumin., 1–9, 29 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S.Y., Gao, D., Wang, L. et al. Influence of Tm3+ Concentration on Long Afterglow and Photostimulated Luminescence Properties of Eu2+-Doped Sr1Al2Si2O8 Blue Phosphors. Russ Phys J 66, 655–665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-023-02989-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-023-02989-y