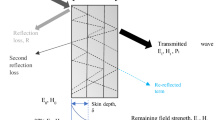
Questions are discussed for the occurrence of an electrically conducting phase in composite (BeO + TiO2)-ceramic with a different amount of added TiO2 leading to UHF-radiation absorption. Strongly reduced TiO2 acts as the absorbing component. Composite (BeO + TiO2)-ceramic compared with (Al2O3 + TiO2)-ceramic is distinguished by increased thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity a higher microwave radiation attenuation coefficient and thermal stability, and may be used in radio electronic technology as an efficient UHF-radiation absorbent, and in other fields of contemporary technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. A. Belyaev, Beryllium Oxide [in Russian], Atomizdat, Moscow (180).
V. S. Kiiko, Yu. N. Makurin, and A. L. Ivanovskii, Ceramics Based on Beryllium Oxide: Preparation, Physicochemical Properties and Application [in Russian], UrO RAN, Ekaterinburg (2006).
G. P. Akishin, S. K. Turnaev, and V. Ya. Vaispapir, “Composition of beryllium oxide ceramics,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 51(5), 377 – 381 (2010).
V. S. Kiiko and V. Ya. Vaispapir, £Thermal conductivity and prospects for using BeO-ceramic in electronic technology,” Steklo Keram., No. 11, 12 – 16 (2014).
V. S. Kiiko, Yu. I. Komolikov, Yu. Makurin, et al., “Rate of ultrasound propagation and absorption in ceramic based on BeO, Al2O3, ZrO2 and SiO2,” Neorgan Materialy, 43(12), 1510 – 1514 (2007).
V. S. Kiiko, S. N. Shabunin, and Yu. N. Makurrin, “Preparation, physicochemical properties, and UHF-radiation transmission by ceramic based on BeO,” Ognenupory Tekhn. Keram., No. 10, 8 – 17 (2004).
V. S. Kiiko, I. A. Dmitriev, Yu. N. makurin, et al., “Preparation and use of transparent berryllia ceramic,” Fiz. Khim. Stekla, 30(1), 149 – 151 (2004).
V. S. Kiiko, “Transparent beryllia ceramics for laser technology and ionizing radiation dosimetry,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 45(4), 266 – 272 (2004).
V. S. Kiiko, M. A. Gorbunova, Yu. N. Makurin, et al., “Microstructure and electric conductivity of composite (BeO + TiO2) ceramics,” Refract. Indust. Ceram., 48(6), 429 – 434 (2007).
V. S. Kiiko, Yu. N. Makurin, A. A. Sofronov, and E. D. Pletneva, “Reaction of a BeO-ceramic ceramic crucible with molten REM,” Steklo Keram., No. 11, 18 – 20 (2002).
V. N. Batygin, N. D. Efimova, A. V. Inozemtseva, and L. G. Mazurova, “Bulk absorbents for powerful RWL,” Élekron. Tekhnika, Ser. 1. Ékektronika SVCh, No. 11, 95 – 102 (1970).
S. G. Mikhailov, “Some properties of titanium-magnesium and titanium beryllium oxide absorbents of UHF-radiation and electron bombardment on their composition,” Ukr. Fiz. Zh., 12(9), 1415 – 1416 (1967).
A. A. Evseev, A. B. Koshelev, and Yu. P. Shalaov, RF Patent 2070180 C 04 B. Method for preparing energy absorbent ceramic, Publ. 12.10.96.
E. A. Novikov, V. S. Kiiko, I. D. Kashcheev, I. D. Zuev, and E. Yu. Zhuravleva, RF Patent 2248336, C 2 C 04 B 35/00, 35/01, G 01 N 33/20. Material for preparing testing stone, Priority of 03.26.2003 Claimant and patent holder GOU VPO UGTU-UPI, Registered in state register 03.20.05.
A. L. Ivanovskii, V. S. Kiiko, G. P. Akishin, and Yu. N. Makurin, RF patent 2326091 C2 C 04 B 35/08. Method for preparing electrical conducting ceramic based on beryllium oxide, Claimant and patent holder GOU VPO UGTU-UPI and IKhTT UrO RAN, Publ. 06.10.2008.
Yu. N. Makurin, M. A. Gorbunova, V. S. Kiiko, et al., “Evaluation of titanium solubility in beryllium oxide based on quantum calculation data,” Steklo. Keram., No. 12, 24 – 25 (2007).
V. S. Kiiko, I. R. Shein, N. A. Zhelonkin, and A. L. Ivanovskii, “Thermal conductivity and ultrasound propagation rate in ceramic based on beryllium oxide,” Ogneupory Tekhn. Keram., No. 4/5, 45 – 48 (2010).
I. I. Milman, A. I. Sjurdo, V. S. Kortov, and Lesz Ja, “TSEE and TL non-stoichiometric BeO–TiO2 ceramics,” Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 65(1 – 4), 401 – 404 (1966).
C. Di Valentin, G. Pacchioni, and A. Selloni, “Theory of carbon doping of titanium dioxide,” Chem. Mater., 17, 6656 – 6665 (2005).
M. V. Kuznetsov, V. S. Kiiko, and A. L. Ivanovskii, “X-ray photoelectronic spectroscopy of complex oxide ceramic: BeO–TiO2–C,” Steklo Keram., No. 10-, 16 – 21 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Novye Ogneupory, No. 12, pp. 36 – 41, December, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiiko, V.S., Pavlov, A.V. Composite (BeO + TiO2)-Ceramic for Electronic Engineering and Other Fields of Technology (Review). Refract Ind Ceram 58, 687–692 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-018-0168-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-018-0168-6