Abstract
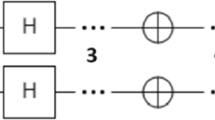
This paper proposes a hybrid quantum genetic algorithm (HQGA) and the core is the use of a new quantum revolving gate strategy and population adaptive retention strategy, and with the Quasi-Newton method. HQGA has the characteristics of fast convergence speed, strong global optimization ability and local detailed optimization. Through the typical complex function, tests show that the optimized quality and efficiency of HQGA are better than traditional quantum genetic algorithms. This algorithm has a good effect in training logistic regression (convex problem) in machine learning.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan, E.: Extended tanh-function method and its applications to nonlinear equations. Phys. Lett. A 277(4–5), 212–218 (2000)
Derek, G., Chris, N., Glen, H., Damien, L.G.: Moose: a parallel computational framework for coupled systems of nonlinear equations. Nucl. Eng. Des. 239(10), 1768–1778 (2009)
Wang, M., Zhou, Y., Li, Z.: Application of a ho-mogeneous balance method to exact solutions of nonlinear equations in mathematical physics. Phys. Lett. A 216(1–5), 67–75 (1996)
Gen, M., Lin, L.: Genetic algorithms. Wiley Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Engineering, pp. 1–15, (2007)
Such, F.P., Madhavan, V., Conti, E., Lehman, J., Stanley, K.O., Clune, J.: Deep neuroevolu-tion: genetic algorithms are a competitive alternative for training deep neural networks for reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.06567, (2017)
Kelley, C.T.: Solving nonlinear equations with Newton’s method, vol. 1. SIAM, (2003)
Qi, L., Sun, J.: A nonsmooth version of Newton’s method. Math. Program. 58(1–3), 353–367 (1993)
Tinney, W.F., Hart, C.E.: Power flow solution by Newton’s method. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 11, 1449–1460 (1967)
Yasar Özban, A.: Some new variants of Newton’s method. Appl. Math. Lett. 17(6), 677–682 (2004)
Chun, C.: Iterative methods improving Newton’s method by the decomposition method. Comput. Math. Appl. 50(10–12), 1559–1568 (2005)
Jinwei, G., Manzhan, G., Cao, C., Xingsheng, G.: A novel competitive co-evolutionary quantum genetic algorithm for stochastic job shop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 37(5), 927–937 (2010)
Lee, J.-C., Lin, W.-M., Liao, G.-C., Tsao, T.-P.: Quantum genetic algorithm for dynamic economic dispatch with valve-point effects and including wind power system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 33(2), 189–197 (2011)
Jinwei, G., Xingsheng, G., Manzhan, G.: A novel parallel quantum genetic algorithm for stochastic job shop scheduling. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 355(1), 63–81 (2009)
Laboudi, Z., Chikhi, S.: Comparison of genetic algorithm and quantum genetic algorithm. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 9(3), 243–249 (2012)
Sabahi, F.: Quantum genetic LMI-based h control with time delay. Int. J. Ind. Electron. Control Optim. 3(1), 1–10 (2020)
Li, B., Pingfang, H., Zhu, N., Lei, F., Xing, L.: Performance analysis and optimization of a CCHP-GSHP coupling system based on quantum genetic algorithm. Sustain. Cities Soc. 46, 101408 (2019)
Lizhen Deng, H., Zhu, Q.Z., Li, Y.: Adaptive top-hat filter based on quantum genetic algorithm for infrared small target detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(9), 10539–10551 (2018)
Chen, P., Yuan, L., He, Y., Luo, S.: An improved SVM classifier based on double chains quantum genetic algorithm and its application in analogue circuit diagnosis. Neurocomputing 211, 202–211 (2016)
Zhang, L., Lv, H., Tan, D., Fang, X., Chen, J., Bao, G., Cai, S.: Adaptive quantum genetic algorithm for task sequence planning of complex assembly systems. Electron. Lett. 54(14), 870–872 (2018)
Li, P.C., Song, K.P., Shang, F.H.: Double chains quantum genetic algorithm with application to neuro-fuzzy controller design. Adv. Eng. Softw. 42(10), 875–886 (2011)
Li, S., Li, P.: Quantum genetic algorithm based on real encoding and gradient information of object function. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 38(8), 1216–1223 (2006)
Steane, A.: Quantum computing. Rep. Prog. Phys. 61(2), 117 (1998)
O’brien, J.L.: Optical quantum computing. Science 318(5856), 1567–1570 (2007)
Leuenberger, M.N., Loss, D.: Quantum computing in molecular magnets. Nature 410(6830), 789–793 (2001)
Qi, X., Palmieri, F.: Theoretical analysis of evolutionary algorithms with an infinite population size in continuous space part II: analysis of the diversification role of crossover. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5(1), 120–129 (1994)
Schmitt, L.M.: Theory of genetic algorithms. Theor. Comput. Sci. 259(1–2), 1–61 (2001)
Abdoun, O., Abouchabaka, J., Tajani C.: Analyzing the performance of mutation operators to solve the travelling salesman problem. arXiv preprint arXiv:1203.3099, (2012)
Wang, Y., Li, Y.-H.: A novel quantum genetic algorithm for tsp. Chin. J. Comput. Chin. Ed. 30(5), 748 (2007)
Prakash, S., Prakash Vidyarthi, D.: A novel scheduling model for computational grid using quantum genetic algorithm. J. Supercomput. 65(2), 742–770 (2013)
Duan, H., Chun-fang, X., Xing, Z.-H.: A hybrid artificial bee colony optimization and quantum evolutionary algorithm for continuous optimization problems. Int. J. Neural Syst. 20(01), 39–50 (2010)
Li, P., Li, S.: Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for continuous space optimization based on Bloch coordinates of qubits. Neurocomputing 72(1–3), 581–591 (2008)
Panchi, L.I.: Quantum genetic algorithm based on Bloch coordinates of qubits and its application. Control Theory Appl. 25(6), 985–989 (2008)
Zaitsev-Zotov, S.V.: Classical to quantum crossover in charge density wave creep at low temperatures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71(4), 605 (1993)
SaiToh, A., Rahimi, R., Nakahara, M.: A quantum genetic algorithm with quantum crossover and mutation operations. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(3), 737–755 (2014)
Yang, J., Li, B., Zhuang, Z.: Research of quantum genetic algorith and its application in blind source separation. J. Electron. (China) 20(1), 62–68 (2003)
Xiao-fenga, Z.H.A.N.G., Gui-fanga, S.U.I., Rana, Z.H.E.N.G., Zhi-nongb, L.I., Guo-weia, Y.A.N.G.: An improved quantum genetic algorithm of quantum revolving gate. Comput. Eng. 04, 56 (2013)
Hua, T., Chen, J., Pei, D., Zhang, W., Zhou, N.: Quantum image encryption algorithm based on image correlation decomposition. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(2), 526–537 (2015)
Xiaohui, Z., Li, C., Peng, Z.: Simulation of quantum cellular automatas based on quantum genetic algorithm [j]. Micronanoelectronic Technology 1, (2011)
Du, T., Hu, Y., Ke, X. : Improved quantum artificial fish algorithm application to distributed network considering distributed generation. Computational intelligence and neuroscience 2015, (2015)
Guo, Y., Wei, L., Xu, X.: A sonar image segmentation algorithm based on quantum-inspired particle swarm optimization and fuzzy clustering. Neural Comput. Appl. 45, 1–8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3890-6
Ariyawansa, K.A.: Deriving collinear scaling algorithms as extensions of quasi-newton methods and the local convergence of DFP and BFGS related collinear scaling algorithms. Math. Program. 49(1–3), 23–48 (1990)
Güler, O., Gürtuna, F., Shevchenko, O.: Duality in quasi-Newton methods and new variational characterizations of the DFP and BFGS updates. Optim. Methods Softw. 24(1), 45–62 (2009)
Powell, M.J.D.: How bad are the BFGS and DFP methods when the objective function is quadratic? Math. Program. 34(1), 34–47 (1986)
Contreras, M., Tapia, R.A.: Sizing the BFGS and DFP updates: numerical study. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 78(1), 93–108 (1993)
Dennis, J.E., Martinez, H.J., Tapia, R.A.: Convergence theory for the structured BFGS secant method with an application to nonlinear least squares. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 61(2), 161–178 (1989)
Powell, M.J.D.: Updating conjugate directions by the BFGS formula. Math. Program. 38(1), 29 (1987)
Xiao-fenga, Z., Gui-fanga, S.U.I., Rana, Z., et al.: An improved quantum genetic algorithm of quantum revolving gate [J]. Comput. Eng. 4, 56 (2013)
Rogers, A., Prugel-Bennett, A.: Genetic drift in genetic algorithm selection schemes. IEEE Trans Evolut. Comput. 3(4), 298–303 (1999)
Tang, K.-Z., Sun, T.-K., Yang, J.-Y.: An improved genetic algorithm based on a novel selection strategy for nonlinear programming problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 35(4), 615–621 (2011)
Li, B.B., Wang, L.: A hybrid quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for multiobjective flow shop scheduling. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 37(3), 576–591 (2007)
CAI, B.B., ZHANG, X.H.: Hybrid quantum genetic algorithm and its application in VRP [j]. Computer Simulation 7, (2010)
Yang, F., Yi-liu, J.I.A.N.G., Zhen-kun, L.I.: Optimal allocation of distributed generation for microgrid based on hybrid quantum genetic algorithm. Power Syst. Prot. Control 41(24), 50–57 (2013)
Juan, D., Liu, Z.G.: A new hybrid quantum genetic algorithm for solving nonlinear equations. Microcomput. Appl. 29(7), 1–5 (2008)
Liu, Z.G., Xu, S.H.: Training method of process neural networks based on hybrid quantum genetic algorithm. Appl. Res. Comput. 26(8), 2898–2901 (2009)
Xianlong, G., Xu, W., Ying, D.: The vehicle routing problem in the case of stochastic demand based on hybrid quantum genetic algorithm. Syst. Eng. 29(3), 53–59 (2011)
Wang, L., Tang, F., Hao, W.: Hybrid genetic algorithm based on quantum computing for numerical optimization and parameter estimation. Appl. Math. Comput. 171(2), 1141–1156 (2005)
Konar, D., Bhattacharyya, S., Sharma, K., Sharma, S., Pradhan, S.R.: An improved hybrid quantum-inspired genetic algorithm (HQIGA) for scheduling of real time task in multiprocessor system. Appl. Soft Comput. 53, 296–307 (2017)
Xiong, Y., Chen, H., Miao, F., Wang, X.: A quantum genetic algorithm to solve combinatorial optimization problem. Acta Electron. Sin. 32(11), 1855–1858 (2004)
Chen, Y.: Research on Quantum Genetic Algorithm Based on Optimization Problems. University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, (2019)
Zhang, G., Li, N., Jin, W., Hu, L.: A novel quantum genetic algorithm and its application and its application. Acta Electron. Sin. 32(3), 476–479 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61772295,61572270 and 61173056); the PHD foundation of Chongqing Normal University No.19XLB003; Supported by the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No.KJZD-M202000501 ); Chongqing Technology Innovation and application development special general project(cstc2020jscx-lyjsA0063). Chongqing Normal University Graduate Scientific Research Innovation Project Grant YKC20042.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mp4 15068 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Zhang, J. An improved hybrid quantum optimization algorithm for solving nonlinear equations. Quantum Inf Process 20, 134 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03067-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03067-3