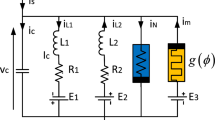
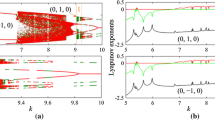
Abstract
This paper introduces and investigates the dynamics of an improved Wilson neuron model with a memristive autapse. The study of the stability of the equilibrium points of the proposed model revealed that it can move from a rest state to a firing state through a Hopf bifurcation. Therefore, the improved model experiences self-excited dynamics. The study of the dynamics of the proposed model revealed neuronal behaviors such as quiescent, bursting, spiking, and hysteretic dynamics characterized by the coexistence of two and three firing patterns for the same set of parameters. In addition, the dynamics of modulated information patterns via the membrane potential related to potential information coding in a network of 500 neurons are presented and discussed. Planar impulse wave solutions of the generic model as initial conditions result in a localized unstable wave pattern under autaptic coupling and magnetic flux time delay. High memristive autaptic coupling and magnetic flux time delay have antagonistic effects on the spatiotemporal patterns. Our results suggest that high autaptic coupling could be a possible route to chaotic and chimera-like behaviors in the network, while high magnetic flux time delay could be an efficient bifurcation parameter in controlling the chaotic and chimera-like behaviors. Finally, a microcontroller implementation of the introduced memristive Wilson neuron has been addressed based on the 32-bit STM32F407ZE development board. Results obtained from the experimental investigations of the model agreed with the numerical ones based on the physically captured phase trajectories and time-domain waveforms.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Bao, H., Liu, W., Ma, J., Wu, H.: Memristor initial-offset boosting in memristive hr neuron model with hidden firing patterns. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 30(10), 2030029 (2020)
Chay, T.R.: Chaos in a three-variable model of an excitable cell. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 16(2), 233–242 (1985)
Chua, L.: Everything you wish to know about memristors but are afraid to ask. In: Handbook of Memristor Networks, pp. 89–157. Springer (2019)
Doubla Isaac, S., Njitacke, Z.T., Kengne, J.: Effects of low and high neuron activation gradients on the dynamics of a simple 3d Hopfield neural network. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 30(11), 2050159 (2020)
Hindmarsh, J., Rose, R.: A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853), 162–164 (1982)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.: A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 221(1222), 87–102 (1984)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500 (1952)
Imani, M.A., Ahmadi, A., RadMalekshahi, M., Haghiri, S.: Digital multiplierless realization of coupled Wilson neuron model. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 12(6), 1431–1439 (2018)
Izhikevich, E.: Fitzhugh–Nagumo model. Scholarpedia 1(9), 1349 (2006)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(6), 1569–1572 (2003)
Ju, Z., Lin, Y., Chen, B., Wu, H., Chen, M., Xu, Q.: Electromagnetic radiation induced non-chaotic behaviors in a Wilson neuron model. Chin. J. Phys. 6, 66 (2022)
Liu, Y., Ma, J., Xu, Y., Jia, Y.: Electrical mode transition of hybrid neuronal model induced by external stimulus and electromagnetic induction. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29(11), 1950156 (2019)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., Ma, J., Song, X.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(3), 1479–1490 (2016)
Ma, J., Yang, Z.Q., Yang, L.J., Tang, J.: A physical view of computational neurodynamics. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 20(9), 639–659 (2019)
Nayfeh, A.H., Balachandran, B.: Applied Nonlinear Dynamics: Analytical, Computational, and Experimental Methods. Wiley, New York (2008)
Njitacke, Z.T., Isaac, S.D., Nestor, T., Kengne, J.: Window of multistability and its control in a simple 3d Hopfield neural network: application to biomedical image encryption. Neural Comput. Appl. 33(12), 6733–6752 (2021)
Njitacke, Z.T., Koumetio, B.N., Ramakrishnan, B., Leutcho, G.D., Fozin, T.F., Tsafack, N., Rajagopal, K., Kengne, J.: Hamiltonian energy and coexistence of hidden firing patterns from bidirectional coupling between two different neurons. Cogn. Neurodyn. 66, 1–18 (2021)
Nouri, M., Hayati, M., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., Abbott, D.: A digital neuromorphic realization of the 2-d Wilson neuron model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 66(1), 136–140 (2018)
Pisarchik, A.N., Jaimes-Reátegui, R., García-Vellisca, M.: Asymmetry in electrical coupling between neurons alters multistable firing behavior. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 28(3), 033605 (2018)
Qi, Y., Watts, A., Kim, J., Robinson, P.A.: Firing patterns in a conductance-based neuron model: bifurcation, phase diagram, and chaos. Biol. Cybern. 107(1), 15–24 (2013)
Tabekoueng Njitacke, Z., Kengne, J., Fotsin, H.B.: Coexistence of multiple stable states and bursting oscillations in a 4d Hopfield neural network. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 39(7), 3424–3444 (2020)
Tabekoueng Njitacke, Z., Laura Matze, C., Fouodji Tsotsop, M., Kengne, J.: Remerging Feigenbaum trees, coexisting behaviors and bursting oscillations in a novel 3d generalized Hopfield neural network. Neural Process. Lett. 52(1), 267–289 (2020)
Takembo, C.N., Mvogo, A., Ekobena Fouda, H.P., Kofané, T.C.: Effect of electromagnetic radiation on the dynamics of spatiotemporal patterns in memristor-based neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(2), 1067–1078 (2019)
Takembo, C.N., Nyifeh, P., Fouda, H.E., Kofane, T.: Modulated wave pattern stability in chain neural networks under high-low frequency magnetic radiation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 66, 126891 (2022)
Tsumoto, K., Kitajima, H., Yoshinaga, T., Aihara, K., Kawakami, H.: Bifurcations in Morris–Lecar neuron model. Neurocomputing 69(4–6), 293–316 (2006)
Wang, C., Guo, S., Xu, Y., Ma, J., Tang, J., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A.: Formation of autapse connected to neuron and its biological function. Complexity 6, 66 (2017)
Wilson, H.R.: Simplified dynamics of human and mammalian neocortical neurons. J. Theor. Biol. 200(4), 375–388 (1999)
Wise, S., Shadmehr, R., Ramachandran, V.: Encyclopedia of the human brain. Retrieved 32 May 2003 (2002)
Xu, Q., Ju, Z., Ding, S., Feng, C., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Electromagnetic induction effects on electrical activity within a memristive Wilson neuron model. Cogn. Neurodyn. 66, 1–11 (2022)
Xu, Q., Ju, Z., Feng, C., Wu, H., Chen, M.: Analogy circuit synthesis and dynamics confirmation of a bipolar pulse current-forced 2d Wilson neuron model. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 230(7), 1989–1997 (2021)
Xu, Q., Liu, T., Feng, C.T., Bao, H., Wu, H.G., Bao, B.C.: Continuous non-autonomous memristive Rulkov model with extreme multistability. Chin. Phys. B 30(12), 128702 (2021)
Xu, Q., Tan, X., Zhu, D., Bao, H., Hu, Y., Bao, B.: Bifurcations to bursting and spiking in the Chay neuron and their validation in a digital circuit. Chaos Solitons Fract. 141, 110353 (2020)
Zhang, G., Wang, C., Alzahrani, F., Wu, F., An, X.: Investigation of dynamical behaviors of neurons driven by memristive synapse. Chaos Solitons Fract. 108, 15–24 (2018)
Zhao, X., Kim, J., Robinson, P.A., Rennie, C.J.: Low dimensional model of bursting neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 36(1), 81–95 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially funded by the Polish National Science Center under the Grant OPUS 14 No. 2017/27/B/ST8/01330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Njitacke, Z.T., Takembo, C.N., Koumetio, B.N. et al. Complex dynamics and autapse-modulated information patterns in memristive Wilson neurons. Nonlinear Dyn 110, 2793–2804 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07738-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07738-3