Abstract
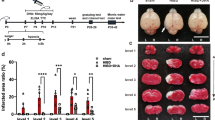
Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) is a leading cause of death and disability in neonatal or perinatal all over the world, seriously affecting children, families and society. Unfortunately, only few satisfactory therapeutic strategies have been developed. It has been demonstrated that Echinacoside (ECH), the major active component of Cistanches Herba, exerts many beneficial effects, including antioxidative, anti-apoptosis, and neuroprotective in the traditional medical practice in China. Previous research has demonstrated that ECH plays a protective effect on ischemic brain injury. This study aimed to investigate whether ECH provides neuroprotection against HIBD in neonatal rats. We subjected 120 seven-day-old Sprague–Dawley rats to cerebral hypoxia–ischemia (HI) and randomly divided into the following groups: sham group, HI group and ECH (40, 80 and 160 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) post-administration group. After 48 h of HI, 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride, Hematoxylin-Eosin and Nissl staining were conducted to evaluate the extent of brain damage. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT) activities, total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) production were assessed to determine the antioxidant capacity of ECH. TUNEL staining and Western blot analysis was performed to respectively estimate the extent of brain cell apoptosis and the expression level of the apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2. Results showed that ECH remarkably reduced the brain infarct volume and ameliorated the histopathological damage to neurons. ECH post-administration helped recovering the antioxidant enzyme activities and decreasing the MDA production. Furthermore, ECH treatment suppressed neuronal apoptosis in the rats with HIBD was by reduced TUNEL-positive neurons, the caspase-3 levels and increased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio. These results suggested that ECH treatment was beneficial to reducing neuronal damage by attenuating oxidative stress and apoptosis in the brain under HIBD.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yildiz EP, Ekici B, Tatli B (2017) Neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an update on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Expert Rev Neurother 17:449–459
Dixon BJ, Reis C, Ho WM, Tang J, Zhang JH (2015) Neuroprotective strategies after neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Int J Mol Sci 16:22368–22401
Fathali N, Lekic T, Zhang JH, Tang J (2010) Long-term evaluation of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in infant rats. Intens Care Med 36:1602
Douglasescobar M, Weiss MD (2015) Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review for the clinician. Jama Pediatrics 169:397
Kurinczuk JJ, Whitekoning M, Badawi N (2010) Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Human Dev 86:329
Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD, Dyet L, Halliday H, Juszczak E, Kapellou O, Levene M, Marlow N, Porter E, Thoresen M, Whitelaw A, Brocklehurst P (2009) Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 361:1349–1358
Nair J, Kumar VHS (2018) Current and emerging therapies in the management of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in neonates. Children (Basel, Switzerland) 5:90
Taylor DL, Edwards AD, Mehmet H (2010) Oxidative metabolism, apoptosis and perinatal brain injury. Brain Pathol 9:93–117
Finkel T, Holbrook NJ (2000) Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 408:239–247
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS, Jung JE, Okami N, Sakata H, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Goeders CE, Chan PH (2011) Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:1505–1517
Dringen R (2000) Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog Neurobiol 62:649–671
Johnston MV, Trescher WH, Ishida A, Nakajima W (2001) Neurobiology of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the developing brain. Pediatr Res 49:735
Zauner A, Daugherty WP, Bullock MR, Warner DS (2002) Brain oxygenation and energy metabolism: part I-biological function and pathophysiology. Neurosurgery 51:289
Porter NA (1984) Chemistry of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 105:273–282
Blomgren K, Leist M, Groc L (2007) Pathological apoptosis in the developing brain. Apoptosis 12:993–1010
Arteaga O, A Á, Revuelta M, Santaolalla F, Urtasun A, Hilario E (2017) Role of antioxidants in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury: new therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci 18:265
Cao L, Miao M, Qiao J, Bai M, Li R (2017) The protective role of verbenalin in rat model of focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:1170–1177
Philchenkov A, Zavelevich M, Kroczak TJ, Los M (2004) Caspases and cancer: mechanisms of inactivation and new treatment modalities. Exp Oncol 26:82
Liu JJ, Yang LL, Dong YH, Zhang B, Ma XQ (2018) Echinacoside, an inestimable natural product in treatment of neurological and other disorders. Molecules 23:41–70
Chen M, Wang X, Hu B, Zhou J, Wang X, Wei W, Zhou H (2018) Protective effects of echinacoside against anoxia/reperfusion injury in H9c2 cells via up-regulating p-AKT and SLC8A3. Biomed Pharmacother 104:52
Li L, Wan G, Han B, Zhang Z (2018) Echinacoside alleviated LPS-induced cell apoptosis and inflammation in rat intestine epithelial cells by inhibiting the mTOR/STAT3 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 104:622–628
Wei LL, Chen H, Jiang Y, Peng-Fei TU, Juan DU, Zhong M, Liu F, Liu CY (2011) Effects of Echinacoside on Lipid Peroxidation in Cerebral Ischemia Rats. Chin J Inf Trad Chin Med 18:36–37
Du J, Chen H, Jiang Y, Tu PF, L C (2010) Protective effect of echinacoside on cerebral ischemia rats. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res 21:1324–1325
Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ (2005) Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: evolution of an animal model. Dev Neurosci 27:81–86
Zhao P, Zhou R, Li HN, Yao WX, Qiao HQ, Wang SJ, Niu Y, Sun T, Li YX, Yu JQ (2015) Oxymatrine attenuated hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via improving antioxidant enzyme activities and inhibiting cell death. Neurochem Int 89:17–27
Zhong M, Chen H, Jiang Y, Tu PF, Liu CL, Zhang WX, Ma JY, Ding H (2012) Effects of echinacoside on striatal extracellular levels of amino acid neurotransmitter in cerebral ischemia rats. Chin Pharmacol Bull 28:361–365
Ma JY, Zhang WX, Chen H, Jiang Y, Tu PF, Ding H (2014) The protective effects of echinacoside on oxidative stress injury in vascular dementia rats. Chin Pharmacol Bull 30:638–642
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsaowu G, Savalos RA, Davidson C, Sharp FR (1990) A semiautomated method for measuring brain infarct volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:290–293
Lin TN, He YY, Wu G, Khan M, Hsu CY (1993) Effect of brain edema on infarct volume in a focal cerebral ischemia model in rats. Stroke 24:117–121
Peng Z, Yang JM, Wang YS, Hao YJ, Li YX, Nan L, Jing W, Yang N, Tao S, Yu JQ (2018) Neuroprotection of cytisine against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice by regulating NR2B-ERK/CREB signal pathway. Neurochem Res 43:1–12
Liu SB, Han J, Zhang N, Tian Z, Li XB, Zhao MG (2011) Neuroprotective effects of oestrogen against oxidative toxicity through activation of G-protein-coupled receptor 30 receptor. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 38:577–585
Jerome YY, Stephen A (2009) Animal models of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Pediatric Neurol 40:156–167
Rice JE, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9:131
Hagberg H, Bona E, Gilland E, Pukasundvall M (1997) Hypoxia-ischaemia model in the 7-day-old rat: possibilities and shortcomings. Acta Pædiatr 86:85–88
Wei LL, Chen H, Jiang Y, Tu PF, Zhong M, Liu F, Liu CY (2011) Determination of ECH on cerebral ischemia injury rat plasma and brain tissue by HPLC method. Chin Pharmacol Bull 27:737–738
Li B, Concepcion K, Meng X, Zhang L (2017) Brain-immune interactions in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Prog Neurobiol 159:50–68
Saito A, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Nishi T, Song YS, Yu F, Liu J, Lee YS, Nito C, Kamada H (2005) Oxidative stress and neuronal death/survival signaling in cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 31:105–116
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem 59:1609–1623
Ditelberg JS, Sheldon RA, Epstein CJ, Ferriero DM (1996) Brain injury after perinatal hypoxia-ischemia is exacerbated in copper/zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. Pediatr Res 39:204–208
Dai C, Liu Y, Dong Z (2017) Tanshinone I alleviates motor and cognitive impairments via suppressing oxidative stress in the neonatal rats after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Mol Brain 10:52
Nair J, Vhs K (2018) Current and emerging therapies in the management of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in neonates. Children 5:99
Lewén A, Matz P, Chan PH (2000) Free radical pathways in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma 17:871
Wang Y, Ren Q, Zhang X, Lu H, Chen J (2018) Neuroprotective mechanisms of calycosin against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 45:537
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Li C, Mo Z, Lei J, Li H, Fu R, Huang Y, Luo S, Zhang L (2018) Edaravone attenuates neuronal apoptosis in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage rat model via suppression of TRAIL signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 99:169
Lorena B, Luis A, Maria JR, Esther A, Eva V, Enrique C, Elena S, Carlos V, Maria C, Ana GR, William H, Jose MO (2019) Neuroprotection by cannabidiol and hypothermia in a piglet model of newborn hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 146:1–11
Landucci E, Filippi L, Gerace E, Catarzi S, Guerrini R, Pellegrini-Giampietro DE (2018) Neuroprotective effects of topiramate and memantine in combination with hypothermia in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in vitro and in vivo. Neurosci Lett 668:103–107
Li MQ, Xu T, Zhou F, Wang MM, Song HX, Xiao X, Lu BY (2018) Neuroprotective effects of four phenylethanoid glycosides on H2O2-induced apoptosis on PC12 cells via the Nrf2/ARE pathway. Int J Mol Sci 19:1135
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 81660261), The Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Science and Technology Support Program (Grant Number 2015BAK45B01), The Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Key Research and Development Project (Grant Number 2017BY079) and the major construction programs of Ningxia Medical University (Grant Number XY201716).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, W., Lan, Xb., Liu, N. et al. Echinacoside Alleviates Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rat by Enhancing Antioxidant Capacity and Inhibiting Apoptosis. Neurochem Res 44, 1582–1592 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02782-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02782-9