Abstract
Introduction
The current WHO classification and methylation status help predict meningioma recurrence and prognosis. However, up to date, there is no circulating biomarker showing clinical value in meningioma diagnosis or classification. Circulating miRNAs showed the potential to be used as cancer biomarkers in various tumours. This research evaluated specific miRNAs, miR-497 and miR-219, as convenient and efficient predictors of meningioma grades.
Methods
We studied serum and exosomal levels of miR-497 in 74 meningioma samples (WHO grade I = 25, WHO grade II = 25, and WHO grade III = 24) and 53 healthy controls. The serum level of miR-219 was studied in 56 meningioma samples WHO grade I = 22, WHO grade II = 14, and WHO grade III = 20). We used qPCR for miRNA quantification. We also tested two different normalisers, endogenous and external, and evaluated their impact on the diagnostic value of miR-497.
Results
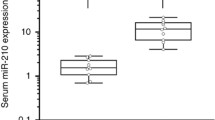
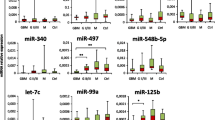
The serum and exosomal levels of miR-497 distinguished meningioma from the control samples. Moreover, miR-497 was a suitable identifier for meningioma grade. When we combined miR-497 and miR-219, the efficacy of the combined biomarker was higher than miR-497 or miR-219 when used individually in meningioma classification. Both miR-497 and miR-219 showed a noticeable change with the methylation class of meningioma.
Conclusion
This study shows that serum miR-497 is an effective and easy-to-measure biomarker for meningioma diagnosis and classification. Moreover, when we combined miR-497 and miR-219, the combined biomarker showed enhanced accuracy in meningioma classification. Furthermore, this is the first study to evaluate the correlation between serum circulating miRNA and the methylation status in meningioma.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Zhao L, Zhao W, Hou Y, Wen C, Wang J, Wu P, Guo Z (2020) An overview of managements in meningiomas. Front Oncol 10:1523. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01523
Goldbrunner R, Stavrinou P, Jenkinson MD, Sahm F, Mawrin C, Weber DC, Preusser M, Minniti G, Lund-Johansen M, Lefranc F et al (2021) EANO guideline on the diagnosis and management of meningiomas. Neuro-oncology 23:1821–1834. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noab150
Goldbrunner R, Minniti G, Preusser M, Jenkinson MD, Sallabanda K, Houdart E, von Deimling A, Stavrinou P, Lefranc F, Lund-Johansen M et al (2016) EANO guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of meningiomas. Lancet Oncol 17:e383–e391. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(16)30321-7
Islim AI, Mohan M, Moon RDC, Srikandarajah N, Mills SJ, Brodbelt AR, Jenkinson MD (2019) Incidental intracranial meningiomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic factors and outcomes. J Neurooncol 142:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03104-3
Nassiri F, Mamatjan Y, Suppiah S, Badhiwala JH, Mansouri S, Karimi S, Saarela O, Poisson L, Gepfner-Tuma I, Schittenhelm J et al (2019) DNA methylation profiling to predict recurrence risk in meningioma: development and validation of a nomogram to optimize clinical management. Neuro-oncology 21:901–910. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz061
Sahm F, Schrimpf D, Stichel D, Jones DTW, Hielscher T, Schefzyk S, Okonechnikov K, Koelsche C, Reuss DE, Capper D et al (2017) DNA methylation-based classification and grading system for meningioma: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 18:682–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30155-9
Euskirchen P, Peyre M (2018) Management of meningioma. La Presse Médicale 47:e245–e252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lpm.2018.05.016
Cui M, Wang H, Yao X, Zhang D, Xie Y, Cui R, Zhang X (2019) Circulating microRNAs in cancer: potential and challenge. Front Genet 10:626
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1840
Chen X, Liang H, Zen K, Zhang C-Y (2016) Secreted microRNAs from tumor cells can suppress immune function. Oncoimmunology 5:e982407
Chen X, Liang H, Zhang J, Zen K, Zhang C-Y (2012) Secreted microRNAs: a new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol 22:125–132
Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E, Rosenwald S, Spector Y, Zepeniuk M, Benjamin H, Shabes N, Tabak S, Levy A (2008) MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol 26:462
Nik Mohamed Kamal NNSB, Shahidan WNS (2020) Non-exosomal and exosomal circulatory microRNAs: which are more valid as biomarkers? Front Pharmacol 10:1500
Yang G, Xiong G, Cao Z, Zheng S, You L, Zhang T, Zhao Y (2016) miR-497 expression, function and clinical application in cancer. Oncotarget 7:55900–55911. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10152
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, Zeng YX, Shao JY (2008) MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA 14:2348–2360. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1034808
Liu Z, Wu S, Wang L, Kang S, Zhao B, He F, Liu X, Zeng Y, Liu J (2019) Prognostic value of microRNA-497 in various cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis mark 2019:2491291–2491291. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2491291
Özata DM, Caramuta S, Velázquez-Fernández D, Akçakaya P, Xie H, Höög A, Zedenius J, Bäckdahl M, Larsson C, Lui W-O (2011) The role of microRNA deregulation in the pathogenesis of adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer 18:643–655. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-11-0082
Xu J-W, Wang T-X, You L, Zheng L-F, Shu H, Zhang T-P, Zhao Y-P (2014) Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) as a target of miR-497 and plasma IGF-1R levels associated with TNM stage of pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 9:e92847. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092847
Itesako T, Seki N, Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T, Yamasaki T, Hidaka H, Yonezawa T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M et al (2014) The microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing: the functional significance of the miR-195/497 cluster. PLoS ONE 9:e84311. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084311
Wang S, Mo Y, Midorikawa K, Zhang Z, Huang G, Ma N, Zhao W, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, Murata M (2015) The potent tumor suppressor miR-497 inhibits cancer phenotypes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting ANLN and HSPA4L. Oncotarget 6(2015):35893–35907. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5651
Shen L, Li J, Xu L, Ma J, Li H, Xiao X, Zhao J, Fang L (2012) miR-497 induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells by targeting Bcl-w. Exp Ther Med 3:475–480. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2011.428
Li W, Jin X, Deng X, Zhang G, Zhang B, Ma L (2014) The putative tumor suppressor microRNA-497 modulates gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion by repressing eIF4E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 449:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.011
Yan J-J, Zhang Y-N, Liao J-Z, Ke K-P, Chang Y, Li P-Y, Wang M, Lin J-S, He X-X (2015) miR-497 suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting VEGFA and AEG-1. Oncotarget 6:29527–29542. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5012
Wang W, Ren F, Wu Q, Jiang D, Li H, Shi H (2014) MicroRNA-497 suppresses angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor A through the Pi3k/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep 32:2127–2133. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2014.3439
Wei C, Luo Q, Sun X, Li D, Song H, Li X, Song J, Hua K, Fang L (2015) MicroRNA-497 induces cell apoptosis by negatively regulating Bcl-2 protein expression at the posttranscriptional level in human breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:7729–7739
Wang L, Li B, Li L, Wang T (2013) MicroRNA-497 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:3499–3502. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.6.3499
Teplyuk NM, Mollenhauer B, Gabriely G, Giese A, Kim E, Smolsky M, Kim RY, Saria MG, Pastorino S, Kesari S (2012) MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro-oncology 14:689–700
López-Aguilar JE, Velázquez-Flores MA, Simón-Martínez LA, Ávila-Miranda R, Rodríguez-Florido MA, Garrido RR-E (2017) Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for pediatric astrocytomas. Arch Med Res 48:323–332
Yue X, Lan F, Hu M, Pan Q, Wang Q, Wang J (2016) Downregulation of serum microRNA-205 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. J Neurosurg 124:122–128
Regazzo G, Terrenato I, Spagnuolo M, Carosi M, Cognetti G, Cicchillitti L, Sperati F, Villani V, Carapella C, Piaggio G et al (2016) A restricted signature of serum miRNAs distinguishes glioblastoma from lower grade gliomas. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0393-0
Negroni C, Hilton DA, Ercolano E, Adams CL, Kurian KM, Baiz D, Hanemann CO (2020) GATA-4, a potential novel therapeutic target for high-grade meningioma, regulates miR-497, a potential novel circulating biomarker for high-grade meningioma. EBioMedicine 59:102941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102941
Zhi F, Shao N, Li B, Xue L, Deng D, Xu Y, Lan Q, Peng Y, Yang Y (2016) A serum 6-miRNA panel as a novel non-invasive biomarker for meningioma. Sci Rep 6:32067. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32067
Schageman J, Zeringer E, Li M, Barta T, Lea K, Gu J, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Vlassov AV (2013) The complete exosome workflow solution: from isolation to characterization of RNA cargo. Biomed Res Int 2013:253957. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/253957
Adams CL, Ercolano E, Ferluga S, Sofela A, Dave F, Negroni C, Kurian KM, Hilton DA, Hanemann CO (2020) A rapid robust method for subgrouping non-NF2 meningiomas according to genotype and detection of lower levels of M2 macrophages in AKT1 E17K mutated tumours. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041273
Madadi S, Soleimani M (2019) Comparison of miR-16 and cel-miR-39 as reference controls for serum miRNA normalization in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem 120:4802–4803. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28174
Wang L, Chen S, Liu Y, Zhang H, Ren N, Ma R, He Z (2020) The biological and diagnostic roles of microRNAs in meningiomas. Rev Neurosci 31:771–778. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2020-0023
Tiberio P, Callari M, Angeloni V, Daidone MG, Appierto V (2015) Challenges in using circulating miRNAs as cancer biomarkers. BioMed Res Int 2015:731479. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/731479
Bustin SA, Beaulieu JF, Huggett J, Jaggi R, Kibenge FS, Olsvik PA, Penning LC, Toegel S (2010) Miqe précis: practical implementation of minimum standard guidelines for fluorescence-based quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Bmc Mol Biol 11(1):74
Benz F, Roderburg C, Vargas Cardenas D, Vucur M, Gautheron J, Koch A, Zimmermann H, Janssen J, Nieuwenhuijsen L, Luedde M et al (2013) U6 is unsuitable for normalization of serum miRNA levels in patients with sepsis or liver fibrosis. Exp Mol Med 45:e42. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2013.81
Wang P, Yang D, Zhang H, Wei X, Ma T, Cheng Z, Hong Q, Hu J, Zhuo H, Song Y et al (2015) Early detection of lung cancer in serum by a panel of microRNA biomarkers. Clin Lung Cancer 16:313-319.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2014.12.006
Schwarzenbach H, da Silva AM, Calin G, Pantel K (2015) Data normalization strategies for microRNA quantification. Clin Chem 61:1333–1342. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2015.239459
Kim KM, Abdelmohsen K, Mustapic M, Kapogiannis D, Gorospe M (2017) RNA in extracellular vesicles. WIREs RNA 8:e1413. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1413
Mashayekhi F, Saberi A, Mashayekhi S (2018) Serum TIMP1 and TIMP2 concentration in patients with different grades of meningioma. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 170:84–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.05.001
Fouladseresht H, Ziaee SM, Erfani N, Doroudchi M (2019) Serum levels of APRIL increase in patients with glioma, meningioma and schwannoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 20:751–756. https://doi.org/10.31557/apjcp.2019.20.3.751
Sofela AA, Hilton DA, Ammoun S, Baiz D, Adams CL, Ercolano E, Jenkinson MD, Kurian KM, Teo M, Whitfield PC et al (2021) Fibulin-2: a novel biomarker for differentiating grade II from grade I meningiomas. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020560
Carneiro V, Cirino M, Panepucci R, Peria F, Tirapelli D, Colli B, Carlotti CG Jr (2021) The role of microRNA 181d as a possible biomarker associated with tumor progression in meningiomas. Cureus 13:e19158. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.19158
Acknowledgements
Tissue and serum samples were obtained from Graz biobank and Lancashire Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, which is part of the UK Brain Archive Information Network (BRAIN UK), which is funded by the Medical Research Council. We thank Brain Tumour Research for supporting this work. Ahmed Abdelrahman was supported by MSCA-ITN-ETN-European Training Networks [An Integrated Platform for Developing Brain Cancer Diagnostic Techniques (AiPBAND) Project ID 764281]. The funders had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, writing of the manuscript, or decision to publish.
Funding
This research was funded by MSCA-ITN-ETN-European Training Networks [An Integrated Platform for Developing Brain Cancer Diagnostic Techniques (AiPBAND) project ID 764281] and Brain Tumour Research (Hanemann).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, AA and COH; methodology, AA and CN; software, AA; validation, AA; formal analysis, AA; investigation, COH; resources, AA, MK, TUP and CLA; data curation, AA; writing—original draft preparation, AA and COH; writing—review and editing, CN, CLA, MK, CM, RV and COH; visualization, COH; supervision, CM, RV and COH.; project administration, COH; funding acquisition, CM, RV and COH. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of UNIVERSITY OF PLYMOUTH (protocol code 17/18-837and 14/15-450) and date of approval 27/ January 2021 for studies involving humans.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the editor-in-chief of this journal on request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelrahman, A., Negroni, C., Sahm, F. et al. miR-497 and 219 in blood aid meningioma classification. J Neurooncol 160, 137–147 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04126-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04126-0