Abstract
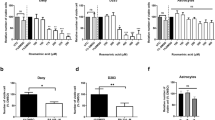
Medulloblastomas (MBs) are the most common malignant brain tumors of childhood. Antitumor agents promoting long-term survival with limited toxicities are thus far lacking. Preliminary findings suggest that retinoic acid (RA) derivatives (retinoids) exert antitumor effects by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing cell differentiation, apoptosis, and growth arrest, and RAs have been specifically shown to induce apoptosis in some MB cells. However, there is no conclusive evidence of retinoids inducing cell growth arrest in MBs. The aim of this study is to investigate whether retinoids play a role in cell-cycle arrest of MB cells. All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) was selected for these studies as it is known to have the capacity of inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in other types of cancer cells. Three MB cell lines (DAOY, D283 and D341) were subjected to ATRA treatment. The proportions of cells in the G0/G1 phase of cell cycle and in apoptosis were evaluated. The results showed that cell growth arrest, rather than apoptosis, was the main mechanism by which RA inhibited cell proliferation in the MB cell line DAOY, but not in the others (D283 and D341). Decreased expression of CyclinD1 and C-myc which regulate the transition of cell cycle was observed in DAOY cells following drug treatment, suggesting that these genes might be involved in ATRA retardation of cell cycle progression. Expression of RARβ, a mediator of the action of retinoids, was also induced by RA in DAOY cells, implying that RAR-β might also be involved in the mechanism of RA-induced cell cycle arrest. In conclusion, we have provided evidence for the first time that RA may induce cell cycle arrest in vitro in DAOY MB cells via inhibition of CyclinD1 or C-myc.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di C, Liao S, Adamson DC, Parrett TJ, Broderick DK, Shi Q, Lengauer C, Cummins JM, Velculescu VE, Fults DW, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Yan H (2005) Identification of OTX2 as a medulloblastoma oncogene whose product can be targeted by all-trans retinoic acid. Cancer Res 65:919–924
Sidell N (1982) Retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition and morphologic differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells in vitro J Natl Cancer Inst 68:589–596
Abemayor E, Sidell N (1989) Human neuroblastoma cell lines as models for the in vitro study of neoplastic and neuronal cell differentiation. Environ Health Perspect 80:3–15
Gumireddy K, Sutton LN, Phillips PC, Reddy CD (2003) All-trans-retinoic acid-induced apoptosis in human medulloblastoma: activation of caspase–3/poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 pathway. Clin Cancer Res 9:4052–4059
Liu J, Guo L, Jun-Wei L, Liu N, Li H (2000) All-trans retinoic acid modulates fas expression and enhances chemosensitivity of human medulloblastoma cells. Int J Mol Med 5:145–149
Liu J, Guo L, Luo Y, Li JW, Li H (2000) All trans-retinoic acid suppresses in vitro growth and down-regulates LIF gene expression as well as telomerase activity of human medulloblastoma cells. Anticancer Res 20:2659–2664
Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 14:1837–1851
Miller JR, Hocking AM, Brown JD, Moon RT (1999) Mechanism and function of signal transduction by the Wnt/beta-catenin and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways. Oncogene 18:7860–7872
Karim R, Tse G, Putti T, Scolyer R, Lee S (2004) The significance of the Wnt pathway in the pathology of human cancers. Pathology 36:120–128
Seidensticker MJ, Behrens J (2000) Biochemical interactions in the wnt pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1495:168–182
Suzui M, Masuda M, Lim JT, Albanese C, Pestell RG, Weinstein IB (2002) Growth inhibition of human hepatoma cells by acyclic retinoid is associated with induction of p21(CIP1) and inhibition of expression of cyclin D1. Cancer Res 62:3997–4006
Easwaran V, Pishvaian M, Salimuddin, Byers S (1999) Cross-regulation of beta-catenin-LEF/TCF and retinoid signaling pathways. Curr Biol 9:1415–1418
Qiu H, Zhang W, El-Nagaar AK, Lippman SM, Lin P, Lotan R, Xu XC (1999) Loss of retinoic acid receptor-β expression is an early event during esophageal carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 155:1519–1523
Gebert JF, Moghal N, Frangioni JV, Sugarbaker DJ, Neel BG (1991) High frequency of retinoic acid receptor β abnormalities in human lung cancer. Oncogene 6:1859–1868
Farias EF, Arasphian A, Bleiweiss IJ, Waxman S, Zelent A, Mira-Y-Lopez R (2002) Retinoic acid receptor α2 is a growth suppressor epigenetically silenced in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cell Growth Differ 13:335–341
Cheung B, Hocker JE, Smith SA, Norris MD, Haber M, Marshall GM (1998) Favorable prognostic significance of high-level retinoic acid receptor β expression in neuroblastoma mediated by effects on cell cycle regulation. Oncogene 17:751–759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Q., Chen, Z., You, J. et al. All-trans-retinoic acid induces cell growth arrest in a human medulloblastoma cell line. J Neurooncol 84, 263–267 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9380-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9380-9