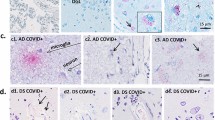
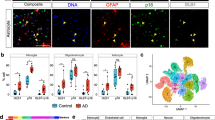
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the death of dopamine neurons, aggregation of α-synuclein, and severe motor impairment. This review examines current evidence on the key roles of neuroinflammation and immune dysfunction in neurodegeneration and development of the disease. Clinical and experimental evidence of microglial activation and the participation of Toll-like receptors, a wide range of chemokines, and pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the dynamics of this disease is presented. Particular attention is paid to the roles of the innate and adaptive immune responses in the mechanisms of systemic inflammation in the brain and periphery. Brain-infiltrating immune cells and their subpopulations have been shown to be involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration; changes in the composition and phenotype of peripheral immune cells and their functional characteristics have been demonstrated. Analysis of immune cell subsets and their ratios identifies fine PD-specific changes in cell populations which provide reliable biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of the course of the disease and for development of new approaches to anti-inflammatory and targeted therapy for PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdurasulova, I. N., Ekimova, I. V., Chernyshev, M. V., et al., “Impaired cognitive functions in Wistar rats in a model of the preclinical stage of Parkinson’s disease,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 69, No. 3, 364–381 (2019).
Aftanas, L. I., Gevorgyan, M. M., Zhanaeva, S. Y., et al., “Therapeutic effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) on neuroinflammation and neuroplasticity in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a placebo-controlled study,” Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 165, 195–199 (2018).
Ahn, J. J., Abu-Rub, M., and Miller, R. H., “B cells in neuroinflammation: New Perspectives and mechanistic insights,” Cells, 10, No. 7, 1605 (2021).
Akhtar, R. S., Licata, J. P., Luk, K. C., et al., “Measurements of auto-antibodies to α-synuclein in the serum and cerebral spinal fluids of patients with Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neurochem., 145, No. 6, 489–503 (2018).
Alperina, E. L., Contribution of the dopaminergic system to the mechanisms of immunomodulation,” Usp. Fiziol. Nauk., 45, No. 3, 45–56 (2014).
Álvarez-Luquín, D. D., Arce-Sillas, A., Leyva-Hernández, J., et al., “Regulatory impairment in untreated Parkinson’s disease is not restricted to Tregs: other regulatory populations are also involved,” J. Neuroinflammation, 16, No. 1, 212 (2019).
Amin, J., Holmes, C., Dorey, R. B., et al., “Neuroinflammation in dementia with Lewy bodies: a human post-mortem study,” Transl. Psychiatry, 10, No. 1, 267 (2020).
Arce-Sillas, A., Sevilla-Reyes, E., Álvarez-Luquín, D. D., et al., “Expression of dopamine receptors in immune regulatory cells,” Neuroimmunomodulation, 26, No. 3, 159–166 (2019).
Baba, Y., Kuroiwa, A., Uitti, R. J., et al., “Alterations of T-lymphocyte populations in Parkinson disease,” Parkinsonism Relat. Disord., 11, No. 8, 493–498 (2005).
Baird, J. K., Bourdette, D., Meshul, C. K., and Quinn, J. F., “The key role of T cells in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis and therapy,” Parkinsonism Relat. Disord., 60, 25–31 (2019).
Balestrino, R. and Schapira, A. H. V., “Parkinson disease,” Eur. J. Neurol, 27, No. 1, 27–42 (2020).
Barcia, C., Ros, C. M., Annese, V., et al., “IFN-γ signaling, with the synergistic contribution of TNF-α, mediates cell specific microglial and astroglial activation in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease,” Cell Death Dis., 2, No. 4, e142 (2011).
Bas, J., Calopa, M., Mestre, M., et al., “Lymphocyte populations in Parkinson’s disease and in rat models of parkinsonism,” J. Neuroimmunol., 113, No. 1, 146–52 (2001).
Belova, O. V., Aref’eva, T. I., and Moskvina, S. N., “Immunoinflammatory aspects of Parkinson’s disease,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr., 120, No. 2, 110–119 (2020).
Bengoa-Vergniory, N., Roberts, R. F., Wade-Martins, R., and Alegre-Aberrate, J., “Alpha-synuclein oligomers: a new hope,” Acta Neuropathol., 134, No. 6, 819–838 (2017).
Benner, E. J., Banerjee, R., Reynolds, A. D., et al., “Nitrated alpha-synuclein immunity accelerates degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons,” PLoS One, 3, No. 1, e1376 (2008).
Bhatia, D., Grozdanov, V., Ruf, W. P., et al., “T-cell dysregulation is associated with disease severity in Parkinson’s Disease,” J. Neuroinflammation, 18, No. 1, 250 (2021).
Blauwendraat, C., Nalls, M. A., and Singleton, A. B., “The genetic architecture of Parkinson’s disease,” Lancet Neurol., 19, No. 2, 170–178 (2020).
Boyko, A. A., Troyanova, N. I., Kovalenko, E. I., and Sapozhnikov, A. M., “Similarity and differences in inflammation-related characteristics of the peripheral immune system of patients with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., 18, No. 12, 2633 (2017).
Braak, H., Del Tredici, K., Rüb, U., et al., “Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease,” Neurobiol. Aging, 24, No. 2, 197–211 (2003).
Brochard, V., Combadière, B., Prigent, A., et al., “Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease,” J. Clin. Invest., 119, No. 1, 182–192 (2009).
Brodacki, B., Staszewski, J., Toczyłowska, B., et al., “Serum interleukin (IL-2, IL-10, IL-6, IL-4), TNFalpha, and INFgamma concentrations are elevated in patients with atypical and idiopathic parkinsonism,” Neurosci. Lett., 441, No. 2, 158–162 (2008).
Burré, J., “The synaptic function of α-synuclein,” J. Parkinsons Dis., 5, No. 4, 699–713 (2015).
Camacho-Hernández, N. P. and Peña-Ortega, F., “Fractalkine/CX3CR1-dependent modulation of synaptic and network plasticity in health and disease,” Neural Plast., 2023, 4637073 (2023).
Campos-Acuña, J., Elgueta, D., and Pacheco, R., “T-cell-driven inflammation as a mediator of the gut-brain axis involved in Parkinson’s disease,” Front. Immunol., 10, 239 (2019).
Cardinale, A., Calabrese, V., de Iure, A., and Picconi, B., “Alpha-synuclein as a prominent actor in the inflammatory synaptopathy of Parkinson’s disease,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22, No. 12, 6517 (2021).
Cebrián, C., Zucca, F. A., Mauri, P., et al., “MHC-I expression renders catecholaminergic neurons susceptible to T-cell-mediated degeneration,” Nat. Commun., 5, 3633 (2014).
Cen, L., Yang, C., Huang, S., et al., “Peripheral lymphocyte subsets as a marker of Parkinson’s disease in a Chinese population,” Neurosci. Bull., 33, No. 5, 493–500 (2017).
Cerri, S., Mus, L., and Blandini, F., “Parkinson’s disease in women and men: What’s the difference?” J. Parkinsons Dis., 9, No. 3, 501–515 (2019).
Chakrabarty, P., Ceballos-Diaz, C., Lin, W. L., et al., “Interferon-γ induces progressive nigrostriatal degeneration and basal ganglia calcification,” Nat. Neurosci., 14, No. 6, 694–696 (2011).
Chen, H., Zhang, S. M., Hernán, M. A., et al., “Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of Parkinson disease,” Arch. Neurol., 60, No. 8, 1059–1064 (2003).
Chen, J., Liu, X., and Zhong, Y., “Interleukin-17A: The key cytokine in neurodegenerative diseases,” Front. Aging Neurosci., 12, 566922 (2020).
Chen, S., Le, W. D., Xie, W. J., et al., “Experimental destruction of substantia nigra initiated by Parkinson disease immunoglobulins,” Arch. Neurol., 55, No. 8, 1075–1080 (1998).
Chen, S., Liu, Y., Niu, Y., et al., “Increased abundance of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and Th17 cells in peripheral blood of newly-diagnosed Parkinson’s disease patients,” Neurosci. Lett., 648, 21–25 (2017).
Chen, X., Feng, W., Ou, R., et al., “Evidence for peripheral immune activation in Parkinson’s disease,” Front. Aging Neurosci., 13, 617370 (2021).
Chen, Y., Qi, B., Xu, W., et al., “Clinical correlation of peripheral CD4+-cell sub-sets, their imbalance and Parkinson’s disease,” Mol. Med. Rep., 12, No. 4, 6105–6111 (2015).
Chen, Z., Chen, S., and Liu, J., “The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease,” Prog. Neurobiol., 169, 1–23 (2018).
Clark, I. A. and Vissel, B., “Therapeutic implications of how TNF links apolipoprotein E, phosphorylated tau, alpha-synuclein, amyloid-beta and insulin resistance in neurodegenerative diseases,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 175, No. 20, 3859–3875 (2018).
Contaldi, E., Magistrelli, L., and Comi, C., “T lymphocytes in Parkinson’s disease,” J. Parkinsons Dis., 12, No. s1, S65–S74 (2022).
Cyster, J. G. and Allen, C. D. C., “B Cell responses: Cell interaction dynamics and decisions,” Cell, 177, No. 3, 524–540 (2019).
Daneman, R. and Prat, A., “The blood–brain barrier,” Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 7, No. 1, a020412 (2015).
Dauer, W. and Przedborski, S., “Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models,” Neuron, 39, No. 6, 889–909 (2003).
Doorn, K. J., Moors, T., Drukarch, B., et al., “Microglial phenotypes and toll-like receptor 2 in the substantia nigra and hippocampus of incidental Lewy body disease cases and Parkinson’s disease patients,” Acta Neuropathol. Commun., 2, 90 (2014).
DuPage, M. and Bluestone, J. A., “Harnessing the plasticity of CD4(+) T cells to treat immune-mediated disease,” Nat. Rev. Immunol., 16, No. 3, 149–163 (2016).
Dursun, E., Gezen-Ak, D., Hanagasi, H., et al., “The interleukin 1 alpha, interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 6 and alpha-2-macroglobulin serum levels in patients with early or late onset Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment or Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neuroimmunol., 283, 50–57 (2015).
Dzamko, N., Gysbers, A., Perera, G., et al., “Toll-like receptor 2 is increased in neurons in Parkinson’s disease brain and may contribute to alpha-synuclein pathology,” Acta Neuropathol., 133, No. 2, 303–319 (2017).
Eidson, L. N., Kannarkat, G. T., Barnum, C. J., et al., “Candidate inflammatory biomarkers display unique relationships with alpha-synuclein and correlate with measures of disease severity in subjects with Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neuroinflammation, 14, No. 1, 164 (2017).
Fellner, L., Irschick, R., Schanda, K., et al., “Toll-like receptor 4 is required for alpha-synuclein dependent activation of microglia and astroglia,” Glia, 61, No. 3, 349–60 (2013).
Ferrari, C. C. and Tarelli, R., “Parkinson’s disease and systemic inflammation,” Parkinsons Dis., 2011, 436813 (2011).
Filiano, A. J., Gadani, S. P., and Kipnis, J., “How and why do T cells and their derived cytokines affect the injured and healthy brain?” Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 18, No. 6, 375–384 (2017).
Funk, N., Wieghofer, P., Grimm, S., et al., “Characterization of peripheral hematopoietic stem cells and monocytes in Parkinson’s disease,” Mov. Disord., 28, No. 3, 392–395 (2013).
Fuzzati-Armentero, M. T., Cerri, S., and Blandini, F., “Peripheral-central neuroimmune crosstalk in Parkinson’s disease: what do patients and animal models tell us?” Front. Neurol., 10, 232 (2019).
Gadani, S. P., Cronk, J. C., Norris, G. T., and Kipnis, J., “IL-4 in the brain: a cytokine to remember,” J. Immunol., 189, No. 9, 4213–4219 (2012).
Galiano-Landeira, J., Torra, A., Vila, M., and Bové, J., “CD8 T cell nigral infiltration precedes synucleinopathy in early stages of Parkinson’s disease,” Brain, 143, No. 12, 3717–3733 (2020).
Gao, H. M., Zhang, F., Zhou, H., et al., “Neuroinflammation and α-synuclein dysfunction potentiate each other, driving chronic progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse of Parkinson’s disease,” Environ. Health Perspect., 119, No. 6, 807–814 (2011).
Garfias, S., Tamaya Domínguez, B., Toledo Rojas, A., et al., “Peripheral blood lymphocyte phenotypes in Alzheimer and Parkinson’s diseases,” Neurologia, 37, No. 2, 110–121 (2022).
Garretti, F., Monahan, C., Sette, A., et al., “T cells, α-synuclein and Parkinson disease,” Handb. Clin. Neurol., 184, 439–455 (2022).
Gerhard, A., “TSPO imaging in parkinsonian disorders,” Clin. Transl. Imaging, 4, 183–190 (2016).
Golovko, M. Y., Barceló-Coblijn, G., et al., “The role of alpha-synuclein in brain lipid metabolism: a downstream impact on brain inflammatory response,” Mol. Cell Biochem., 326, No. 1–2, 55–66 (2009).
González, H., Contreras, F., and Pacheco, R., “Regulation of the neurodegenerative process associated to Parkinson’s disease by CD4+ T-cells,” J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol., 10, No. 4, 561–575 (2015).
González, H., Contreras, F., Prado, C., et al., “Dopamine receptor D3 expressed on CD4+ T cells favors neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons during Parkinson’s disease,” J. Immunol., 190, No. 10, 5048–5056 (2013).
Grigoryan, G. A., Gray, J. A., Rashid, T., et al., “Conditionally immortal neuroepithelial stem cell grafts restore spatial learning in rats with lesions at the source of cholinergic forebrain projections cholinergic forebrain projections,” Restor. Neurol. Neurosci., 17, No. 4, 1 (2000).
Grozdanov, V., Bliederhaeuser, C., Ruf, W. P., et al., “Inflammatory dysregulation of blood monocytes in Parkinson’s disease patients,” Acta Neuropathol., 128, No. 5, 651–663 (2014).
Gruden, M. A., Sewell, R. D., Yanamandra, K., et al., “Immunoprotection against toxic biomarkers is retained during Parkinson’s disease progression,” J. Neuroimmunol., 233, No. 1–2, 221–227 (2011).
Gruden, M. A., Yanamandra, K., Kucheryanu, V. G., et al., “Correlation between protective immunity to α-synuclein aggregates, oxidative stress and inflammation,” Neuroimmunomodulation, 19, No. 6, 334–342 (2012).
Gupta, V., Garg, R. K., and Khattri, S., “Levels of IL-8 and TNF-α decrease in Parkinson’s disease,” Neurol Res., 38, No. 2, 98–102 (2016).
Harms, A. S., Ferreira, S. A., and Romero-Ramos, M., “Periphery and brain, innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson’s disease,” Acta Neuropathol., 141, No. 4, 527–545 (2021).
Harms, A. S., Thome, A. D., Yan, Z., et al., “Peripheral monocyte entry is required for alpha-synuclein induced inflammation and neurodegeneration in a model of Parkinson disease,” Exp. Neurol., 300, 179–187 (2018).
Heidari, A., Yazdanpanah, N., and Rezaei, N., “The role of Toll-like receptors and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neuroinflammation, 19, No. 1, 135 (2022).
Hickman, S., Izzy, S., Sen, P., et al., “Microglia in neurodegeneration,” Nat. Neurosci., 21, No. 10, 1359–1369 (2018).
Hirsch, E. C. and Standaert, D. G., “Ten unsolved questions about neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease,” Mov. Disord., 36, No. 1, 16–24 (2021).
Horvath, I., Iashchishyn, I. A., Forsgren, L., and Morozova-Roche, L. A., “Immunochemical detection of α-synuclein autoantibodies in Parkinson’s Disease: Correlation between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels,” ACS Chem. Neurosci., 8, No. 6, 1170–1176 (2017).
Hu, Z. X., Song, W. N., Lu, X. D., et al., “Peripheral T lymphocyte immunity and l-dopamine in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents., 32, No. 3, 687–691 (2018).
Huang, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, X. Q., et al., “A dysfunction of CD4+ T lymphocytes in peripheral immune system of Parkinson’s disease model mice,” Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi, 30, No. 6, 567–576 (2014).
Iba, M., Kim, C., Sallin, M., et al., “Neuroinflammation is associated with infiltration of T cells in Lewy body disease and α-synuclein transgenic models,” J. Neuroinflammation, 17, No. 1, 214 (2020).
Idova, G. V., Alperina, E. L., and Cheido, M. A., “Contribution of brain dopamine, serotonin and opioid receptors in the mechanisms of neuroimmunomodulation: evidence from pharmacological analysis,” Int. Immunopharmacol., 12, No. 4, 618–625 (2012).
Idova, G. V., Alperina, E. L., Gevorgyan, M. M., et al., “Content of peripheral blood T- and B-cell subpopulations in transgenic A53T mice of different age (a model of Parkinson’s disease),” Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 170, No. 4, 401–404 (2021).
Idova, G. V., Alperina, E. L., Zhanaeva, S. Ya., et al., “Expression of Tolllike receptors TLR2 and TLR4 type on immune cells and production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in a transgenic model of Parkinson’s disease,” Patogenez, 20, No. 3, 38–43 (2022).
Jiang, S., Gao, H., Luo, Q., et al., “The correlation of lymphocyte subsets, natural killer cell, and Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis,” Neurol. Sci., 38, No. 8, 1373–1380 (2017).
Kalia, L. V. and Lang, A. E., “Parkinson’s disease,” Lancet, 386, No. 9996, 896–912 (2015).
Kalkonde, Y. V., Morgan, W. W., Sigala, J., et al., “Chemokines in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease: absence of CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 does not protect against striatal neurodegeneration,” Brain Res., 1128, No. 1, 1–11 (2007).
Kam, T. I., Hinkle, J. T., Dawson, T. M., and Dawson, V. L., “Microglia and astrocyte dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease,” Neurobiol. Dis., 144, 105028 (2020).
Kannarkat, G. T., Boss, J. M., and Tansey, M. G., “The role of innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson’s disease,” J. Parkinsons Dis., 3, No. 4, 493–514 (2013).
Karpenko, M. N., Vasilishina, A. A., Gromova, E. A., et al., “Interleukin-1β, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, interleukin-6, interleukin-10, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in CSF and serum in relation to the clinical diversity of Parkinson’s disease,” Cell. Immunol., 327, 77–82 (2018).
Kawano, M., Takagi, R., Saika, K., et al., “Dopamine regulates cytokine secretion during innate and adaptive immune responses,” Int. Immunol., 30, No. 12, 591–606 (2018).
Kessel, A., Haj, T., Peri, R., et al., “Human CD19(+)CD25(high) B regulatory cells suppress proliferation of CD4(+) T cells and enhance Foxp3 and CTLA-4 expression in T-regulatory cells,” Autoimmun. Rev., 11, No. 9, 670–677 (2012).
Khakh, B. S. and Sofroniew, M. V., “Diversity of astrocyte functions and phenotypes in neural circuits,” Nat. Neurosci., 18, No. 7, 942–952 (2015).
Kim, C., Ho, D. H., Suk, J. E., et al., “Neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia,” Nat. Commun., 4, 1562 (2013).
King, E. and Thomas, A., “Systemic inflammation in Lewy body diseases: A systematic review,” Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord., 31, No. 4, 346–356 (2017).
Klein, C. and Westenberger, A., “Genetics of Parkinson’s disease,” Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med., 2, No. 1, a008888 (2012).
Kortekaas, R., Leenders, K. L., van Oostrom, J. C., et al., “Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo,” Ann. Neurol., 57, No. 2, 176–179 (2005).
Kouli, A., Camacho, M., Allinson, K., and Williams-Gray, C. H., “Neuroinflammation and protein pathology in Parkinson’s disease dementia,” Acta Neuropathol. Commun., 8, No. 1, 211 (2020).
Kustrimovic, N., Comi, C., Magistrelli, L., et al., “Parkinson’s disease patients have a complex phenotypic and functional Th1 bias: cross-sectional studies of CD4+ Th1/Th2/T17 and Treg in drug-naïve and drug-treated patients,” J. Neuroinflammation, 15, No. 1, 205 (2018).
La Vitola, P., Balducci, C., Baroni, M., et al., “Peripheral inflammation exacerbates α-synuclein toxicity and neuropathology in Parkinson’s models,” Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol., 47, No. 1, 43–60 (2021).
Lai, T. T., Kim, Y. J., Ma, H. I., and Kim, Y. E., “Evidence of inflammation in Parkinson’s disease and its contribution to synucleinopathy,” J. Mov. Disord., 15, No. 1, 1–14 (2022).
Lavisse, S., Goutal, S., Wimberley, C., et al., “Increased microglial activation in patients with Parkinson disease using [18F]-DPA714 TSPO PET imaging,” Parkinsonism Relat. Disord., 82, 29–36 (2021).
Li, R., Tropea, T. F., Baratta, L. R., et al., “Abnormal B-cell and Tfh-cell profiles in patients with Parkinson disease: A cross-sectional study,” Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm., 9, No. 2, e1125 (2021a).
Li, W., Luo, Y., Xu, H., et al., “Imbalance between T helper 1 and regulatory T cells plays a detrimental role in experimental Parkinson’s disease in mice,” J. Int. Med. Res., 49, No. 4, 300060521998471(2021b).
Lindestam Arlehamn, C. S., Dhanwani, R., Pham, J., et al., “α-Synuclein-specific T cell reactivity is associated with preclinical and early Parkinson’s disease,” Nat. Commun., 11, No. 1, 1875 (2020).
Lira, A., Kulczycki, J., Slack, R., et al., “Involvement of the Fc gamma receptor in a chronic N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of dopaminergic loss,” J. Biol. Chem., 286, No. 33, 28783–28793 (2011).
Liu, Z., Huang, Y., Cao, B. B., et al., “Th17 cells induce dopaminergic neuronal death via LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease,” Mol. Neurobiol., 54, No. 10, 7762–7776 (2017).
Liu, Z., Zhai, X. R., Du, Z. S., et al., “Dopamine receptor D2 on CD4+T cells is protective against neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease,” Brain Behav. Immun., 98, 110–121 (2021).
Luo, P., Chu, S. F., Zhang, Z., et al., “Fractalkine/CX3CR1 is involved in the cross-talk between neuron and glia in neurological diseases,” Brain Res. Bull., 146, 12–21 (2019).
MacMahon Copas, A. N., McComish, S. F., Fletcher, J. M., and Caldwell, M. A., “The Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: A complex interplay between astrocytes, microglia, and T lymphocytes?” Front. Neurol., 12, 666737 (2021).
Magistrelli, L., Storelli, E., Rasini, E., et al., “Relationship between circulating CD4+ T lymphocytes and cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” Brain Behav. Immun., 89, 668–674 (2020).
Majbour, N. K., Aasly, J. O., Hustad, E., et al., “CSF total and oligomeric α-synuclein along with TNF-α as risk biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease: a study in LRRK2 mutation carriers,” Transl. Neurodegener., 9, No. 1, 15 (2020).
McGeer, P. L., Itagaki, S., Boyes, B. E., and McGeer, E. G., “Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains,” Neurology, 38, No. 8, 1285–1291 (1988).
McGinley, A. M., Sutton, C. E., Edwards, S. C., et al., “Interleukin-17A serves a priming role in autoimmunity by recruiting IL-1β-producing myeloid cells that promote pathogenic T cells,” Immunity, 52, No. 2, 342–356 e6 (2020).
Melzer, N., Hicking, G., Bittner, S., et al., “Excitotoxic neuronal cell death during an oligodendrocyte-directed CD8+ T cell attack in the CNS gray matter,” J. Neuroinflammation, 10, 121 (2013).
Milyukhina, I. V., Karpenko, M. N., and Klimenko, V. M., “Clinical parameters and blood and cerebrospinal fluid cytokine levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” Klinich. Med., 93, No. 1, 51–55 (2015).
Nagatsu, T., Mogi, M., Ichinose, H., and Togari, A., “Cytokines in Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neural Transm. Suppl., 58, 143–151 (2000).
Nash, K. R., Moran, P., Finneran, D. J., et al., “Fractalkine over expression suppresses α-synuclein-mediated neurodegeneration,” Mol. Ther., 23, No. 1, 17–23 (2015).
Nissen, S. K., Ferreira, S. A., Nielsen, M. C., et al., “Soluble CD163 changes indicate monocyte association with cognitive deficits in Parkinson’s disease,” Mov. Disord., 36, No. 4, 963–976 (2021).
Niwa, F., Kuriyama, N., Nakagawa, M., and Imanishi, J., “Effects of peripheral lymphocyte subpopulations and the clinical correlation with Parkinson’s disease,” Geriatr. Gerontol. Int., 12, No. 1, 102–107 (2012).
O’Shea, J. J. and Paul, W. E., “Mechanisms underlying lineage commitment and plasticity of helper CD4+ T cells,” Science, 327, 1098 (2010).
Orr, C. F., Rowe, D. B., Mizuno, Y., et al., “A possible role for humoral immunity in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease,” Brain, 128, No. 11, 2665–2674 (2005).
Parillaud, V. R., Lornet, G., Monnet, Y., et al., “Analysis of monocyte infiltration in MPTP mice reveals that microglial CX3CR1 protects against neurotoxic over-induction of monocyte-attracting CCL2 by astrocytes,” J. Neuroinflammation, 14, No. 1, 60 (2017).
Pawelec, P., Ziemka-Nalecz, M., Sypecka, J., and Zalewska, T., “The impact of the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis in neurological disorders,” Cells, 9, No. 10, 2277 (2020).
Pey, P., Pearce, R. K., Kalaitzakis, M. E., et al., “Phenotypic profile of alternative activation marker CD163 is different in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease,” Acta Neuropathol. Commun., 2, 21 (2014).
Pirozhkov, S. V., Terebilina, N. N., and Litvitskii, P. F., “The role of inflammasomes in the development of nervous and mental diseases,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr., 118, No. 12, 81–91 (2018).
Prots, I. and Winner, B., “Th17 cells: a promising therapeutic target for Parkinson’s disease?” Expert Opin. Ther. Targets, 23, No. 4, 309–314 (2019).
Pukhal’skii, A. L., Shmarina, G. V., and Aleshkin, V. A., “Regulatory T cells: modern approaches to optimizing their numbers,” Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 8, 24–33 (2011).
Qu, Y., Li, J., Qin, Q., et al., “A systematic review and meta-analysis of inflammatory biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease,” NPJ Parkinson’s Dis., 9, No. 1, 18 (2023).
Ransohoff, R. M., Liu, L., and Cardona, A. E., “Chemokines and chemokine receptors: multipurpose players in neuroinflammation,” Int. Rev. Neurobiol., 82, 187–204 (2007).
Reale, M., Iarlori, C., Thomas, A., et al., “Peripheral cytokines profile in Parkinson’s disease,” Brain Behav. Immun., 23, No. 1, 55–63 (2009).
Reynolds, A. D., Banerjee, R., Liu, J., et al., “Neuroprotective activities of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease,” J. Leukoc. Biol., 82, 1083–1094 (2007).
Reynolds, A. D., Stone, D. K., Hutter, J. A., et al., “Regulatory T cells attenuate Th17 cell-mediated nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a model of Parkinson’s disease,” J. Immunol., 184, 2261–2271 (2010).
Rosser, E. C. and Mauri, C., “Regulatory B cells: origin, phenotype, and function,” Immunity, 42, No. 4, 607–612 (2015).
Rostami, J., Fotaki, G., Sirois, J., et al., “Astrocytes have the capacity to act as antigen-presenting cells in the Parkinson’s disease brain,” J. Neuroinflammation, 17, No. 1, 119 (2020).
Sabatino, J., J., Jr., Pröbstel, A. K., and Zamvil, S. S., “B cells in autoimmune and neurodegenerative central nervous system diseases,” Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 20, No. 12, 728–745 (2019).
Saunders, J. A., Estes, K. A., Kosloski, L. M., et al., “CD4+ regulatory and effector/memory T cell subsets profile motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol., 7, No. 4, 927–938 (2012).
Schetters, S. T. T., Gomez-Nicola, D., Garcia-Vallejo, J. J., and Van Kooyk, Y., “Neuroinflammation: Microglia and T cells get ready to tango,” Front. Immunol., 8, 1905 (2018).
Sergeyeva, T. N. and Sergeyev, V. G., “Administration of LPS-stimulated autologous macrophages induces α-synuclein aggregation in dopaminergic neurons of rat brain,” Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 150, No. 4, 406–408 (2011).
Shi, Y., Wei, B., Li, L., et al., “Th17 cells and inflammation in neurological disorders: Possible mechanisms of action,” Front. Immunol., 13, 932152, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.932152 (2022).
Sommer, A., Fadler, T., Dorfmeister, E., et al., “Infiltrating T lymphocytes reduce myeloid phagocytosis activity in synucleinopathy model,” J. Neuroinflammation, 13, No. 1, 174 (2016).
Sommer, A., Marxreiter, F., Krach, F., et al., “Th17 lymphocytes induce neuronal cell death in a human iPSC-based model of Parkinson’s disease,” Cell Stem Cell, 23, No. 1, 123–131.e6 (2018).
Stefanis, L., Emmanouilidou, E., Pantazopoulou, M., et al., “How is alpha-synuclein cleared from the cell?” J. Neurochem., 150, No. 5, 577–590 (2019).
Stevens, C. H., Rowe, D., Morel-Kopp, M. C., et al., “Reduced T helper and B lymphocytes in Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neuroimmunol., 252, No. 1–2, 95–99 (2012).
Su, Y., Shi, C., Wang, T., et al., “Dysregulation of peripheral monocytes and pro-inflammation of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neurol., 269, No. 12, 6386–6394 (2022).
Sulzer, D. and Edwards, R. H., “The physiological role of α-synuclein and its relationship to Parkinson’s Disease,” J. Neurochem., 150, No. 5, 475–486 (2019).
Sulzer, D., Alcalay, R. N., Garretti, F., et al., “T cells from patients with Parkinson’s disease recognize α-synuclein peptides,” Nature, 546, No. 7660, 656–661 (2017).
Sun, C., Zhao, Z., Yu, W., et al., “Abnormal subpopulations of peripheral blood lymphocytes are involved in Parkinson’s disease,” Ann. Transl. Med., 7, No. 22, 637 (2019).
Sweeney, M. D., Zhao, Z., Montagne, A., et al., “Blood–brain barrier: From physiology to disease and back,” Physiol. Rev., 99, No. 1, 21–78 (2019).
Tan, E. K., Chao, Y. X., West, A., et al., “Parkinson disease and the immune system – associations, mechanisms and therapeutics,” Nat. Rev. Neurol., 16, No. 6, 303–318 (2020).
Tansey, M. G., Wallings, R. L., Houser, M. C., et al., “Inflammation and immune dysfunction in Parkinson disease,” Nat. Rev. Immunol., 22, No. 11, 657–673 (2022).
Tentillier, N., Etzerodt, A., Olesen, M. N., et al., “Anti-inflammatory modulation of microglia via CD163-targeted glucocorticoids protects dopaminergic neurons in the 6-OHDA Parkinson’s disease model,” J. Neurosci., 36, No. 36, 9375–9390 (2016).
Terada, T., Yokokura, M., Yoshikawa, E., et al., “Extrastriatal spreading of microglial activation in Parkinson’s disease: a positron emission tomography study,” Ann. Nucl. Med., 30, No. 8, 579–587 (2016).
Theodore, S., Cao, S., McLean, P. J., and Standaert, D. G., “Targeted overexpression of human alpha-synuclein triggers microglial activation and an adaptive immune response in a mouse model of Parkinson disease,” J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 67, No. 12, 1149–1158 (2008).
Thome, A. D., Standaert, D. G., and Harms, A. S., “Fractalkine signaling regulates the inflammatory response in an α-synuclein model of Parkinson disease,” PLoS One, 10, No. 10, e0140566 (2015).
Tian, J., Dai, S. B., Jiang, S. S., et al., “Specific immune status in Parkinson’s disease at different ages of onset,” NPJ Parkinson’s Dis, 8, No. 1, 5 (2022).
Ugrumov, M., “Development of early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: Illusion or reality?” CNS Neurosci. Ther., 26, No. 10, 997–1009 (2020).
Usenko, T. S., Nikolaev, M. A., Miliukhina, I. V., et al., “Plasma cytokine profile in synucleinophaties with dementia,” J. Clin. Neurosci., 78, 323–326 (2020).
Voronina, N. A., Kucheryanu, V. G., Vetrilé, L. A., et al., “Studies of the effect of hemantan on the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the nigrocaudate complex of the mouse brain with experimental parkinsonism,” Patogenez, 19, No. 2, 45–49 (2021).
Wang, P., Luo, M., Zhou, W., et al., “Global characterization of peripheral b cells in parkinson’s disease by single-cell RNA and BCR sequencing,” Front. Immunol., 13, 814239 (2022).
Wang, P., Yao, L., Luo, M., et al., “Single-cell transcriptome and TCR profiling reveal activated and expanded T cell populations in Parkinson’s disease,” Cell Discov., 7, No. 1, 52 (2021).
Wang, W., Nguyen, L. T., Burlak, C., et al., “Caspase-1 causes truncation and aggregation of the Parkinson’s disease-associated protein α-synuclein,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 113, No. 34, 9587–9592 (2016).
Weiss, F., Labrador-Garrido, A., Dzamko, N., and Halliday, G., “Immune responses in the Parkinson’s disease brain,” Neurobiol. Dis., 168, 105700 (2022).
Wijeyekoon, R. S., Kronenberg-Versteeg, D., Scott, K. M., et al., “Monocyte function in Parkinson’s disease and the impact of autologous serum on phagocytosis,” Front. Neurol., 9, 870 (2018).
Williams-Gray, C. H., Wijeyekoon, R., Yarnall, A. J., et al., “Serum immune markers and disease progression in an incident Parkinson’s disease cohort (ICICLE-PD),” Mov. Disord., 31, 995–1003 (2016).
Williams, G. P., Schonhoff, A. M., Jurkuvenaite, A., et al., “CD4 T cells mediate brain inflammation and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease,” Brain, 144, No. 7, 2047–2059 (2021).
Williams, G. P., Schonhoff, A. M., Sette, A., and Lindestam Arlehamn, C. S., “Central and peripheral inflammation: connecting the immune responses of Parkinson’s disease,” J. Parkinsons Dis., 12, No. s1, S129–S136 (2022).
Xiao, W., Shameli, A., Harding, C. V., et al., “Late stages of hematopoiesis and B cell lymphopoiesis are regulated by α-synuclein, a key player in Parkinson’s disease,” Immunobiology, 219, No. 11, 836–844 (2014).
Yan, Y., Jiang, W., et al., “Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome,” Cell, 160, 62–73 (2015).
Yan, Z., Yang, W., Wei, H., et al., “Dysregulation of the adaptive immune system in patients with early-stage Parkinson disease,” Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm., 8, No. 5, e1036 (2021).
Yang, J., Ran, M., Li, H., et al., “New insight into neurological degeneration: Inflammatory cytokines and blood-brain barrier,” Front. Mol. Neurosci., 15, 1013933 (2022).
Yu, S. Y., Zuo, L. J., Wang, F., et al., “Potential biomarkers relating pathological proteins, neuroinflammatory factors and free radicals in PD patients with cognitive impairment: a cross-sectional study,” BMC Neurol., 14, 113 (2014).
Zhanaeva, S. Ya., Alperina, E. L., Gevorgyan, M. M., et al., “B cells in peripheral blood in Parkinson’s disease. Clinical and experimental data,” Sib. Vestn. Psikh. Narkol., 3, No. 108, 11–16 (2020).
Zhang, S., Sun, C., Zhang, L., et al., “Clinical analysis of subpopulation of peripheral T and B lymphocytes in Chinese Parkinson’s disease patients,” Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 94, No. 47, 3726–3730 (2014).
Zhu, J., Yamane, H., and Paul, W. E., “Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations,” Annu. Rev. Immunol., 28, 445 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 73, No. 4, pp. 454–478, July–August, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Idova, G.V., Alperina, E.L. & Zhanaeva, S.Y. Neuroinflammation and Immune Dysfunction in the Mechanisms of Development of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci Behav Physi 53, 1534–1550 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01549-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01549-8