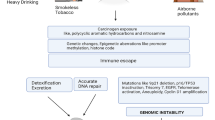
Abstract
The objective of the review is to summarize available literary data on the role and prognostic value of molecular biological markers p53, UBE2C, CD147, STAT3, VEGF in the carcinogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). To date, researches have been studying HNSCC molecular and genetic characteristics and obtaining information about new molecular biological markers that have different functional significance in tumor progression. This review presents current data on protein molecules involved in the HNSCC development, as well as in the formation of drug resistance mechanisms in tumors. The considered markers can be used not only for prognosis but also for developing a new approach to treatment, including patients resistant to therapy or recurrent HNSCC. However, the introduction of these markers into practice requires further examination of their functions and larger-scale studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The author confirms that all data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article. Furthermore, primary and secondary sources and data supporting the findings of this study were all publicly available at the time of submission.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018 Nov) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Reid PA, Wilson P, Li Y, Marcu LG, Bezak E Current understanding of cancer stem cells: review of their radiobiology and role in head and neck cancers. Head Neck 2017 Sep;39(9):1920–1932. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24848. Epub 2017
Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration (2017) Global, Regional, and National Cancer incidence, mortality, years of Life Lost, Years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol 3(4):524–548. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688
Machiels JP, René Leemans C, Golusinski W, Grau C, Licitra L, Gregoire V, EHNS Executive Board (2020 Nov) Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 31(11):1462–1475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.011
Marur S, Forastiere AA (2016) Mar;91(3):386 – 96 Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Update on Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.12.017
Pai SI, Westra WH (2009) Molecular pathology of head and neck cancer: implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Annu Rev Pathol 4:49–70. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092158
Koyfman SA, Ismaila N, Crook D, D’Cruz A, Rodriguez CP, Sher DJ et al Management of the Neck in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol 2019 Jul 10;37(20):1753–1774. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.01921
Leemans CR, Snijders PJF, Brakenhoff RH (2018 May) The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 18(5):269–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2018.11
Rassy E, Nicolai P, Pavlidis N (2019 Oct) Comprehensive management of HPV-related squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck of unknown primary. Head Neck 41(10):3700–3711. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.25858
Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nat 2015 Jan 29; 517(7536):576–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14129
Seiwert TY, Zuo Z, Keck MK, Khattri A, Pedamallu CS, Stricker T et al Integrative and comparative genomic analysis of HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 1;21(3):632 – 41. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3310
Alsahafi E, Begg K, Amelio I, Raulf N, Lucarelli P, Sauter T, Tavassoli M Clinical update on head and neck cancer: molecular biology and ongoing challenges. Cell Death Dis 2019 Jul 15;10(8):540. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1769-9
O’Sullivan B, Brierley J, Byrd D, Bosman F, Kehoe S, Kossary C et al (2017 Jul) The TNM classification of malignant tumours-towards common understanding and reasonable expectations. Lancet Oncol 18(7):849–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30438-2
Chung CH, Gillison ML Human papillomavirus in head and neck cancer: its role in pathogenesis and clinical implications. Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Nov 15;15(22):6758-62. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0784
Amit M, Takahashi H, Dragomir MP, Lindemann A, Gleber-Netto FO, Pickering CR et al Loss of p53 drives neuron reprogramming in head and neck cancer. Nat 2020 Feb ;578(7795):449–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-1996-3
Liu PF, Chen CF, Shu CW, Chang HM, Lee CH, Liou HH et al (2020) UBE2C is a potential biomarker for Tumorigenesis and Prognosis in Tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Diagnostics (Basel). 4(9):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090674
Yu B, Zhang Y, Wu K, Wang L, Jiang Y, Chen W et al (2019 Feb) CD147 promotes progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via NF-kappa B signaling. J Cell Mol Med 23(2):954–966. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13996
Micaily I, Johnson J, Argiris A An update on angiogenesis targeting in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers Head Neck 2020 Apr 6;5:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41199-020-00051-9
Ni H, Sun H, Zheng M, Bian T, Liu J, Li X, Zhang J, Liu Y (2021 Jan) Mining database for the expression and clinical significance of STAT family in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Transl Oncol 14(1):100976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100976
Cho J, Johnson DE, Grandis JR (2018 Jan) Therapeutic implications of the Genetic Landscape of Head and Neck Cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 28(1):2–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2017.08.005
Farah CS (2021 May) Molecular landscape of head and neck cancer and implications for therapy. Ann Transl Med 9(10):915. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-6264
Rehmani HS, Issaeva N (2020 Jul) EGFR in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: exploring possibilities of novel drug combinations. Ann Transl Med 8(13):813. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.04.07
Perisanidis C Prevalence of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Domain Mutations in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Cohort Study and Systematic Review. In Vivo. 2017 Jan 2;31(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11020
Ho AL, Brana I, Haddad R, Bauman J, Bible K, Oosting S, Wong DJ et al Tipifarnib in Head and Neck squamous cell carcinoma with HRAS mutations. J Clin Oncol 2021 Jun 10;39(17):1856–1864. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.20.02903
Mountzios G, Rampias T, Psyrri A (2014) The mutational spectrum of squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck: targetable genetic events and clinical impact. Ann Oncol 25:1889–1900
Novotný J, Bandúrová V, Strnad H, Chovanec M, Hradilová M, Šáchová J et al (2020) Analysis of HPV-Positive and HPV-Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Paired Normal Mucosae Reveals Cyclin D1 Deregulation and Compensatory Effect of Cyclin D2. Cancers (Basel). Mar 26;12(4):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040792
Santos-de-Frutos K, Segrelles C, Lorz C (2019) Hippo pathway and YAP signaling alterations in squamous cancer of the head and neck. J Clin Med 8(12):2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122131
Lepikhova T, Karhemo PR, Louhimo R, Yadav B, Murumägi A, Kulesskiy E et al (2018) Sep;17(9):2060–2071 Drug-Sensitivity Screening and Genomic Characterization of 45 HPV-Negative Head and Neck Carcinoma Cell Lines for Novel Biomarkers of Drug Efficacy. Mol Cancer Ther. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0733. Epub 2018 Jul 3. PMID: 29970484
Cochicho D, Esteves S, Rito M, Silva F, Martins L, Montalvão P, Cunha M et al (2022) PIK3CA Gene Mutations in HNSCC: Systematic Review and Correlations with HPV Status and Patient Survival. Cancers (Basel). Mar 2;14(5):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051286
Narayan P, Prowell TM, Gao JJ, Fernandes LL, Li E, Jiang X, Qiu J et al FDA Approval Summary: Alpelisib Plus Fulvestrant for Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 1;27(7):1842–1849. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3652
Jin N, Keam B, Cho J, Lee MJ, Kim HR, Torosyan H et al Therapeutic implications of activating noncanonical PIK3CA mutations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Invest 2021 Nov 15;131(22):e150335. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI150335
Li L, Li M, Wang X (2020 Apr) Cancer type-dependent correlations between TP53 mutations and antitumor immunity. DNA Repair (Amst) 88:102785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102785
Hsu PJ, Yan K, Shi H, Izumchenko E, Agrawal N (2020 Mar) Molecular biology of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 102:104552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104552
Duffy MJ, Synnott NC, Crown J (2017 Sep) Mutant p53 as a target for cancer treatment. Eur J Cancer 83:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.06.023
Redman-Rivera LN, Shaver TM, Jin H, Marshall CB, Schafer JM, Sheng Q et al Acquisition of aneuploidy drives mutant p53-associated gain-of-function phenotypes. Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 31;12(1):5184. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25359-z
Zhao D, Tahaney WM, Mazumdar A, Savage MI, Brown PH (2017 Nov) Molecularly targeted therapies for p53-mutant cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci 74(22):4171–4187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2575-0
Ock CY, Son B, Keam B et al (2016) Identification of genomic mutations associated with clinical outcomes of induction chemotherapy in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142(4):873–883
Niehr F, Eder T, Pilz T et al (2018) Multilayered OMICs-based analysis of a head and neck cancer model of cisplatin resistance reveals intratumoral heterogeneity and treatment-induced clonal selection. Clin Cancer Res 24(1):158–168
Gadhikar MA, Sciuto MR, Alves MV Chk1/2 inhibition overcomes the cisplatin resistance of head and neck cancer cells secondary to the loss of functional p53. Mol Cancer Ther. ;12(9):1860–1873. 41)Ragos V, S, Mastronikolis N, Tsiambas E, Baliou E, Mastronikolis N, Tsoukalas S et al (2013) N, E Patsouri E, P Fotiades P. p53 mutations in oral cavity carcinoma. J BUON. 2018 Nov-Dec;23(6):1569–1572. PMID: 30610778
Caponio VCA, Troiano G, Adipietro I, Zhurakivska K, Arena C, Mangieri D et al (2020 Oct) Computational analysis of TP53 mutational landscape unveils key prognostic signatures and distinct pathobiological pathways in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Br J Cancer 123(8):1302–1314. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-0984-6
Hashmi AA, Hussain ZF, Hashmi SK, Irfan M, Khan EY, Faridi N et al Immunohistochemical over expression of p53 in head and neck Squamous cell carcinoma: clinical and prognostic significance. BMC Res Notes. 2018 Jul 3;11(1):433. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3547-7
Monteiro LS, Diniz-Freitas M, Garcia-Caballero T, Warnakulasuriya S, Forteza J, Fraga M (2012 Aug) Combined cytoplasmic and membranous EGFR and p53 overexpression is a poor prognostic marker in early stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 41(7):559–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0714.2012.01142.x
Khan H, Gupta S, Husain N, Misra S, Mps N, Jamal N et al Correlation between expressions of Cyclin-D1, EGFR and p53 with chemoradiation response in patients of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma. BBA Clin 2014 Nov 21;3:11–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2014.11.004
Bajaj S, Alam SK, Roy KS, Datta A, Nath S, Roychoudhury S E2 Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme, UBE2C Gene, Is Reciprocally Regulated by Wild-type and Gain-of-Function Mutant p53. J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 1;291(27):14231–14247. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.731398. Epub 2016 Apr 28. PMID: 27129209; PMCID: PMC4933179
Dastsooz H, Cereda M, Donna D, Oliviero S A Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis of UBE2C in Cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 7;20(9):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092228
Clague MJ, Urbé S Ubiquitin: same molecule, different degradation pathways. Cell. 2010 Nov 24;143(5):682-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.012
Clague MJ, Barsukov I, Coulson JM, Liu H, Rigden DJ, Urbé S (2013 Jul) Deubiquitylases from genes to organism. Physiol Rev 93(3):1289–1315. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00002.2013
Clague MJ, Heride C, Urbé S (2015 Jul) The demographics of the ubiquitin system. Trends Cell Biol 25(7):417–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2015.03.002
Hao Z, Zhang H, Cowell J (2012 Jun) Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2C: molecular biology, role in tumorigenesis, and potential as a biomarker. Tumour Biol 33(3):723–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0291-1
Garnett MJ, Mansfeld J, Godwin C, Matsusaka T, Wu J, Russell P et al (2009 Nov) UBE2S elongates ubiquitin chains on APC/C substrates to promote mitotic exit. Nat Cell Biol 11(11):1363–1369. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1983
Nath S, Banerjee T, Sen D, Das T, Roychoudhury S Spindle assembly checkpoint protein Cdc20 transcriptionally activates expression of ubiquitin carrier protein UbcH10. J Biol Chem. 2011 May 6;286(18):15666-77. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.160671
Xiang C, Yan HC Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 C (UBE2C) may play a dual role involved in the progression of thyroid carcinoma. Cell Death Discov 2022 Mar 24;8(1):130. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-022-00935-4
Kim YJ, Lee G, Han J, Song K, Choi JS, Choi YL et al (2020 Jan) UBE2C overexpression aggravates patient outcome by promoting Estrogen-Dependent/Independent cell proliferation in early hormone receptor-positive and HER2-Negative breast Cancer. Front Oncol 23:9:1574. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01574
Zhang HQ, Zhao G, Ke B, Ma G, Liu GL, Liang H et al (2018 Mar) Overexpression of UBE2C correlates with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(6):1665–1671. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201803_14578
Liu Y, Huang F, Chen H, Peng Q, Zhao C, Miao L Expression of UBE2C in lung adenocarcinoma based on database analysis and its clinical significance. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2020 Sept 28;45(9):1044–1052. English, Chinese. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2020.190189
Wang Y, Shi F, Tao R, Wu J, Gu J, Yang R et al The relationship between UBE2C and AGGF1 overexpression and Tumor Angiogenesis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag Res 2021 Jul 30;13:5919–5930. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S320393
Wei Z, Liu Y, Qiao S, Li X, Li Q, Zhao J et al (2019 Jun) Identification of the potential therapeutic target gene UBE2C in human hepatocellular carcinoma: an investigation based on GEO and TCGA databases. Oncol Lett 17(6):5409–5418. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10232
Shen Z, Jiang X, Zeng C, Zheng S, Luo B, Zeng Y et al High expression of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 2 C (UBE2C) correlates with nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression. BMC Cancer 2013 Apr 15;13:192. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-192
Jin Z, Zhao X, Cui L, Xu X, Zhao Y, Younai F et al UBE2C promotes the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020 Mar 5;523(2):389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.12.064
Wang R, Song Y, Liu X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Li L et al (2017 Apr) UBE2C induces EMT through Wnt/βcatenin and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways by regulating phosphorylation levels of Aurora-A. Int J Oncol 50(4):1116–1126. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.3880
Liu Y, Zhao R, Chi S, Zhang W, Xiao C et al UBE2C is upregulated by Estrogen and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via p53 in Endometrial Cancer. Mol Cancer Res 2020 Feb;18(2):204–215. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0561
Pietruszewska W, Bojanowska-Poźniak K, Kobos J Matrix metalloproteinases MMP1, MMP2, MMP9 and their tissue inhibitors TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3 in head and neck cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Otolaryngol Pol 2016 Jun 30;70(3):32–43. https://doi.org/10.5604/00306657.1202546
Landras A, Reger de Moura C, Jouenne F, Lebbe C, Menashi S, Mourah S CD147 is a Promising Target of Tumor Progression and a prognostic biomarker. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 16;11(11):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111803
Li L, Dong X, Peng F, Shen L Integrin β1 regulates the invasion and radioresistance of laryngeal cancer cells by targeting CD147. Cancer Cell Int 2018 Jun 7;18:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0578-z
Fusella F, Seclì L, Busso E, Krepelova A, Moiso E, Rocca S et al The IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway requires Morgana to drive breast cancer metastasis. Nat Commun 2017 Nov 21;8(1):1636. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01829-1
Cui HY, Guo T, Wang SJ, Zhao P, Dong ZS, Zhang Y et al Dimerization is essential for HAb18G/CD147 promoting tumor invasion via MAPK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Mar 16;419(3):517 – 22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.049
Matsumoto T, Nagashio R, Ryuge S, Igawa S, Kobayashi M, Fukuda E et al Basigin expression as a prognostic indicator in stage I pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Pathol Int 2018 Apr;68(4):232–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/pin.12646
Knutti N, Huber O, Friedrich K (2019 Jan) CD147 (EMMPRIN) controls malignant properties of breast cancer cells by interdependent signaling of wnt and JAK/STAT pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 451(1–2):197–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3406-9
Lu M, Wu J, Hao ZW, Shang YK, Xu J, Nan G et al Basolateral CD147 induces hepatocyte polarity loss by E-cadherin ubiquitination and degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma progress. Hepatol 2018 Jul;68(1):317–332. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29798
Zheng HC, Gong BC CD147 expression was positively linked to aggressiveness and worse prognosis of gastric cancer: a meta and bioinformatics analysis. Oncotarget 2017 Aug 9;8(52):90358–90370. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20089
Zhou Z, Long J, Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Tang L et al Targeted degradation of CD147 proteins in melanoma. Bioorg Chem 2020 Dec ;105:104453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104453
Suzuki S, Honda K, Nanjo H, Iikawa N, Tsuji T, Kawasaki Y et al CD147 expression correlates with lymph node metastasis in T1-T2 squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Oncol Lett 2017 Oct;14(4):4670–4676. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6808
Muramatsu T (2016 May) Basigin (CD147), a multifunctional transmembrane glycoprotein with various binding partners. J Biochem 159(5):481–490. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvv127
Khayati F, Pérez-Cano L, Maouche K, Sadoux A, Boutalbi Z, Podgorniak MP et al (2015) EMMPRIN/CD147 is a novel coreceptor of VEGFR-2 mediating its activation by VEGF. Oncotarget 6(12):9766–9780. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2870
Shibuya M (2011 Dec) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) signaling in angiogenesis: a crucial target for Anti- and pro-angiogenic therapies. Genes Cancer 2(12):1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911423031
Goel HL, Mercurio AM (2013 Dec) VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer 13(12):871–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3627
Frezzetti D, Gallo M, Maiello MR, D’Alessio A, Esposito C, Chicchinelli N et al VEGF as a potential target in lung cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2017 Oct;21(10):959–966. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2017.1371137
Liu Y, Tamimi RM, Collins LC, Schnitt SJ, Gilmore HL, Connolly JL et al (2011 Aug) The association between vascular endothelial growth factor expression in invasive breast cancer and survival varies with intrinsic subtypes and use of adjuvant systemic therapy: results from the Nurses’ Health Study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129(1):175–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1432-3
Pang L, Wang J, Fan Y, Xu R, Bai Y, Bai L (2018) Correlations of TNM staging and lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer with MRI features and VEGF expression. Cancer Biomark 23(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-181287
Mukherjee S, Pal M, Mukhopadhyay S, Das I, Hazra R, Ghosh S et al VEGF expression to support targeted therapy in ovarian surface epithelial neoplasms. J Clin Diagn Res 2017 Apr;11(4):EC43-EC46. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2017/24670.9737
Butkiewicz D, Gdowicz-Kłosok A, Krześniak M, Rutkowski T, Krzywon A, Cortez AJ et al (2020) Association of Genetic Variants in ANGPT/TEK and VEGF/VEGFR with Progression and Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Radiotherapy or Radiochemotherapy. Cancers (Basel). Jun 9;12(6):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061506
Chen L, Lin G, Chen K, Liang R, Wan F, Zhang C et al VEGF promotes migration and invasion by regulating EMT and MMPs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer. 2020 Oct 21;11(24):7291–7301. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.46429
Hu H, Chen Y, Tan S, Wu S, Huang Y, Fu S et al The Research Progress of Antiangiogenic Therapy, Immune Therapy and Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol 2022 Feb 23;13:802846. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.802846
Meder L, Schuldt P, Thelen M, Schmitt A, Dietlein F, Klein S et al (2018) Combined vegf and Pd-L1 blockade Displays Synergistic Treatment Effects in an Autochthonous Mouse Model of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res 78(15):4270–4281. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-2176
Feng F, Wang B, Sun X, Zhu Y, Tang H, Nan G et al (2017 Jan) Metuzumab enhanced chemosensitivity and apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 2(1):51–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2016.1276126
Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B, Huang W, Tian Y, Fu X Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 2020 Sep 24;19(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01258-7
Wang Y, Shen Y, Wang S, Shen Q, Zhou X The role of STAT3 in leading the crosstalk between human cancers and the immune system. Cancer Lett 2018 Feb 28;415:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.12.003
Guo C, Yang G, Khun K, Kong X, Levy D, Lee P et al Activation of Stat3 in renal tumors. Am J Transl Res 2009 Feb 28;1(3):283–90
Don-Doncow N, Marginean F, Coleman I, Nelson PS, Ehrnström R, Krzyzanowska A et al (2017 Mar) Expression of STAT3 in prostate Cancer metastases. Eur Urol 71(3):313–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.018
Wu CJ, Sundararajan V, Sheu BC, Huang RY, Wei LH (2019) Activation of STAT3 and STAT5 Signaling in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Progression: Mechanism and Therapeutic Opportunity. Cancers (Basel). Dec 19;12(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010024
Ma JH, Qin L, Li X Role of STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Commun Signal 2020 Feb 28;18(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-0527-z
Mohrherr J, Uras IZ, Moll HP, Casanova E (2020) STAT3: Versatile Functions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers (Basel). Apr 29;12(5):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051107
Geiger JL, Grandis JR, Bauman JE The STAT3 pathway as a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer: barriers and innovations. Oral Oncol 2016 May ;56:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.11.022
Lee H, Jeong AJ, Ye SK (2019 Jul) Highlighted STAT3 as a potential drug target for cancer therapy. BMB Rep 52(7):415–423. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.7.152
Johnson DE, O’Keefe RA, Grandis JR (2018 Apr) Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15(4):234–248. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.8
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui VWY, Bauman JE, Grandis JR (2020 Nov) Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 26(1):92. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00224-3
Bu LL, Yu GT, Deng WW, Mao L, Liu JF, Ma SR et al Targeting STAT3 signaling reduces immunosuppressive myeloid cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 2016 Jan 19;5(5):e1130206. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2015.1130206
Jia C, Wang G, Wang T, Fu B, Zhang Y, Huang L et al Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the transglutaminase 2-dependent IL-6/IL6R/STAT3 axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci 2020 Jul 19;16(14):2542–2558. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.45446
Heichler C, Scheibe K, Schmied A, Geppert CI, Schmid B, Wirtz S et al (2020 Jul) STAT3 activation through IL-6/IL-11 in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes colorectal tumour development and correlates with poor prognosis. Gut 69(7):1269–1282. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319200
Bu LL, Yu GT, Wu L, Mao L, Deng WW, Liu JF et al STAT3 induces immunosuppression by upregulating PD-1/PD-L1 in HNSCC. J Dent Res 2017 Aug;96(9):1027–1034. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034517712435
Jung K, Kang H, Mehra R Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancers Head Neck 2018 Jun 4;3:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41199-018-0030-z
Sun S, Wu Y, Guo W, Yu F, Kong L, Ren Y et al Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 1;24(11):2665–2677. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2248
Hyytiäinen A, Wahbi W, Väyrynen O, Saarilahti K, Karihtala P, Salo T et al (2021) Angiogenesis inhibitors for Head and Neck squamous cell Carcinoma Treatment: is there still hope? Front Oncol. 1411:683570. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.683570
de Aguiar RB, de Moraes JZ (2019) Exploring the immunological MechanismsUnderlying the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor activity in tumors. Front Immunol 10:1023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01023
Lin Z, Zhang Q, Luo W (2016) Angiogenesis inhibitors as therapeutic agents in Cancer: Challenges and future directions. Eur J Pharmacol 793:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.10.03
Ahn PH, Machtay M, Anne PR, Cognetti D, Keane WM, Wuthrick E et al (2018) Phase I trial using induction ciplatin, Docetaxel, 5-FU and Erlotinib followed by cisplatin, Bevacizumab and Erlotinib with Concurrent Radiotherapy for Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 41:441–446. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0000000000000317
Argiris A, Bauman JE, Ohr J, Gooding WE, Heron DE, Duvvuri U et al (2016) Phase II randomized trial of Radiation Therapy, Cetuximab, and Pemetrexed with or without Bevacizumab in patients with locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Ann Oncol 27:1594–1600. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw204
Salama JK, Haraf DJ, Stenson KM, Blair EA, Witt ME, Williams R et al (2011) A randomized phase II study of 5-Fluorouracil, Hydroxyurea, and twice-daily Radiotherapy compared with Bevacizumab plus 5-Fluorouracil, Hydroxyurea, and twice-daily Radiotherapy for Intermediate-Stage and T4N0-1 Head and Neck cancers. Ann Oncol 22:2304–2309. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdq73
Argiris A, Li S, Savvides P, Ohr JP, Gilbert J, Levine MA, Chakravarti A et al Phase III Randomized Trial of Chemotherapy With or Without Bevacizumab in Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Dec 1;37(34):3266–3274. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.00555
Folkman J (2006) Antiangiogenesis in Cancer therapy–endostatin and its mechanisms of action. Exp Cell Res 312:594–607. 10.1016/ j.yexcr.2005.11.015
Kang M, Wang F, Liao X, Zhou P, Wang R (2018) Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy Combined with Endostar has similar Efficacy but weaker Acute adverse reactions than IMRT Combined with Chemotherapy in the treatment of locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med (Baltim) 97:e11118. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000011118
Jin T, Li B, Chen X-ZA, Phase II (2013) Trial of Endostar Combined with Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Chemotherapy in patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NCT01612286). Oncol Res 21:317–323. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504014X13983417587401
Ye W, Liu R, Pan C, Jiang W, Zhang L, Guan Z et al (2014) Multicenter Randomized Phase 2 clinical trial of a recombinant human endostatin adenovirus in patients with Advanced Head and Neck Carcinoma. Mol Ther J Am Soc Gene Ther 22:1221–1229. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2014.53
Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B et al (2020) Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 19:145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01258-7
Yu GT, Mao L, Wu L, Deng WW, Bu LL, Liu JF et al (2018 Nov) Inhibition of SRC family kinases facilitates anti-CTLA4 immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(22):4223–4234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2863-3
Gelain A, Mori M, Meneghetti F, Villa S (2019) Signal Transducer and Activator of transcription protein 3 (STAT3): an update on its direct inhibitors as promising Anticancer Agents. Curr Med Chem 26(27):5165–5206. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867325666180719122729
Jonker DJ, Nott L, Yoshino T, Gill S, Shapiro J, Ohtsu A et al (2018) Napabucasin versus placebo in refractory advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:263–270
Chen Z, Xing J, Zhang S Anti-human hepatoma monoclonal antibody Hab18 Light/Heavy chain Variable Region Gene, and use Thereof. EP Patent 20030711796, 29 December 2004.
Wang M, Zhang S, Sun Q, Yang X, Wang Y et al (2019) Dual effects of an anti-CD147 antibody for esophageal cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther 20(12):1443–1452. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2019.1647052
Salim KY, Maleki Vareki S, Danter WR, Koropatnick J COTI-2, a novel small molecule that is active against multiple human cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2016 Jul 5;7(27):41363–41379. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9133
Maleki Vareki S, Salim KY, Danter WR, Koropatnick J Novel anti-cancer drug COTI-2 synergizes with therapeutic agents and does not induce resistance or exhibit cross-resistance in human cancer cell lines. PLoS One 2018 Jan 24;13(1):e0191766. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191766
Lindemann A, Patel AA, Silver NL, Tang L, Liu Z, Wang L et al COTI-2, a Novel Thiosemicarbazone Derivative, exhibits Antitumor Activity in HNSCC through p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res 2019 Sep 15;25(18):5650–5662. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0096
Synnott NC, O’Connell D, Crown J, Duffy MJ (2020 Jan) COTI-2 reactivates mutant p53 and inhibits growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 179(1):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05435-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Sergey V. Vtorushin, Sergei S. Naumov, Denis E. Kulbakin. Literature review/writing/revision: Sergei S. Naumov, Sergey V. Vtorushin, Nadezhda V. Krakhmal, Denis E. Kulbakin. All Authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All Authors declare no actual, potential, or perceived conflicts interest that would prejudice the impartiality of the study.
Compliance with ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naumov, S.S., Kulbakin, D.E., Krakhmal, N.V. et al. Molecular and biological factors in the prognosis of head and neck squamous cell cancer. Mol Biol Rep 50, 7839–7849 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08611-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08611-1