Abstract
Background
Recently, urinary exosomal miRNAs are gaining increasing attention as their expression profiles are often associated with specific diseases and they exhibit great potential as noninvasive biomarkers for the diagnosis of various diseases. The present study was aimed to evaluate the expression status of selected miRNAs (miR-1, miR-215-5p, miR-335-5p and let-7a-5p) in urine samples from children with NS [steroid sensitive (SSNS)] and [steroid resistant (SRNS)] along with healthy control group.
Methods
MicroRNA isolation was carried out in urine samples collected from SSNS (100 nos), SRNS (100 nos), and healthy controls (50 nos) using MiRNeasy Mini Kit, followed by cDNA conversion for all the four selected miRNAs using Taqman advanced miRNA cDNA synthesis kit and their expression was quantified by Taqman Advanced miRNA assay kits using Real Time PCR Machine and Rotogen-Q in SSNS and SRNS patients and healthy control subjects.
Results
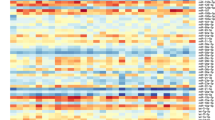
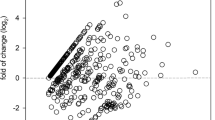
Quantification of all the four miRNAs (miR-1, mir-215, miR-335, let-7a) were found to be upregulated in both SSNS and SRNS as compared to control group. Further, the comparison of microRNAs within the case groups revealed significant downregulation of three microRNAs—miR-1, miR-215, miR- 335 and upregulation of let-7a in SRNS group as compared to SSNS. The t-test performed for all the four miRNAs was found to be statistically significant.
Conclusions
The aberrant expression of all the four microRNAs in both SSNS and SRNS as compared to healthy subjects may serve as novel biomarkers to distinguish between NS and healthy controls. The differential expression of microRNA let-7a is useful to discriminate SSNS and SRNS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagga A (2008) Revised guidelines for management of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Indian J Nephrol 18:31–39. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-4065.41289
Bierzynska A, Saleem M (2017) Recent advances in understanding and treating nephrotic syndrome. F1000Research 6:121. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.10165.1
Mekahli D, Liutkus A, Ranchin B, Yu A, Bessenay L, Girardin E, Van Damme-Lombaerts R, Palcoux JB, Cachat F, Lavocat MP, Bourdat-Michel G, Nobili F, Cochat P (2009) Long-term outcome of idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter study. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1525–1532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1138-5
Hjorten R, Anwar Z, Reidy KJ (2016) Long-term outcomes of childhood onset nephrotic syndrome. Front Pediatr 4:53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2016.00053
Luo Y, Wang C, Chen X, Zhong T, Cai X, Chen S, Shi Y, Hu J, Guan X, Xia Z, Wang J, Zen K, Zhang CY, Zhang C (2013) Increased serum and urinary microRNAs in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin Chem 59:658–666. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2012.195297
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Chen T, Wang C, Yu H, Ding M, Zhang C, Lu X, Zhang CY, Zhang C (2019) Increased urinary exosomal microRNAs in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. EBioMedicine 39:552–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.018
Szeto CC (2014) Urine miRNA in nephrotic syndrome. Clin Chim Acta 436:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2014.06.016
Erturk E, Cecener G, Egeli U, Tunca B, Tezcan G, Gokgoz S, Tolunay S, Tasdelen I (2014) Expression status of let-7a and miR-335 among breast tumors in patients with and without germ-line BRCA mutations. Mol Cell Biochem 395:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2113-4
Gao L, Yang Y, Xu H, Liu R, Li D, Hong H, Qin M, Wang Y (2014) MiR-335 functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer by targeting OCT4. Tumour Biol 35:8309–8318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2092-9
Sun Z, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Qiu B, Liu K, Dong G (2014) MicroRNA-335 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting ZEB2. Med Oncol 31:982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0982-8
Cao J, Cai J, Huang D, Han Q, Chen Y, Yang Q, Yang C, Kuang Y, Li D, Wang Z (2014) miR-335 represents an independent prognostic marker in epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 141:437–442. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCPLYTZGB54ISZC
Bai XY, Ma Y, Ding R, Fu B, Shi S (2011) miR-335 and miR-34a promote renal senescence by suppressing mitochondrial antioxidative enzymes. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1252–1261. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2010040367
Wang H, Li M, Zhang R, Wang Y, Zang W, Ma Y, Zhao G, Zhang G (2013) Effect of miR-335 upregulation on the apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer cell A549 and H1299. Tumour Biol 34:3101–3109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0878-9
Yang B, Huang J, Liu H, Guo W, Li G (2016) miR-335 directly, while miR-34a indirectly modulate survivin expression and regulate growth, apoptosis, and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Tumour Biol 37:1771–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3951-8
White NMA, Khella HWZ, Grigull J, Adzovic S, Youssef YM, Honey RJ, Stewart R, Pace KT, Bjarnason GA, Jewett MAS, Evans AJ, Gabril M, Yousef GM (2011) miRNA profiling in metastatic renal cell carcinoma reveals a tumour-suppressor effect for miR-215. Br J Cancer 105:1741–1749. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.401
Ribal MJ, Molecular profiling of renal cancer: the journey to clinical application. Eur Urol 59:731–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.01.039
Lu C, Zhou D, Wang Q, Liu W, Yu F, Wu F, Chen C (2020) Crosstalk of microRNAs and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2415324
Fardi M, Alivand M, Baradaran BM, Hagh F, Solali S (2019) The crucial role of ZEB2: from development to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer complexity. J Cell Physiol 234:14783–14799. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28277
Jin J, Wang Y, Zhao L, Zou W, Tan M, He Q (2020) Exosomal miRNA-215-5p derived from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of podocytes by inhibiting ZEB2. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2685305
Tao G, Martin JF (2013) MicroRNAs get to the heart of development. Elife 2:e01710. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01710
Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2016) Cardiac-specific miRNA in cardiogenesis, heart function, and cardiac pathology (with focus on myocardial infarction). J Mol Cell Cardiol 94:107–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.03.015
Wang T, Zhum H, Yang S, Fei X (2019) Let-7a-5p may participate in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy through targeting HMGA2. Mol Med Rep 19:4229–4237. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10057
Perakis S, Speicher MR (2017) Emerging concepts in liquid biopsies. BMC Med 15:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-017-0840-6
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, Huang KH, Lee MJ, Galas DJ, Wang K (2010) The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem 56:1733–1741. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405
Buschmann D, Haberberger A, Kirchner B, Spornraft M, Riedmaier I, Schelling G, Pfaffl MW (2016) Toward reliable biomarker signatures in the age of liquid biopsies-how to standardize the small RNA-Seq workflow. Nucleic Acids Res 44:5995–6018. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw545
Tsuji K, Kitamura S, Wada J (2020) MicroRNAs as biomarkers for nephrotic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 22:88. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010088
Gbadegesin RA, Hall G, Adeyemo A, Hanke N, Tossidou I, Burchette J, Wu G, Homstad A, Sparks MA, Gomez J, Jiang R, Alonso A, Lavin P, Conlon P, Korstanje R, Stander MC, Shamsan G, Barua M, Spurney R, Singhal PC, Kopp JB, Haller H, Howell D, Pollak MR, Shaw AS, Schiffer M, Winn MP (2014) Mutations in the gene that encodes the F-actin binding protein anillin cause FSGS. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:1991–2002. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2013090976
Sellin L, Huber TB, Gerke P, Quack I, Pavenstadt H, Walz G (2003) NEPH1 defines a novel family of podocin interacting proteins. FASEB J 17:115–117. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-0242fje
Donoviel DB, Freed DD, Vogel H, Potter DG, Hawkins E, Barrish JP, Mathur BN, Turner CA, Geske R, Montgomery CA, Starbuck M, Brandt M, Gupta A, Ramirez-Solis R, Zambrowicz BP, Powell DR (2001) Proteinuria and perinatal lethality in mice lacking NEPH1, a novel protein with homology to nephrin. Mol Cell Biol 21:4829–4836. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.21.14.4829-4836
Solanki AK, Widmeier E, Arif E, Sharma S, Daga A, Srivastava P, Kwon SH, Hugo H, Nakayama M, Mann N, Majmundar AJ, Tan W et al (2019) Mutations in KIRREL1, a slit diaphragm component, cause steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 96:883–889
Schwarz K, Simons M, Reiser J, Saleem MA, Faul C, Kriz W, Shaw AS, Holzman LB, Mundel P (2001) Podocin, a raft-associated component of the glomerular slit diaphragm, interacts with CD2AP and nephrin. J Clin Invest 108:1621–1629
Shih NY, Li J, Karpitskii V, Nguyen A, Dustin ML, Kanagawa O, Miner JH (1999) Shaw AS congenital nephrotic syndrome in mice lacking CD2-associated protein. Science 286:312–315. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5438.312
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge DBT for supporting to carry out this work
Funding
Funding was provided by Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology (Ref No: BT/PR30523/BIC/101/1121/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest and they are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dandapani, M.C., Venkatesan, V., Charmine, P. et al. Differential urinary microRNA expression analysis of miR-1, miR-215, miR-335, let-7a in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Mol Biol Rep 49, 6591–6600 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07500-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07500-3