Abstract
Background
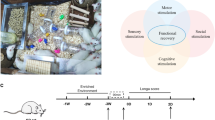
Growing evidence, including our previous studies, has demonstrated that an enriched environment (EE) after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury improves neurofunctional recovery in rats. However, whether EE exposure prior to injury could play a neuroprotective role in stroke has seldom been investigated. In this study, we examined the neuroprotective effects of prior exposure to EE and investigated the potential anti-apoptotic effect in rats after cerebral I/R injury.
Methods and results
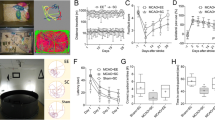
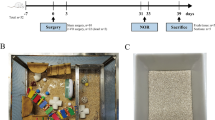
Rats were housed in EE or standard conditions (SC) for four weeks and then randomly assigned to receive 120 min of right middle cerebral occlusion (MCAO) or sham operation. Based on the housing environment and the procedure they underwent, the rats were divided into the following three groups: preischemic EE + MCAO (PIEE), preischemic SC + MCAO (PISC) and preischemic SC + sham-operated (sham). Forty-eight hours after the operation, the rats were subjected to a series of assessments. We found that prior exposure to EE improved functional outcomes, reduced infarct volume and attenuated histological damage. The apoptotic cell numbers in the ischemic penumbra cortex decreased in PIEE group, as did the p53, PUMA, Bax and AIF expression levels. The protein expression of Bcl-2 and HSP70 was increased in the PIEE group compared with the PISC group. PIEE treatment also significantly increased the BDNF level in the ischemic penumbra. In addition, inhibition of cell apoptosis and upregulation of BDNF expression levels were correlated with the improved functional recovery of MCAO rats.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that EE preconditioning inhibited cell apoptosis and upregulated BDNF expression in the penumbra of MCAO rats, which may contribute to neurofunctional recovery after stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS et al (2022) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 145:e153–e639. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001052
Su Y, Chen X, Ye XF, Sun HY, Wu F, Dong Q, Cheng X, Wu D (2020) The value of ADAMTS13 in predicting clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke receiving thrombolysis. Front Neurol 11:799. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00799
Kempermann G (2019) Environmental enrichment, new neurons and the neurobiology of individuality. Nat Rev Neurosci 20:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0120-x
White JH, Bartley E, Janssen H, Jordan LA, Spratt N (2015) Exploring stroke survivor experience of participation in an enriched environment: a qualitative study. Disabil Rehabil 37:593–600. https://doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2014.935876
Deng YH, Dong LL, Zhang YJ, Zhao XM, He HY (2021) Enriched environmentboosts the post-stroke recovery of neurological function by promoting autophagy. Neural Regen Res 16:813–819. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.297084
Chen X, Zhang X, Liao W, Wan Q (2017) Effect of physical and social components of enriched environment on astrocytes proliferation in rats after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res 42:1308–1316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2172-x
Zhang X, Chen XP, Lin JB, Xiong Y, Liao WJ, Wan Q (2017) Effect of enriched environment on angiogenesis and neurological functions in rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1655:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.11.001
Gonçalves LV, Herlinger AL, Ferreira TAA, Coitinho JB, Pires RGW, Martins-Silva C (2018) Environmental enrichment cognitive neuroprotection in an experimental model of cerebral ischemia: biochemical and molecular aspects. Behav Brain Res 348:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.04.023
Geng J, Zhang Y, Li S, Li S, Wang J, Wang H, Aa J, Wang G (2019) Metabolomic profiling reveals that reprogramming of cerebral glucose metabolism is involved in ischemic preconditioning-induced neuroprotection in a rodent model of ischemic stroke. J Proteome Res 18:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00339
Wang J, Zhang W, Ma B, Zhang H, Fan Z, Li M, Li X (2021) A novel biscoumarin derivative dephosphorylates ERK and alleviates apoptosis induced by mitochondrial oxidative damage in ischemic stroke mice. Life Sci 264:118499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118499
Mitsios N, Gaffney J, Krupinski J, Mathias R, Wang Q, Hayward S, Rubio F, Kumar P, Kumar S, Slevin M (2007) Expression of signaling molecules associated with apoptosis in human ischemic stroke tissue. Cell Biochem Biophys 47:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1385/cbb:47:1:73
Yi X, Zhou Q, Sui G, Ren G, Tan L, Li J, Bao S (2021) Interactions among variants in P53 apoptotic pathway genes are associated with neurologic deterioration and functional outcome after acute ischemic stroke. Brain Behav 11:e01492. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1492
Modi J, Menzie-Suderam J, Xu H, Trujillo P, Medley K, Marshall ML, Tao R, Prentice H, Wu JY (2020) Mode of action of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) as a novel therapy for stroke in a mouse model. J Biomed Sci 27:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-019-0597-7
Han J, Goldstein LA, Hou W, Gastman BR, Rabinowich H (2010) Regulation of mitochondrial apoptotic events by p53-mediated disruption of complexes between antiapoptotic Bcl-2 members and Bim. J Biol Chem 285:22473–22483. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.081042
Hong LZ, Zhao XY, Zhang HL (2010) p53-mediated neuronal cell death in ischemic brain injury. Neurosci Bull 26:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-010-1111-0
Ng TKS, Ho CSH, Tam WWS, Kua EH, Ho RC (2019) Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci 20:257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020257
Otsuka S, Sakakima H, Sumizono M, Takada S, Terashi T, Yoshida Y (2016) The neuroprotective effects of preconditioning exercise on brain damage and neurotrophic factors after focal brain ischemia in rats. Behav Brain Res 303:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.049
Almeida S, Laço M, Cunha-Oliveira T, Oliveira CR, Rego AC (2009) BDNF regulates BIM expression levels in 3-nitropropionic acid-treated cortical neurons. Neurobiol Dis 35:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.06.006
Grisotto C, Taïlé J, Planesse C, Diotel N, Gonthier MP, Meilhac O, Couret D (2021) High-fat diet aggravates cerebral infarct, hemorrhagic transformation and neuroinflammation in a mouse stroke model. Int J Mol Sci 22:4571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094571
Wu SP, Wang N, Zhao L (2021) Network pharmacology reveals the mechanism of activity of Tongqiao Huoxue Decoction extract against middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Pharmacol 11:572624. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.572624
He WM, Ying-Fu L, Wang H, Peng YP (2019) Delayed treatment of α5 GABAA receptor inverse agonist improves functional recovery by enhancing neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat MCAO model. Sci Rep 9:2287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38750-0
Liao S, Wu JN, Liu RM et al (2020) A novel compound DBZ ameliorates neuroinflammation in LPS-stimulated microglia and ischemic stroke rats: role of Akt (Ser473)/GSK3β(Ser9)-mediated Nrf2 activation. Redox Biol 36:101644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101644
Lu D, Ho ES, Mai H, Zang J, Liu Y, Li Y, Yang B, Ding Y, Tsang CK, Xu A (2020) Identification of blood circular rnas as potential biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci 14:81. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00081
Gao H, Wang D, Wang YL, Mao JP, Jiang S, Yang XL (2021) Pramipexole attenuates 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease by mediating the Nurr1/NF-κB pathway. Mol Biol Rep 48:3079–3087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06343-8
Xian Y, Federspiel JJ, Grau-Sepulveda M, Hernandez AF, Schwamm LH, Bhatt DL, Smith EE, Reeves MJ, Thomas L, Webb L, Bettger JP, Laskowitz DT, Fonarow GC, Peterson ED (2016) Risks and benefits associated with prestroke antiplatelet therapy among patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. JAMA Neurol 73:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3106
Zhang X, Liu JY, Liao WJ, Chen XP (2021) Differential effects of physical and social enriched environment on angiogenesis in male rats after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Hum Neurosci 15:622911. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.622911
Zhang Y, Xu D, Qi H, Yuan Y, Liu H, Yao S, Yuan S, Zhang J (2018) Enriched environment promotes post-stroke neurogenesis through NF-κB-mediated secretion of IL-17A from astrocytes. Brain Res 1687:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.030
Tang Y, Li MY, Zhang X, Jin X, Liu J, Wei PH (2019) Delayed exposure to environmental enrichment improves functional outcome after stroke. J Pharmacol Sci 140:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2019.05.002
Wen L, Liu L, Li J, Tong L, Zhang K, Zhang Q, Li C (2019) NDRG4 protects against cerebral ischemia injury by inhibiting p53-mediated apoptosis. Brain Res Bull 146:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.12.010
Ren D, Tu HC, Kim H, Wang GX, Bean GR, Takeuchi O, Jeffers JR, Zambetti GP, Hsieh JJ, Cheng EH (2010) BID, BIM, and PUMA are essential for activation of the BAX- and BAK-dependent cell death program. Science 330:1390–1393. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1190217
Liao X, Fan Y, Hou J, Chen X, Xu X, Yang Y, Shen J, Mi P, Huang X, Zhang W, Cao H, Hong X, Hu T, Zhan YY (2019) Identification of chaetocin as a potent non-ROS-mediated anticancer drug candidate for gastric cancer. J Cancer 10:3678–3690. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.32803
Cho BB, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2008) Caspase-independent programmed cell death following ischemic stroke. J Invest Surg 21:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941930802029945
Shin BN, Kim DW, Kim IH, Park JH, Ahn JH, Kang IJ, Lee YL, Lee CH, Hwang IK, Kim YM, Ryoo S, Lee TK, Won MH, Lee JC (2019) Down-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 attenuates p53-dependent apoptosis of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons following transient cerebral ischemia. Sci Rep 9:13032. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49623-x
Yi H, Huang G, Zhang K, Liu S, Liu S, Xu W (2018) HSP70 protects rats and hippocampal neurons from central nervous system oxygen toxicity by suppression of NO production and NF-κB activation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 243:770–779. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370218773982
Zhao Z, Sabirzhanov B, Wu J, Faden AI, Stoica BA (2015) Voluntary exercise preconditioning activates multiple antiapoptotic mechanisms and improves neurological recovery after experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 32:1347–1360. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2014.3739
Sabirzhanov B, Stoica BA, Hanscom M, Piao CS, Faden AI (2012) Over-expression of HSP70 attenuates caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways and inhibits neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 123:542–554. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07927.x
Kim JY, Han Y, Lee JE, Yenari MA (2018) The 70-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp70) as a therapeutic target for stroke. Expert Opin Ther Targets 22:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2018.1439477
Zhang X, Xue Z, Zhu S, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Dou J, Zhang J, Ito Y, Guo Z (2022) Diosgenin revealed potential effect against cerebral ischemia reperfusion through HIKESHI/HSP70/NF-κB anti-inflammatory axis. Phytomedicine 99:153991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153991
Seo JH, Park HS, Park SS, Kim CJ, Kim DH, Kim TW (2019) Physical exercise ameliorates psychiatric disorders and cognitive dysfunctions by hippocampal mitochondrial function and neuroplasticity in post-traumatic stress disorder. Exp Neurol 322:113043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113043
Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Grãos MM, Carvalho RF, Carvalho AP, Duarte CB (2005) Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ 12:1329–1343. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401662
Glab JA, Mbogo GW, Puthalakath H (2017) BH3-only proteins in health and disease. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 328:163–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2016.08.005
Chen MR, Dai P, Wang SF, Song SH, Wang HP, Zhao Y, Wang TH, Liu J (2016) BDNF overexpression exhibited bilateral effect on neural behavior in SCT mice associated with AKT signal pathway. Neurochem Res 41:2585–2597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1970-5
Cheng CY, Kao ST, Lee YC (2020) Angelica sinensis extract protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the hippocampus by activating p38 MAPK-mediated p90RSK/p-bad and p90RSK/CREB/BDNF signaling after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 252:112612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.112612
Cirulli F, Berry A, Chiarotti F, Alleva E (2004) Intrahippocampal administration of BDNF in adult rats affects short-term behavioral plasticity in the Morris water maze and performance in the elevated plus-maze. Hippocampus 14:802–807. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.10220
Funding
This study was financially supported by Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20202BABL216034) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82002401, No.81902304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiuping Chen designed and conducted the experiments and wrote the original draft. Xin Zhang analyzed the data and revised the original draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
The protocol was approved by the Animal Experimental Committee of Wuhan University at Wuhan, China (No. WP2020-08059).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Zhang, X. Effect of prior exposure to enriched environment on cellular apoptosis after experimental stroke. Mol Biol Rep 49, 6541–6551 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07494-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07494-y