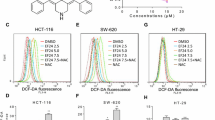
Abstract
Background
We investigated the apoptotic effects of curcumin in the colon carcinoma cell line SW480.
Methods and results
Cells were treated with 40–200 μM curcumin for 24, 48, and 72 h, and the IC50 values were determined for each time interval. BrdU, caspase-3, and TUNEL staining results and the gene expression of FADD, CASP8, and CASP3 were evaluated. Curcumin treatments significantly inhibited cell proliferation and significantly induced apoptosis for 24, 48, and 72 h. The proportion of BrdU-stained cells in the control groups were 58%, 57% and 61% and 28%, 27%, and 30% in the curcumin treatment groups at 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. The proportion of apoptotic cells was 28%, 29%, and 28% in the control groups and 59%, 61%, and 60% in the curcumin treatment groups at 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. As expected, caspase-3 staining also revealed a higher number of apoptotic cells in curcumin treatment groups at 24, 48, and 72 h compared to controls. The proportion of Caspase-3-stained cells in the control groups were 23%, 25%, and 24% and 59%, 60%, and 62% in the curcumin treatment groups at 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. To prove caspase-3 staining results, FADD, CASP8, and CASP3 gene expressions were evaluated by real-time qPCR. Unlike the immunohistochemical results, no statistically significant upregulation was found at 24 and 48 h, while relative gene expressions of FADD, CASP8, and CASP3 was significantly upregulated at 72 h. The expression level increase was 0.88-, 1.19-, and 2.11-fold for FADD, 1.25-, 1.29-, and 1.59-fold for CASP8, and 1.33-, 1.46-, and 3.00-fold for CASP3 at 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively.
Conclusions
These results suggest that curcumin may be a potential protective or treatment agent against colon cancer; however, further studies on curcumin-rich diets and curcumin bioavailability are required.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Favoriti P, Carbone G, Greco M, Pirozzi F, Pirozzi REM, Corcione F (2016) Worldwide burden of colorectal cancer: a review. Updat Surg 68(1):7–11
Fearon ER (2011) Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 6:479–507
Yang SY, Sales KM, Fuller B, Seifalian AM, Winslet MC (2009) Apoptosis and colorectal cancer: implications for therapy. Trends Mol Med 15(5):225–233
Huerta S, Goulet EJ, Livingston EH (2006) Colon cancer and apoptosis. Am J Surg 191(4):517–526
Stoian M, State N, Stoica V, Radulian G (2014) Apoptosis in colorectal cancer. J Med Life 7(2):160
Watson A (2004) Apoptosis and colorectal cancer. Gut 53(11):1701–1709
Graham S, Dayal H, Swanson M, Mittelman A, Wilkinson G (1978) Diet in the epidemiology of cancer of the colon and rectum. J Natl Cancer Inst 61(3):709–714
Slattery M (2000) Diet, lifestyle, and colon cancer. Semin Gastrointest Dis 11:142–146
Durko L, Malecka-Panas E (2014) Lifestyle modifications and colorectal cancer. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep 10(1):45–54
Sharma R, Gescher A, Steward W (2005) Curcumin: the story so far. Eur J Cancer 41(13):1955–1968
Kawamori T, Lubet R, Steele VE, Kelloff GJ, Kaskey RB, Rao CV, Reddy BS (1999) Chemopreventive effect of curcumin, a naturally occurring anti-inflammatory agent, during the promotion/progression stages of colon cancer. Can Res 59(3):597–601
Yalçın AS, Yılmaz AM, Altundağ EM, Koçtürk S (2017) Kurkumin, kuersetin ve çay kateşinlerinin anti-kanser etkileri. Marmara Pharm J 21(1):19–29
Kasi PD, Tamilselvam R, Skalicka-Woźniak K, Nabavi SF, Daglia M, Bishayee A, Pazoki-toroudi H, Nabavi SM (2016) Molecular targets of curcumin for cancer therapy: an updated review. Tumor Biol 37:13017–13028
Gupta SC, Patchva S, Aggarwal BB (2013) Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials. AAPS J 15(1):195–218
Majumdar AP, Banerjee S, Nautiyal J, Patel BB, Patel V, Du J, Yu Y, Elliott AA, Levi E, Sarkar FH (2009) Curcumin synergizes with resveratrol to inhibit colon cancer. Nutr Cancer 61(4):544–553
Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S (2006) Molecular targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 71(10):1397–1421
Hosseini A, Ghorbani A (2015) Cancer therapy with phytochemicals: evidence from clinical studies. Avicenna J Phytomed 5(2):84–97
Hu T, Li Z, Gao C-Y, Cho CH (2016) Mechanisms of drug resistance in colon cancer and its therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol 22(30):6876
Watson JL, Hill R, Yaffe PB, Greenshields A, Walsh M, Lee PW, Giacomantonio CA, Hoskin DW (2010) Curcumin causes superoxide anion production and p53-independent apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett 297(1):1–8
Park J, Conteas CN (2010) Anti-carcinogenic properties of curcumin on colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2(4):169–176
Çelik DA, Gurbuz N, Toğay VA, Özçelik N (2020) Ochratoxin a causes cell cycle arrest in g1 and g1/s phases through p53 in hk-2 cells. Toxicon 180:11–17
Bimonte S, Barbieri A, Leongito M, Piccirillo M, Giudice A, Pivonello C, De Angelis C, Granata V, Palaia R, Izzo F (2016) Curcumin anticancer studies in pancreatic cancer. Nutrients 8(7):433
Johnson JJ, Mukhtar H (2007) Curcumin for chemoprevention of colon cancer. Cancer Lett 255(2):170–181
Prasad CP, Rath G, Mathur S, Bhatnagar D, Ralhan R (2009) Potent growth suppressive activity of curcumin in human breast cancer cells: modulation of wnt/β-catenin signaling. Chem Biol Interact 181(2):263–271
Liu D, Chen Z (2013) The effect of curcumin on breast cancer cells. J Breast Cancer 16(2):133–137
Giladi N, Kazanov D, Shpitz B, Aroch I, Kraus S, Arber N (2010) Curcumin potentiates the pro-apoptotic effects of sulindac sulfone in colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19(sup1):S117–S124
Radhakrishnan VM, Kojs P, Young G, Ramalingam R, Jagadish B, Mash EA, Martinez JD, Ghishan FK, Kiela PR (2014) Ptyr(421) cortactin is overexpressed in colon cancer and is dephosphorylated by curcumin: involvement of non-receptor type 1 protein tyrosine phosphatase (ptpn1). PLoS ONE 9(1):e85796
Watson JL, Hill R, Lee PW, Giacomantonio CA, Hoskin DW (2008) Curcumin induces apoptosis in hct-116 human colon cancer cells in a p21-independent manner. Exp Mol Pathol 84(3):230–233
Su C-C, Lin J-G, Li T-M, Chung J-G, Yang J-S, Ip S-W, Lin W-C, Chen G-W (2006) Curcumin-induced apoptosis of human colon cancer colo 205 cells through the production of ros, ca2+ and the activation of caspase-3. Anticancer Res 26(6B):4379–4389
Rana C, Piplani H, Vaish V, Nehru B, Sanyal S (2015) Downregulation of pi3-k/akt/pten pathway and activation of mitochondrial intrinsic apoptosis by diclofenac and curcumin in colon cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 402(1):225–241
Guo Ld, Chen Xj, Hu Yh, Yu Zj, Wang D, Liu Jz (2013) Curcumin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells by activating the mitochondria apoptotic pathway. Phytother Res 27(3):422–430
Bush JA, Cheung K-JJ, Li G (2001) Curcumin induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells through a fas receptor/caspase-8 pathway independent of p53. Exp Cell Res 271(2):305–314
Xiang L, He B, Liu Q, Hu D, Liao W, Li R, Peng X, Wang Q, Zhao G (2020) Antitumor effects of curcumin on the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of human colorectal carcinoma hct-116 cells. Oncol Rep 44(5):1997–2008
Alinezhad V, Alinezhad H, Ataee R, Ataie A (2017) Utilization of curcumine and nanocurcumine compounds in cancer therapy. Pharm Biomed Res 3(3):1–11
Yang X, Li Z, Wang N, Li L, Song L, He T, Sun L, Wang Z, Wu Q, Luo N (2015) Curcumin-encapsulated polymeric micelles suppress the development of colon cancer in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep 5(1):1–15
Song G, Mao Y, Cai Q, Yao L, Ouyang G, Bao S (2005) Curcumin induces human ht-29 colon adenocarcinoma cell apoptosis by activating p53 and regulating apoptosis-related protein expression. Braz J Med Biol Res 38(12):1791–1798
Cen L, Hutzen B, Ball S, DeAngelis S, Chen CL, Fuchs JR, Li CL, Li PK, Lin JY (2009) New structural analogues of curcumin exhibit potent growth suppressive activity in human colorectal carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-9-99
Ismail NI, Othman I, Abas F, Lajis NH, Naidu R (2020) The curcumin analogue, ms13 (1, 5-bis (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1, 4-pentadiene-3-one), inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in primary and metastatic human colon cancer cells. Molecules 25(17):3798
Park C, Kim GY, Kim GD, Choi BT, Park Y-M, Choi YH (2006) Induction of g2/m arrest and inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 activity by curcumin in human bladder cancer t24 cells. Oncol Rep 15(5):1225–1231
Dou HQ, Shen RH, Tao JX, Huang LC, Shi HZ, Chen H, Wang YX, Wang T (2017) Curcumin suppresses the colon cancer proliferation by inhibiting wnt/beta-catenin pathways via mir-130a. Front Pharmacol 8:877
Tang J, Yang J (2019) Curcumin inhibits viability and promotes apoptosis by modulating mir-17/caspase-9 pathway in colorectal cancer. Trop J Pharm Res 18(12):2531
Funding
This work was supported by Süleyman Demirel University Scientific Research Support Coordination Unit under Grant Number [4693-D2-16].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no any kind of competing interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuz Türel, G., Şahin Calapoğlu, N., Bayram, D. et al. Curcumin induces apoptosis through caspase dependent pathway in human colon carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep 49, 1351–1360 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06965-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06965-y