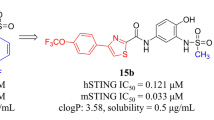
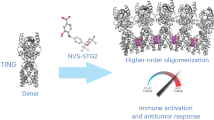
Abstract
STING is an important immune-associated protein that localizes in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Upon being activated by its agonists, STING triggers the IRF and NF-κB pathways, which generates type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines, and ultimately primes the innate immune responses to achieve valid antitumor efficacy. We designed and synthesized a series of benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide derivatives. Through STING-agonistic activity evaluation, compounds 12d and 12e exhibited marginal human STING-activating activities. Western blot analysis demonstrated that both 12d and 12e treatment increased the phosphorylation of the downstream signaling molecules (TBK1 and IRF3) of STING. The proposed binding mode of 12d/12e and STING protein displayed that two canonical hydrogen bonds, a π-π stacking interaction, as well as a π-cation interaction formed between the agonist and the CDN-binding domain of STING protein.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishikawa H, Barber GN (2008) STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 455:674–678
Ager CR, Reilley MJ, Nicholas C, Bartkowiak T, Jaiswal AR, Curran MA (2017) Intratumoral STING activation with T-cell checkpoint modulation generates systemic antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Res 5:676–684
Gao P, Ascano M, Wu Y, Barchet W, Gaffney BL, Zillinger T, Serganov AA, Liu Y, Jones RA, Hartmann G, Tuschl T, Patel DJ (2013) Cyclic [G(2′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. Cell 153:1094–1107
Tsuchiya Y, Jounai N, Takeshita F, Ishii KJ, Mizuguchi K (2016) Ligand-induced ordering of the C-terminal tail primes STING for phosphorylation by TBK1. EBioMedicine 9:87–96
Xie ZQ, Wang Z, Fan FY, Zhou JP, Hu ZX, Wang QX, Wang XY, Zeng QZ, Zhang Y, Qiu JX, Zhou XQ, Xu H, Bai H, Zhan ZS, Ding J, Zhang HB, Duan WH, Yu XK, Geng MY (2022) Structural insights into a shared mechanism of human STING activation by a potent agonist and an autoimmune disease-associated mutation. Cell Discov 8:133
Shang GJ, Zhang CG, Chen ZJ, Bai XC, Zhang XW (2019) Cryo-EM structures of STING reveal its mechanism of activation by cyclic GMP-AMP. Nature 567:389–393
Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 339:786–791
Chen Q, Sun L, Chen ZJ (2016) Regulation and function of the cGAS-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat Immunol 17:1142–1149
Li XD, Wu J, Gao D, Wang H, Sun L, Chen ZJ (2013) Pivotal roles of cGAS-cGAMP signaling in antiviral defense and immune adjuvant effects. Science 341:1390–1394
Barber GN (2014) STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing pathways. Trends Immunol 35:88–93
Takashima K, Takeda Y, Oshiumi H, Shime H, Okabe M, Ikawa M, Matsumoto M, Seya T (2016) STING in tumor and host cells cooperatively work for NK cell-mediated tumor growth retardation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478:1764–1771
Fuertes MB, Kacha AK, Kline J, Woo S-R, Kranz DM, Murphy KM, Gajewski TF (2011) Host type I IFN signals are required for antitumor CD8+ T cell responses through CD8{alpha}+ dendritic cells. J Exp Med 208:2005–2016
Diamond MS, Kinder M, Matsushita H, Mashayekhi M, Dunn GP, Archambault JM, Lee H, Arthur CD, White JM, Kalinke U, Murphy KM, Schreiber RD (2011) Type I interferon is selectively required by dendritic cells for immune rejection of tumors. J Exp Med 208:1989–2003
Zhang H, You Q-D, Xu X-L (2020) Targeting stimulator of interferon genes (STING): a medicinal chemistry perspective. J Med Chem 63:3785–3816
Corrales L, Glickman LH, McWhirter SM, Kanne DB, Sivick KE, Katibah GE, Woo S-R, Lemmens E, Banda T, Leong JJ, Metchette K, Dubensky TW Jr, Gajewski TF (2015) Direct activation of STING in the tumor microenvironment leads to potent and systemic tumor regression and immunity. Cell Rep 11:1018–1030
Duvall JR, Thomas JD, Bukhalid RA, Catcott KC, Bentley KW, Collins SD, Eitas T, Jones BD, Kelleher EW, Lancaster K, Protopopova M, Ray SS, Ter-Ovanesyan E, Xu L, Yang L, Zurita J, Damelin M, Toader D, Lowinger TB (2023) Discovery and optimization of a STING agonist platform for application in antibody drug conjugates. J Med Chem 66:10715–10733
Gomelsky M (2011) cAMP, c-di-GMP, c-di-AMP and now cGMP: bacteria use them all! Mol Microbiol 79:562–565
Ablasser A, Hornung V (2013) DNA sensing unchained. Cell Res 23:585–587
Feng X, Liu D, Li Z, Bian J (2020) Bioactive modulators targeting STING adaptor in cGAS-STING pathway. Drug Discov Today 25:230–237
Shanahan CA, Gaffney BL, Jones RA, Strobel SA (2013) Identification of c-di-GMP derivatives resistant to an EAL domain phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry 52:365–377
Gao P, Zillinger T, Wang W, Ascano M, Dai P, Hartmann G, Tuschl T, Deng L, Barchet W, Patel DJ (2014) Binding-pocket and lid-region substitutions render human STING sensitive to the species-specific drug DMXAA. Cell Rep 8:1668–1676
Pryde DC, Middya S, Banerjee M, Shrivastava R, Basu S, Ghosh R, Yadav DB, Surya A (2020) The discovery of potent small molecule activators of human STING. Eur J Med Chem 209:112869
Lu D, Shang G, Li J, Lu Y, Bai XC, Zhang X (2022) Activation of STING by targeting a pocket in the transmembrane domain. Nature 604:557–562
Pan BS, Perera SA, Piesvaux JA, Presland JP, Schroeder GK, Cumming JN, Trotter BW, Altman MD, Buevich AV, Cash B, Cemerski S, Chang W, Chen Y, Dandliker PJ, Feng G, Haidle A, Henderson T, Jewell J, Kariv I, Knemeyer I, Kipinja J, Lacey BM, Laskey J, Lesburg CA, Liang R, Long BJ, Lu M, Ma Y, Minnihan EC, O’Donnell G, Otte R, Price L, Rakhilina L, Sauvagnat B, Sharma S, Tyagarajan S, Woo H, Wyss DF, Xu S, Bennett DJ, Addona GH (2020) An orally available non-nucleotide STING agonist with antitumor activity. Science 369:eaba6098
Ramanjulu JM, Pesiridis GS, Yang J, Concha N, Singhaus R, Zhang S-Y, Tran J-L, Moore P, Lehmann S, Eberl HC, Muelbaier M, Schneck JL, Clemens J, Adam M, Mehlmann J, Romano J, Morales A, Kang J, Leister L, Graybill TL, Charnley AK, Ye G, Nevins N, Behnia K, Wolf AI, Kasparcova V, Nurse K, Wang L, Puhl AC, Li Y, Klein M, Hopson CB, Guss J, Bantscheff M, Bergamini G, Reilly MA, Lian Y, Duffy KJ, Adams J, Foley KP, Gough PJ, Marquis RW, Smothers J, Hoos A, Bertin J (2018) Design of amidobenzimidazole STING receptor agonists with systemic activity. Nature 564:439–443
Pan B-S, Perera SA, Piesvaux JA, Presland JP, Schroeder GK, Cumming JN, Trotter BW, Altman MD, Buevich AV, Cash B, Cemerski S, Chang W, Chen Y, Dandliker PJ, Feng G, Haidle A, Henderson T, Jewell J, Kariv I, Knemeyer I, Kopinja J, Lacey BM, Laskey J, Lesburg CA, Liang R, Long BJ, Lu M, Ma Y, Minnihan EC, Odonnell G, Otte R, Price L, Rakhilina L, Sauvagnat B, Sharma S, Tyagarajan S, Woo H, Wyss DF, Xu S, Bennett DJ, Addona GH (2020) An orally available non-nucleotide STING agonist with antitumor activity. Science 369:eaba6098
Sali TM, Pryke KM, Abraham J, Liu A, Archer I, Broeckel R, Staverosky JA, Smith JL, Al-Shammari A, Amsler L, Sheridan K, Nilsen A, Streblow DN, DeFilippis VR (2015) Characterization of a novel human-specific STING agonist that elicits antiviral activity against emerging alphaviruses. PLoS Pathog 11:e1005324
Acknowledgements
We thank Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (no. CASIMM0120215010), the Lingang Laboratory (No. LG202103-02-08), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 21ZR1475700) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ synthesized the compounds, performed the molecular docking study, and prepared the manuscript. XW and DZ conducted the biological assays of the compounds, and also prepared the manuscript. ZZ and WD designed and supervised this work and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, R., Wang, X., Zhang, D. et al. Design, synthesis, and STING-agonistic activity of benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide derivatives. Mol Divers (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10736-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10736-1