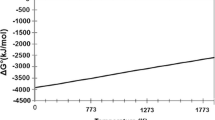
Consumption of rare-earth metal (REM) oxides, such as cerium and lanthanum, is significantly lower than their production. This discrepancy is attributed to the complex extraction of all REMs, where the share of cerium is approximately 40%. This article proposes a method for processing REM oxides for their use as master alloys in ferrous metallurgy products. REMs, in the form of modifiers for steels and alloys, are widely used. However, despite their wide usage, owing to the complexity of the REM production technology, they tend to have a high market value. This study explores the preparation of a cerium carbide (CeC2) master alloy for the modification of steels and cast irons. The proposed method aims to reduce the cost of the alloying process and simultaneously increase the demand for REM oxides. Using a high-temperature synthesis process, CeC2 was obtained for the modification of steel and cast iron. For this purpose, cerium dioxide (CeO2), graphite (C), and ARMCO-iron (Fe) were mixed in a specific percentage ratio by weight: 5.4% C, 19.5% CeO2, and 75.1% Fe. Following this, the reaction mixture was heated in a furnace to a temperature of 1650°C and held for 30 min, with a residual pressure in the furnace of 10–1 mbar. The synthesis was performed in the temperature range of 1300–1650°C, with the highest reaction rate of at a temperature of 1520°C. Both elemental and X-ray diffraction analyses indicated that CeO2 was the end product of the synthesis process. The master alloy does not undergo hydrolysis because CeC2 is synthesized in the liquid phase of iron. It has been established that the technology for producing a cerium carbide alloy involving high-temperature heating in a resistive furnace, enables the production of a material with reproducible properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Laura and B. Bras, “Rare earth metal recycling,” in: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Intern. Symp. on Sustainable Systems and Technology (2011), pp. 1–6.
N. Krishnamurthy, C. K. Gupta, and R. Earth, “Metals and alloys by electrolytic methods, mineral processing and extractive metallurgy review,” Int. J., 22 (4–6), 477–507 (2002); https://doi.org/10.1080/08827500208547426.
D. K. Sahoo, H. Singh, and N. Krishnamurthy, “Current efficiency in electro-winning of lanthanum and cerium metals from molten chloride electrolytes,” Rare Met., 32, 305–311 (2013); https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0060-y.
L. Yanqiang, W. Lijun, and G. Junbo, “Thermodynamic analysis of cerium inclusion formed in spring steel used in fastener of high-speed railway,” Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 3, 720–726 (2013).
W.-C. Jiao, H.-B. Li, H. Feng, Z.-H. Jiang, L.-F. Xia, S.-C. Zhang, H.-C. Zhu, and W. Wu, “Evolutions of micro- and macrostructure by cerium treatment in as-cast AISI M42 high-speed steel,” Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 5 (2020); https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01912-x.
Gd. Zhao, Xm. Zang, Wm. Li, Z. Zhao, and Dj. Li, “Foundry C. Study on primary carbides precipitation in H13 tool steel regarding cooling rate during solidification,” China Foundry, 17, 235–244 (2020); https://doi.org/10.1007/s41230-020-9092-8.
Y. Huang, G. Cheng, M. Zhu, and W. Dai, “Effect of cerium on the behavior of primary carbides in cast H13 steels,” Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 52b, 700–713 (2021); https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-02042-0.
Xy. Qiao, X. Han, Zj He, Z. Zhuang, X. Yang, and Fx. Mao, “Effect of cerium addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast high grade knives steel,” China Iron Steel Res. Inst. Group (2022); https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00798-0.
L. Xiao, Y. Ii-chun, Y. Lin, and G. Xue-zhong, “Effect of Ce on inclusions and impact property of 2Cr13 stainless steel,” J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 17, 59–64 (2010); https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60198-7.
Y.-W. Xu, S.-H. Song, and J.-W. Wang, “Effect of rare earth cerium on the creep properties of modified 9Cr-1Mo heat-resistant steel,” Mater. Lett., 161, 616–619 (2015); https://doi.org/10.3390/met6080187.
S. Zhu, B. Yan, “Effects of Cerium on weld solidification crack sensitivity of 441 ferritic stainless steel,” Metals, 9, 372 (2019); https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030372.
C. Xin and X. Qian, “Reviews on technical routes for chemicals production from carbide acetylene,” Prog. Chem., 6(01), 62–84 (1994). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080858.
C. Liu, R. I. Revilla, Z. Liu, D. Zhanga, X. Lia, and H. Terryn, “Effect of inclusions modified by rare earth elements (Ce, La) on localized marine corrosion in Q460NH weathering steel,” Corros. Sci., 129, 82–90 (2017); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2017.10.001.
H. Liu, P. Fua, H. Liu, Y. Cao, C. Sun, N. Du, and D. Li, “Effects of rare earth elements on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of 718H pre-hardened mold steel,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 50, 245–256 (2020); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.12.035.
L. Chen, X. Ma, L. Wang, and X. Ye, “Effect of rare earth element yttrium addition on microstructures and properties of a 21Cr-11Ni austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel,” Mater. Des., 32(4), 2206–2212 (2010); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.11.022.
Q. Ren, Z. Hu, L. Cheng, and L. Zhang, “Effect of rare earth elements on magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steels,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 560, 169624 (2022); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169624.
Zhang Fei, Zhao Wei, Zhang Wengao, Liao Zexin, Xiang Xinhua, Gou Haojie, Li Zulai, Wei He, Wu Xing, and Shan Quan, “Microstructure, mechanical properties and wear resistance of rare earth doped WC/steel matrix composites: Experimental and calculations,” Ceram. Int., 49, No. 2, 2638–2647 (2023); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.244.
Z. Adabavazeh, W. S. Hwang, and Y. H. Su, “Effect of adding cerium on microstructure and morphology of Ce-based inclusions formed in low-carbon steel,” Sci. Rep., 7, 46503 (2017); https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46503.
L. N. Bartlett and B. R. Avila, “Grain refinement in lightweight advanced high-strength steel castings,” Int. J. Met., 10, No. 4, 401–420 (2016); https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0048-0.
F. Haakonsen, J. K. Solberg, O. S. Klevan, and C. V. D. Eijk, “Grain refinement of austenitic manganese steels,” AISTech 2011 Proceedings, 2, 763–771 (2011).
E. T. Turkdogan, Physical Chemistry of High Temperature Technology [in Russian], Academic Press (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, Vol. 67, No. 10, pp. 69–76, October, 2023. Russian DOI https://doi.org/10.52351/00260827_2023_10_69.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nikulin, I.S., Nikulicheva, T.B., Anosov, N.V. et al. Processing of Rare Earth Metal Oxide for Use as a Master Alloy in the Metallurgical Industry. Metallurgist 67, 1506–1515 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-024-01643-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-024-01643-3