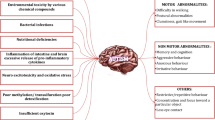
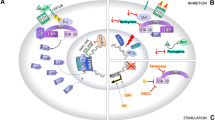
Abstract
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are a family of complex neurodevelopmental disorders, characterized mainly through deficits in social behavior and communication. While the causes giving rise to autistic symptoms are numerous and varied, the treatment options and therapeutic avenues are still severely limited. Nevertheless, a number of signalling pathways have been implicated in the pathogenesis of the disease, and targeting these pathways might provide insight into potential treatments and future strategies. Importantly, alterations in inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction have been noted in the brains of ASD patients, and among the pathways involved in these processes is the Nrf2 cascade. This particular pathway has been hypothesized to be involved in inducing both, inflammatory and anti-inflammatory/neuroprotective effects in the brain, sparking an interest in its use in ASD. Sulforaphane, a sulfur-containing phytochemical present mainly in cruciferous plants like broccoli and cabbage, has shown efficacy in activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway, which in turn brings about a protective effect on neuronal cells, especially against mitochondrial dysfunction. Its efficacy against ASD has not yet been evaluated, and in this paper, we attempt to discuss the therapeutic potential of this agent in the therapy of autism, with special emphasis on the role of the Nrf2 pathway in the disorder.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data has been included.
Code availability
Not Applicable.
References
Balachandar V, Rajagopalan K, Jayaramayya K, Jeevanandam M, Iyer M (2020) Mitochondrial dysfunction: a hidden trigger of autism? Genes Dis 8(5):629–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2020.07.002
Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A, Donato R (2018) Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1865:721–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBAMCR.2018.02.010
Bhandari R, Kaur J, Kaur S, Kuhad A (2021) The Nrf2 pathway in psychiatric disorders: pathophysiological role and potential targeting. Expert Opin Ther Targets 25:115–139. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2021.1887141
Bittker S (2016) Antioxidant sulfur compounds: potential therapies for autism? J Autism 3:3. https://doi.org/10.7243/2054-992X-3-3
Bjørklund G, Meguid NA, El-Bana MA, Tinkov AA, Saad K, Dadar M, Hemimi M, Skalny AV, Hosnedlová B, Kizek R, Osredkar J, Urbina MA, Fabjan T, El-Houfey AA, Kałużna-Czaplińska J, Gątarek P, Chirumbolo S (2020) Oxidative stress in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol Neurobiol 57:2314–2332. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12035-019-01742-2
Brose RD, Shin G, Mcguinness MC, Schneidereith T, Purvis S, Dong GX, Keefer J, Spencer F, Smith KD (2012) Activation of the stress proteome as a mechanism for small molecule therapeutics. Hum Mol Genet 21:4237–4252. https://doi.org/10.1093/HMG/DDS247
Bryan HK, Olayanju A, Goldring CE, Park BK (2013) The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and -independent mechanisms of regulation. Biochem Pharmacol 85(6):705–717
Canning P, Sorrell FJ, Bullock AN (2015) Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med 88:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FREERADBIOMED.2015.05.034
Carpita B, Muti D, Dell’Osso L (2018) Oxidative stress, maternal diabetes, and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3717215
Castejon AM, Spaw JA (2014) Autism and oxidative stress interventions: impact on autistic behavior. Austin J Pharmacol Ther 2(2):1015
Chauhan A, Gu F, Essa MM, Wegiel J, Kaur K, Brown WT, Chauhan V (2011) Brain region-specific deficit in mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes in children with autism. J Neurochem 117(2):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07189.x
Chung L, Bey AL, Jiang YH (2012) Synaptic plasticity in mouse models of autism spectrum disorders. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 16(6):369–78. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.6.369
Fahey JW, Talalay P (1999) Antioxidant functions of sulforaphane: a potent inducer of phase II detoxication enzymes. Food Chem Toxicol 37:973–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-6915(99)00082-4
Frye Re, Rossignol DA (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction can connect the diverse medical symptoms associated with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Pediatr Res 2011 69(5.2):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1203/pdr.0b013e318212f16b
Gaona-Gaona L, Molina-Jijón E, Tapia E, Zazueta C, Hernández-Pando R, Calderón-Oliver M, Zarco-Márquez G, Pinzón E, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2011) Protective effect of sulforaphane pretreatment against cisplatin-induced liver and mitochondrial oxidant damage in rats. Toxicology 286:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOX.2011.04.014
Giulivi C, Zhang YF, Omanska-Klusek A, Ross-Inta C, Wong S, Hertz-Picciotto I, Tassone F, Pessah IN (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism. JAMA 303(21):2389–2396. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.1706
Goodfellow MJ, Borcar A, Proctor JL, Greco T, Rosenthal RE, Fiskum G (2020) Transcriptional activation of antioxidant gene expression by Nrf2 protects against mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal death associated with acute and chronic neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol 328. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EXPNEUROL.2020.113247
Gordon A, Geschwind DH (2020) Human in vitro models for understanding mechanisms of autism spectrum disorder. Mol Autism 11(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-020-00332-7
Gu Y, Dee CM (2011) Interaction of free radicals, matrix metalloproteinases and caveolin-1 impacts blood-brain barrier permeability. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 3:1216. https://doi.org/10.2741/222
Guerrero-Beltrán CE, Calderón-Oliver M, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Chirino YI (2012) Protective effect of sulforaphane against oxidative stress: recent advances. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:503–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ETP.2010.11.005
Haas RH, Parikh S, Falk MJ, Saneto RP, Wolf NI, Darin N, Cohen BH (2007) Mitochondrial disease: a practical approach for primary care physicians. Pediatrics 120:1326–1333. https://doi.org/10.1542/PEDS.2007-0391
Indika NR, Deutz NEP, Engelen MPKJ, Peiris H, Wijetunge S, Perera R (2021) Sulfur amino acid metabolism and related metabotypes of autism spectrum disorder: a review of biochemical evidence for a hypothesis. Biochimie 184:143–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2021.02.018
James SJ, Rose S, Melnyk S, Jernigan S, Blossom S, Pavliv O, Gaylor DW (2009) Cellular and mitochondrial glutathione redox imbalance in lymphoblastoid cells derived from children with autism. FASEB J 23(8):2374-83. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.08-128926
Jo H, Schieve LA, Rice CE, Yeargin-Allsopp M, Tian LH, Blumberg SJ, Kogan MD, Boyle CA (2015) Age at Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnosis by race, ethnicity, and primary household language among children with special health care needs, United States, 2009–2010. Matern Child Health J 19:1687–1697. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10995-015-1683-4
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV.IMMUNOL.18.1.621
Kensler TW, Egner PA, Agyeman AS, Visvanathan K, Groopman JD, Chen J-G, Chen T-Y, Fahey JW, Talalay P (2013) Keap1-nrf2 signaling: a target for cancer prevention by sulforaphane. Top Curr Chem 329:163–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/128_2012_339
Kobayashi M, Li L, Iwamoto N, Nakajima-Takagi Y, Kaneko H, Nakayama Y, Eguchi M, Wada Y, Kumagai Y, Yamamoto M (2009) The antioxidant defense system Keap1-Nrf2 comprises a multiple sensing mechanism for responding to a wide range of chemical compounds. Mol Cell Biol 29:493. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01080-08
Lee DF, Kuo HP, Liu M, Chou CK, Xia W, Du Y et al (2009) KEAP1 E3 ligase-mediated downregulation of NF-κB signaling by targeting IKKβ. Mol Cell 36(1):131–140
Liao X, Li Y (2020) Nuclear factor Kappa B in Autism Spectrum Disorder: a systematic review. Pharmacol Res 159. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHRS.2020.104918
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/SIGTRANS.2017.23
Lord C, Elsabbagh M, Baird G, Veenstra-Vanderweele J (2018) Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet 392:508–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31129-2
Mandic-Maravic V, Mitkovic-Voncina M, Pljesa-Ercegovac M, Savic-Radojevic A, Djordjevic M, Pekmezovic T, Grujicic R, Ercegovac M, Simic T, Lecic-Tosevski D, Pejovic-Milovancevic M (2019) Autism Spectrum Disorders and perinatal complications-is oxidative stress the connection? Front Psychiatry 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPSYT.2019.00675
Maraslioglu M, Weber R, Korff S, Blattner C, Nauck C, Henrich D et al (2013) Activation of NF-κB after chronic ethanol intake and haemorrhagic shock/resuscitation in mice. Br J Pharmacol 170(3):506–518
Mazzoli R, Pessione E (2016) The neuro-endocrinological role of microbial glutamate and GABA signaling. Front Microbiol 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2016.01934
McGuinness G, Kim Y (2020) Sulforaphane treatment for autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. EXCLI J 19:892–903. https://doi.org/10.17179/EXCLI2020-2487
Minshew NJ, Goldstein G, Dombrowski SM, Panchalingam K, Pettegrew JW (1993) A preliminary 31P MRS study of autism: evidence for undersynthesis and increased degradation of brain membranes. Biol Psychiatry 33(11–12):762–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3223(93)90017-8
Naik US, Gangadharan C, Abbagani K, Nagalla B, Dasari N, Manna SK (2011) A study of nuclear transcription factor Kappa-B in childhood autism. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19488. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019488
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2022) PubChem compound summary for CID 6602383, glucoraphanin. Retrieved December 10, 2022 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Glucoraphanin
O’Mealey GB, Berry WL, Plafker SM (2017) Sulforaphane is a Nrf2-independent inhibitor of mitochondrial fission. Redox Biol 11:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.REDOX.2016.11.007
Paladino S, Conte A, Caggiano R, Pierantoni GM, Faraonio R (2018) Nrf2 pathway in age-related neurological disorders: insights into MicroRNAs. Cell Physiol Biochem 47:1951–1976. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491465
Pangrazzi L, Balasco L, Bozzi Y (2020) Oxidative stress and immune system dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int J Mol Sci 21:3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21093293
Parker W, Hornik CD, Bilbo S, Holzknecht ZE, Gentry L, Rao R, Lin SS, Herbert MR, Nevison CD (2017) The role of oxidative stress, inflammation and acetaminophen exposure from birth to early childhood in the induction of autism. J Int Med Res 45:407–438. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060517693423
Perrotta G (2019) Autism spectrum disorder: definition, contexts, neural correlates and clinical strategies. Neurol Neurother Open Access J 4(2). https://doi.org/10.23880/nnoaj-16000136
Roberts RA, Laskin DL, Smith CV, Robertson FM, Allen EMG, Doorn JA, Slikker W (2009) Nitrative and oxidative stress in toxicology and disease. Toxicol Sci 112:4–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/TOXSCI/KFP179
Rossignol DA, Frye RE (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 17:290–314. https://doi.org/10.1038/MP.2010.136
Ruhee RT, Suzuki K (2020) The integrative role of sulforaphane in preventing inflammation, oxidative stress and fatigue: a review of a potential protective phytochemical. Antioxidants 9(6):1–13
Russo SJ, Wilkinson MB, Mazei-Robison MS, Dietz DM, Maze I, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Graham A, Birnbaum SG, Green TQ, Robison B, Lesselyong A, Perrotti LI, Bolaños CA, Kumar A, Clark MS, Neumaier JF, Neve RL, Bhakar AL, Barker PA, Nestler EJ (2009) Nuclear factor kB signaling regulates neuronal morphology and cocaine reward. J Neurosci 29:3529–3537. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6173-08.2009
Sedlak TW, Nucifora LG, Koga M, Shaffer LS, Higgs C, Tanaka T, Wang AM, Coughlin JM, Barker PB, Fahey JW, Sawa A (2018) Sulforaphane augments glutathione and influences brain metabolites in human subjects: a clinical pilot study. Mol Neuropsychiatry 3:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487639
Shih R, Wang CY, Yang CM (2015) NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front Mol Neurosci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNMOL.2015.00077/PDF
Shiina A, Kanahara N, Sasaki T, Oda Y, Hashimoto T, Hasegawa T, Yoshida T, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2015) An open study of sulforaphane-rich broccoli sprout extract in patients with schizophrenia. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 13:62–67. https://doi.org/10.9758/CPN.2015.13.1.62
Sivandzade F, Prasad S, Bhalerao A, Cucullo L (2019) NRF2 and NF-қB interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol 21. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.REDOX.2018.11.017
Socała K, Nieoczym D, Kowalczuk-Vasilev E, Wyska E, Wlaź P (2017) Increased seizure susceptibility and other toxicity symptoms following acute sulforaphane treatment in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 326:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TAAP.2017.04.010
Srikantha P, Hasan Mohajeri M (2019) The possible role of the microbiota-gut-brain-axis in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS20092115
Sun Y, Yang T, Mao L, Zhang F (2017) Sulforaphane protects against brain diseases: roles of cytoprotective enzymes. Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis Stroke 4. https://doi.org/10.26420/AUSTINJCEREBROVASCDISSTROKE.2017.1054
Tang G, Gutierrez Rios P, Kuo SH, Akman HO, Rosoklija G, Tanji K, Dwork A, Schon EA, DiMauro S, Goldman J, Sulzer D (2013) Mitochondrial abnormalities in temporal lobe of autistic brain. Neurobiol Dis 54:349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NBD.2013.01.006
Theoharides TC, Tsilioni I, Patel AB, Doyle R (2016) Atopic diseases and inflammation of the brain in the pathogenesis of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Transl Psychiatry 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/TP.2016.77
Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M (2009) Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 27:693–733. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV.IMMUNOL.021908.132641
Vomhof-DeKrey EE, Picklo MJ (2012) The Nrf2-antioxidant response element pathway: a target for regulating energy metabolism. J Nutr Biochem 23(10):1201–1206
Weissman JR, Kelley RI, Bauman ML, Cohen BH, Murray KF, Mitchell RL, Kern RL, Natowicz MR (2008) Mitochondrial disease in Autism Spectrum Disorder patients. Cohort Anal 3(11):e3815. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003815
Yagishita Y, Fahey JW, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Kensler TW (2019) Broccoli or sulforaphane: is it the source or dose that matters? Molecules 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES24193593
Yang J, Fu X, Liao X, Li Y (2020) Nrf2 activators as dietary phytochemicals against oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorders: a systematic review. Front Psychiatry 11:1299. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPSYT.2020.561998/BIBTEX
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ranjana Bhandari: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-Review, Editing & Visualization. Ali Shah & Manasi Varma: Literature Search, data collection & Writing-Original Draft. Ranjana Bhandari : Final Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the contributing authors have given consent for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, A., Varma, M. & Bhandari, R. Exploring sulforaphane as neurotherapeutic: targeting Nrf2-Keap & Nf-Kb pathway crosstalk in ASD. Metab Brain Dis 39, 373–385 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01224-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01224-4