Abstract
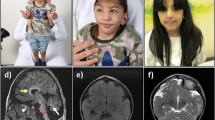
Sandhoff disease is a rare neurodegenerative and autosomal recessive disorder, which is characterized by a defect in ganglioside metabolism. Also, it is caused by mutations in the HEXB gene for the β-subunit isoform 1 of β-N-acetyl hexosaminidase. In the present study, an Iranian 14- month -old girl with 8- month history of unsteady walking and involuntary movements was described. In this regard, biochemical testing showed some defects in the normal activity of beta-hexosaminidase protein. Following sequencing of HEXB gene, a homozygous c.833C > T mutation was identified in the patient’s genome. After recognition of p.A278V, several different in silico methods were used to assess the mutant protein stability, ranging from mutation prediction methods to ligand docking. The p.A278V mutation might be disruptive because of changing the three-dimensional folding at the end of the 5th alpha helix. According to the medical prognosis, in silico and structural analyses, it was predicted to be disease cause.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The activity of β-Hexosaminidase was measured via dried blood spots (DBSs) on filter.
Genomic DNA extraction using FlexiGene DNA Kit (QIAGEN).
Sequencing on an ABI 3700 sequencer (Kosar Company, Tehran).
The sequence alteration was assessed by the in-silico prediction algorithms SIFT and Polyphen-2.
The structures of Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta using UCSF Chimera 1.8.1, online Swiss-Prot server, RaptorX.
protein–ligand docking was calculated from Hex 8.0.0 software.
Abbreviations
- GDL:
-
2-Acetamido-2-Deoxy-D-Glucono-1,5-Lactone
- NAG:
-
N-acetyl-d-lucosamine
- EDO:
-
1,2-ethanediol
- MRI:
-
Brain magnetic resonance imaging
- MD:
-
Molecular Dynamics
- DBSs:
-
Dried blood spots
- PDB:
-
Protein databank
References
Abiri M, Talebi S, Uitto J, Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, Shirzad T, Salehpour S, Zeinali S (2016) Co-existence of phenylketonuria either with maple syrup urine disease or Sandhoff disease in two patients from Iran: emphasizing the role of consanguinity. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 29:1215–1219. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2016-0096
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations a. Nat Publ Gr 7:248–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0410-248
Apweiler R, Bairoch A, Bougueleret L et al (2009) The universal protein resource (UniProt) 2009. Nucleic Acids Res 37:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn664
Aryan H, Aryani O, Banihashemi K, Zaman T, Houshmand M (2012) Novel mutations in sandhoff disease: a molecular analysis among Iranian cohort of infantile patients. Iran J Public Health 41:112–118
Banerjee P, Siciliano L, Oliveri D, McCabe NR, Boyers MJ, Horwitz AL, Li SC, Dawson G (1991) Molecular basis of an adult form of beta-hexosaminidase B deficiency with motor neuron disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:108–115
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.235
Chamoles NA, Blanco M, Gaggioli D, Casentini C (2002) Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases: enzymatic diagnosis in dried blood spots on filter paper: retrospective diagnoses in newborn-screening cards. Clin Chim Acta 318:133–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-8981(02)00002-5
Ebrahimzadeh-Vesal R, Hosseini S, Moghaddassian M, Abbaszadegan MR (2017) Identification of novel missense HEXB gene mutation in Iranian-child with juvenile Sandhoff disease. Meta Gene 12:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mgene.2017.01.008
Gaignard P, Fagart J, Niemir N, Puech JP, Azouguene E, Dussau J, Caillaud C (2013) Characterization of seven novel mutations on the HEXB gene in French Sandhoff patients. Gene 512:521–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.09.124
Gomez-Lira M, Perusi C, Brutti N, Farnetani MA, Margollicci MA, Rizzuto N, Pignatti PF, Salviati A (1995) A 48-bp insertion between exon 13 and 14 of the HEXB gene causes infantile-onset Sandhoff disease. Hum Mutat 6:260–262. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.1380060313
Gort L, De Olano N, Macías-vidal J, Josep M (2012) GM2 gangliosidoses in Spain : analysis of the HEXA and HEXB genes in 34 Tay – Sachs and 14 Sandhoff patients ☆. Gene 506:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.06.080
Hou Y, McInnes B, Hinek A, Karpati G, Mahuran D (1998) A Pro504 → Ser substitution in the β-subunit of β-hexosaminidase a inhibits α-subunit hydrolysis of G(M2) ganglioside, resulting in chronic Sandhoff disease. J Biol Chem 273:21386–21392. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.33.21386
Hou Y, Vocadlo D, Withers S, Mahuran D (2000) Role of Arg 211 in the active site of human -Hexosaminidase B †. Society 39:6219–6227
Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A (2006) Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:821–834. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2132
Kumar P (2009) Henikoff S, Ng PC. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm 4:1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.86
Lakshmi S, Anitha G, Vinoth S (2015) A rare case of Sandhoff disease: two in the same family. Int J Contemp Pediatr 2:42. https://doi.org/10.5455/2349-3291.ijcp20150210
Leslie EM, Deeley RG, Cole SPC (2005) Multidrug resistance proteins: role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204:216–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.10.012
Lindgreen A (2004) Juvenile Sandhoff disease - nine new cases and a review of the literature. J Bus Ethics 51:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1023/B
Maier T, Strater N, Schuette CG, Klingenstein R, Sandhoff K, Saenger W (2003) The X-ray crystal structure of human β-hexosaminidase B provides new insights into Sandhoff disease. J Mol Biol 328:669–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00311-5
Mohebbi A, Mohammadi S, Memarian A (2016) Prediction of HBF-0259 interactions with hepatitis B virus receptors and surface antigen secretory factors. VirusDisease 27:234–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-016-0333-9
Neote K, Mcinnes B, Mahuran DJ, Gravel RA Structure and Distribution of an Alu-type Deletion Mutation in Sandhoff Disease
Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL (2006) How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:993–996. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2199
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF chimera - a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Rodrigues CHM, Pires DEV, Ascher DB (2018) DynaMut: predicting the impact of mutations on protein conformation, flexibility and stability. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W350–W355. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky300
Rubin M, Karpati G, Wolfe LS, Carpenter S, Klavins MH, Mahuran DJ (1988) Adult onset motor neuronopathy in the juvenile type of hexosaminidase a and B deficiency. J Neurol Sci 87:103–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510X(88)90058-5
Sangalli MGA, Mottes M, Perusi C, et al (1995) A common hexosaminidase gene mutation in adult Sandhoff disease patients. 417–418
Tavasoli AR, Parvaneh N, Ashrafi MR, Rezaei Z, Zschocke J, Rostami P (2018) Clinical presentation and outcome in infantile Sandhoff disease: a case series of 25 patients from Iranian neurometabolic bioregistry with five novel mutations Dr. Segolene Ayme. Orphanet J Rare Dis 13:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0876-5
Wang SZ, Cachón-González MB, Stein PE, Lachmann RH, Corry PC, Wraith JE, Cox TM (2008) A novel HEXB mutation and its structural effects in juvenile Sandhoff disease. Mol Genet Metab 95:236–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.08.007
Yamada K, Takado Y, Kato YS, Yamada Y, Ishiguro H, Wakamatsu N (2013) Characterization of the mutant β-subunit of β-hexosaminidase for dimer formation responsible for the adult form of Sandhoff disease with the motor neuron disease phenotype. J Biochem 153:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvs131
Yasui N, Takaoka Y, Nishio H, Nurputra DK, Sekiguchi K, Hamaguchi H, Kowa H, Maeda E, Sugano A, Miura K, Sakaeda T, Kanda F, Toda T (2013) Molecular pathology of Sandhoff disease with p.Arg505Gln in HEXB: application of simulation analysis. J Hum Genet 58:611–617. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2013.68
Yoshizawa T, Kohno Y, Nissato S, Shoji S (2002) Compound heterozygosity with two novel mutations in the HEXB gene produces adult Sandhoff disease presenting as a motor neuron disease phenotype. J Neurol Sci 195:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-510X(02)00007-2
Yun Y, Lee S (2015) A case Refort of Sandhoff disease. Iran J Public Health 21:281–285. https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2005.19.1.68
Yun Y, Lee S (2005) A case refort of Sandhoff disease. Korean J Ophthalmol 19:68–72. https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2005.19.1.68
Zampieri S, Cattarossi S, Maria A et al (2012) Sequence and copy number analyses of HEXB gene in patients affected by Sandhoff disease : functional characterization of 9 novel sequence variants. 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041516
Zarghooni M, Bukovac S, Tropak M, Callahan J, Mahuran D (2004) An α-subunit loop structure is required for GM2 activator protein binding by β-hexosaminidase a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324:1048–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.159
Zhang W, Zeng H, Huang Y, et al (2016) Clinical , biochemical and molecular analysis of five Chinese patients with Sandhoff disease. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9819-9
Acknowledgements
We thank the parent s patient and also thank all physicians who supported us via examination, provision of blood samples and etc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z Rahmani was the major contributor in writing the manuscript, involved in protein modelling and revision response. A Banisadr performed protein modeling, structure alignment and ligand docking, took part in writing the manuscript and revision response. V Ghodsinezhad investigated the phylogenetic background and performed in silico analysis, took part in writing the manuscript. M Dibaj help to find similar works and gave hand to justify the final version of manuscript. O Aryani diagnosed and interpreted the patient data regarding the sandhoff disease. Also supervised the whole project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
We have taken informed consent from the patient’s parent.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Consent for publication
The participant has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Scientific style
We have not used any special drug or pesticide.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Dr. Omid Aryani has recently passed away. This article is dedicated to him.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmani, Z., Banisadr, A., Ghodsinezhad, V. et al. P. Ala278Val mutation might cause a pathogenic defect in HEXB folding leading to the Sandhoff disease. Metab Brain Dis 37, 2669–2675 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00669-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00669-9