Abstract
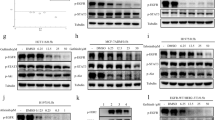
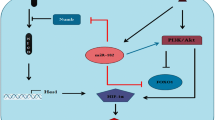
The epidermal growth factor receptor 1 (EGFR) plays a crucial role in the progression of various malignant tumors and is considered a potential target for treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). However, the effectiveness of representative tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) used in EGFR-targeted therapy is limited in TNBC patients. In our study, we observed that the TNBC cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 exhibited resistance to Gefitinib. Treatment with Gefitinib caused an upregulation of Fascin-1 (FSCN1) protein expression and a downregulation of miR-221-3p in these cell lines. However, sensitivity to Gefitinib was significantly improved in both cell lines with either inhibition of FSCN1 expression or overexpression of miR-221-3p. Our luciferase reporter assay confirmed that FSCN1 is a target of miR-221-3p. Moreover, Gefitinib treatment resulted in an upregulation of phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-STAT3) in MDA-MB-231 cells. Using Stattic, a small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3, we observed a significant enhancement in the inhibitory effect of Gefitinib on the growth, migration, and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. Additionally, Stattic treatment upregulated miR-221-3p expression and downregulated FSCN1 mRNA and protein expression. A strong positive correlation was noted between the expression of STAT3 and FSCN1 in breast cancer tissues. Furthermore, patients with high expression levels of both STAT3 and FSCN1 had a worse prognosis. Our findings suggest that elevated FSCN1 expression is linked to primary resistance to EGFR TKIs in TNBC. Moreover, we propose that STAT3 regulates the expression of miR-221-3p/FSCN1 and therefore modulates resistance to EGFR TKI therapy in TNBC. Combining EGFR TKI therapy with inhibition of FSCN1 or STAT3 may offer a promising new therapeutic option for TNBC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the datasets used and/or analyzed in the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–49
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A (2023) Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 73:17–48
Boyle P (2012) Triple-negative breast cancer: epidemiological considerations and recommendations. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 6):vi7–vi12
Li CY, Wang P, Zhang S, Liu Y, Zhang J (2013) Clinicopathological features and prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi [Chin J Oncol] 35:463–467
Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V (2007) Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer registry. Cancer 109:1721–1728
Parise CA, Bauer KR, Brown MM, Caggiano V (2009) Breast cancer subtypes as defined by the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) among women with invasive breast cancer in California, 1999–2004. Breast J 15:593–602
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, Burgess AW (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res 284:31–53
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Lee JT, Chang F, Bertrand FE, Navolanic PM, Terrian DM, Franklin RA, D’Assoro AB, Salisbury JL, Mazzarino MC et al (2006) Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv Enzyme Regul 46:249–279
Park HS, Jang MH, Kim EJ, Kim HJ, Lee HJ, Kim YJ, Kim JH, Kang E, Kim SW, Kim IA, Park SY (2014) High EGFR gene copy number predicts poor outcome in triple-negative breast cancer. Modern Pathol 27:1212–22
Wang CQ, Li Y, Huang BF, Zhao YM, Yuan H, Guo D, Su CM, Hu GN, Wang Q, Long T, Wang Y, Tang CH et al (2017) EGFR conjunct FSCN1 as a novel therapeutic strategy in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Rep 7:15654
Corkery B, Crown J, Clynes M, O’Donovan N (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol 20:862–867
Lev S (2020) Targeted therapy and drug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer: the EGFR axis. Biochem Soc Trans 48:657–665
Baselga J, Albanell J, Ruiz A, Lluch A, Gascon P, Guillem V, Gonzalez S, Sauleda S, Marimon I, Tabernero JM, Koehler MT, Rojo F (2005) Phase II and tumor pharmacodynamic study of gefitinib in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:5323–5333
von Minckwitz G, Jonat W, Fasching P, du Bois A, Kleeberg U, Luck HJ, Kettner E, Hilfrich J, Eiermann W, Torode J, Schneeweiss A (2005) A multicentre phase II study on gefitinib in taxane- and anthracycline-pretreated metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 89:165–172
Carey LA, Rugo HS, Marcom PK, Mayer EL, Esteva FJ, Ma CX, Liu MC, Storniolo AM, Rimawi MF, Forero-Torres A, Wolff AC, Hobday TJ et al (2012) TBCRC 001: randomized phase II study of cetuximab in combination with carboplatin in stage IV triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 30:2615–2623
Baselga J, Gomez P, Greil R, Braga S, Climent MA, Wardley AM, Kaufman B, Stemmer SM, Pego A, Chan A, Goeminne JC, Graas MP et al (2013) Randomized phase II study of the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:2586–2592
Grothey A, Hashizume R, Ji H, Tubb BE, Patrick CW Jr, Yu D, Mooney EE, McCrea PD (2000) C-erbB-2/ HER-2 upregulates fascin, an actin-bundling protein associated with cell motility, in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 19:4864–4875
Kim SJ, Choi IJ, Cheong TC, Lee SJ, Lotan R, Park SH, Chun KH (2010) Galectin-3 increases gastric cancer cell motility by up-regulating fascin-1 expression. Gastroenterology 138(1035–45):e1-2
Wu D, Chen L, Liao W, Ding Y, Zhang Q, Li Z, Liu L (2010) Fascin1 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and correlates with tumor invasion. Ann Oncol 21:589–596
Zhao J, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Tian F, Ma N, Liu T, Gu Z, Wang Y (2010) Upregulated fascin1 in non-small cell lung cancer promotes the migration and invasiveness, but not proliferation. Cancer Lett 290:238–247
Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, Fujimura L, Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Matsubara H (2010) miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 127:2804–2814
Tan VY, Lewis SJ, Adams JC, Martin RM (2013) Association of fascin-1 with mortality, disease progression and metastasis in carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 11:52
Yoder BJ, Tso E, Skacel M, Pettay J, Tarr S, Budd T, Tubbs RR, Adams JC, Hicks DG (2005) The expression of fascin, an actin-bundling motility protein, correlates with hormone receptor-negative breast cancer and a more aggressive clinical course. Clin Cancer Res 11:186–192
Esnakula AK, Ricks-Santi L, Kwagyan J, Kanaan YM, DeWitty RL, Wilson LL, Gold B, Frederick WA, Naab TJ (2014) Strong association of fascin expression with triple negative breast cancer and basal-like phenotype in African-American women. J Clin Pathol 67:153–160
Wang CQ, Tang CH, Chang HT, Li XN, Zhao YM, Su CM, Hu GN, Zhang T, Sun XX, Zeng Y, Du Z, Wang Y et al (2016) Fascin-1 as a novel diagnostic marker of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Med 5:1983–1988
Takabatake D, Fujita T, Shien T, Kawasaki K, Taira N, Yoshitomi S, Takahashi H, Ishibe Y, Ogasawara Y, Doihara H (2007) Tumor inhibitory effect of gefitinib (ZD1839, Iressa) and taxane combination therapy in EGFR-overexpressing breast cancer cell lines (MCF7/ADR, MDA-MB-231). Int J Cancer 120:181–188
Yamasaki F, Zhang D, Bartholomeusz C, Sudo T, Hortobagyi GN, Kurisu K, Ueno NT (2007) Sensitivity of breast cancer cells to erlotinib depends on cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activity. Mol Cancer Ther 6:2168–2177
Lakhani SREI, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ (2012) WHO classification of tumours of the breast, 4th edn. IARC Press, Lyon
Yang WT, Bu H (2020) Updates in the 5(th) edition of WHO classification of tumours of the breast. Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi = Chin J Pathol 49:400–5
Chen J, Yao Y, Gong C, Yu F, Su S, Chen J, Liu B, Deng H, Wang F, Lin L, Yao H, Su F et al (2011) CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer Cell 19:541–555
Li X, Liu X, Xu W, Zhou P, Gao P, Jiang S, Lobie PE, Zhu T (2013) c-MYC-regulated miR-23a/24-2/27a cluster promotes mammary carcinoma cell invasion and hepatic metastasis by targeting Sprouty2. J Biol Chem 288:18121–18133
Wang CQ, Wang Y, Huang BF, Tang CH, Du Z, Zeng Y, Wang Q, Shao JK, Jin LL (2020) High expression of both resistin and fascin-1 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Biomed Res Int 2020:8753175
Zeng Y, Tang CH, Wang Y, Lu HJ, Huang BF, Wang Q, Shao JK, Jin LL, Wang CQ, Teng LS (2020) Combined high resistin and EGFR expression predicts a poor prognosis in breast cancer. Biomed Res Int 2020:8835398
Wang CQ, Tang CH, Wang Y, Huang BF, Hu GN, Wang Q, Shao JK (2022) Upregulated WTAP expression appears to both promote breast cancer growth and inhibit lymph node metastasis. Sci Rep 12:1023
Li H, Duhachek-Muggy S, Qi Y, Hong Y, Behbod F, Zolkiewska A (2012) An essential role of metalloprotease-disintegrin ADAM12 in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135:759–769
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P, Narod SA (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 13:4429–4434
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, Harris L, Hait W, Toppmeyer D (2006) Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:5652–5657
Yoneda K, Imanishi N, Ichiki Y, Tanaka F (2019) Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR-mutations. J UOEH 41:153–163
Wu SG, Shih JY (2018) Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 17:38
van Cruijsen H, Giaccone G, Hoekman K (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor and angiogenesis: opportunities for combined anticancer strategies. Int J Cancer 117:883–888
Zhou Y, Wang S, Wu W, Ling J, Li H, Jia Q, Zheng J, Zheng X, Yu R, Wu Q, Shi Y, Lieftink C et al (2023) Sustained activation of EGFR-ERK1/2 signaling limits the response to tigecycline-induced mitochondrial respiratory deficiency in liver cancer. EBioMedicine 87:104397
He B, Zhao Z, Cai Q, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Shi S, Xie H, Peng X, Yin W, Tao Y, Wang X (2020) miRNA-based biomarkers, therapies, and resistance in Cancer. Int J Biol Sci 16:2628–2647
Budakoti M, Panwar AS, Molpa D, Singh RK, Busselberg D, Mishra AP, Coutinho HDM, Nigam M (2021) Micro-RNA: the darkhorse of cancer. Cell Signal 83:109995
Fridrichova I, Zmetakova I (2019) MicroRNAs contribute to breast cancer invasiveness. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111361
Koleckova M, Janikova M, Kolar Z (2018) MicroRNAs in triple-negative breast cancer. Neoplasma 65:1–13
Wang L, Zhou Y, Jiang L, Lu L, Dai T, Li A, Chen Y, Zhang L (2021) CircWAC induces chemotherapeutic resistance in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting miR-142, upregulating WWP1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cancer 20:43
Li Y, Liang Y, Sang Y, Song X, Zhang H, Liu Y, Jiang L, Yang Q (2018) MiR-770 suppresses the chemo-resistance and metastasis of triple negative breast cancer via direct targeting of STMN1. Cell Death Dis 9:14
Han M, Hu J, Lu P, Cao H, Yu C, Li X, Qian X, Yang X, Yang Y, Han N, Dou D, Zhang F et al (2020) Exosome-transmitted miR-567 reverses trastuzumab resistance by inhibiting ATG5 in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 11:43
Jang JY, Kim YG, Nam SJ, Keam B, Kim TM, Jeon YK, Kim CW (2016) Targeting adenine nucleotide translocase-2 (ANT2) to overcome resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 15:1387–1396
Chen JC, Su YH, Chiu CF, Chang YW, Yu YH, Tseng CF, Chen HA, Su JL (2014) Suppression of dicer increases sensitivity to gefitinib in human lung cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol 21(Suppl 4):S555–S563
Du J, Wang L, Li C, Yang H, Li Y, Hu H, Li H, Zhang Z (2016) MicroRNA-221 targets PTEN to reduce the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to gefitinib through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Tumour Biol 37:3939–3947
Banerjee K, Resat H (2016) Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: a review. Int J Cancer 138:2570–2578
Li Y, Wang Y, Shi Z, Liu J, Zheng S, Yang J, Liu Y, Yang Y, Chang F, Yu W (2019) Clinicopathological and prognostic role of STAT3/p-STAT3 in breast cancer patients in China: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 9:11243
Jiang L, Ren L, Chen H, Pan J, Zhang Z, Kuang X, Chen X, Bao W, Lin C, Zhou Z, Huang D, Yang J et al (2020) NCAPG confers trastuzumab resistance via activating SRC/STAT3 signaling pathway in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 11:547
Shou J, You L, Yao J, Xie J, Jing J, Jing Z, Jiang L, Sui X, Pan H, Han W (2016) Cyclosporine A sensitizes human non-small cell lung cancer cells to gefitinib through inhibition of STAT3. Cancer Lett 379:124–133
Wu K, Chang Q, Lu Y, Qiu P, Chen B, Thakur C, Sun J, Li L, Kowluru A, Chen F (2013) Gefitinib resistance resulted from STAT3-mediated Akt activation in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 4:2430–2438
Li Q, Zhang D, Chen X, He L, Li T, Xu X, Li M (2015) Nuclear PKM2 contributes to gefitinib resistance via upregulation of STAT3 activation in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep 5:16082
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81802660).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CQW: designed the experiments. LLJ, HJL, JKS, and YW: performed the experiments. CQW, LLJ, HJL, and SPL: analyzed the data. BFH and GNH: were responsible for management of the clinical samples. The manuscript was written by CQW and revised by HCJ. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, LL., Lu, HJ., Shao, JK. et al. Relevance and mechanism of STAT3/miR-221-3p/Fascin-1 axis in EGFR TKI resistance of triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cell Biochem (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04907-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04907-9