Abstract
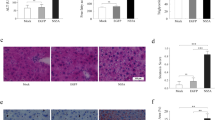
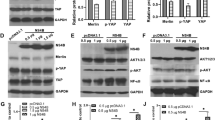
The effects of hepatocyte steatosis on hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA replication and HBV-related antigen secretion are incompletely understood. The aims of this study are to explore the effects and mechanism of hepatocyte steatosis on HBV replication and secretion. Stearic acid (SA) and oleic acid (OA) were used to induce HepG2.2.15 cell steatosis in this study. The expressions of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), phosphorylation of protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) kinase (p-PERK), and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (p-eIF2α) were detected by Western blotting (WB). HBV DNA, HBsAg, and HBeAg in the supernatant were determined by real-time fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Intracellular HBV DNA, HBsAg level, and HBV RNA were measured by real-time fluorescent PCR, WB, and real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR, respectively. The results showed that SA and OA significantly increased intracellular lipid droplets and triglyceride levels. SA and OA significantly induced GRP78, p-PERK, and p-eIF2α expressions from 24 to 72 h. 4-phenylbutyric acid (PBA) alleviated ER stress induced by SA. SA promoted intracellular HBsAg and HBV DNA accumulation; however, it inhibited the transcript of HBV 3.5 kb mRNA and S mRNA. The secretion of HBsAg and HBV DNA inhibited by SA or OA could be partially restored by pretreatment with PBA but not by inhibiting GRP78 expression with siRNA. Hepatocyte steatosis inhibits HBsAg and HBV DNA secretion via induction of ER stress in hepatocytes, but not via induction of GRP78.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Eslam M, George J, Al Mahtab M, Akbar SMF, Jia J, Tian Q, Aggarwal R, Muljono DH, Omata M, Ooka Y, Han KH, Lee HW, Jafri W, Butt AS, Chong CH, Lim SG, Pwu RF, Chen DS (2020) Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: a Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(2):167–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30342-5
Zhang J, Lin S, Jiang D, Li M, Chen Y, Li J, Fan J (2020) Chronic hepatitis B and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: conspirators or competitors? Liver Int 40(3):496–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14369
Wang L, Wang Y, Liu S, Zhai X, Zhou G, Lu F, Zhao J (2019) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with lower hepatitis B viral load and antiviral response in pediatric population. J Gastroenterol 54(12):1096–1105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01594-6
Hu D, Wang H, Wang Y, Wan X, Yan W, Luo X, Ning Q (2018) Non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis attenuates hepatitis B virus replication in an HBV-immunocompetent mouse model. Hepatol Int 12(5):438–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-018-9877-7
Wong VW-S, Wong GL-H, Chu WC-W, Chim AM-L, Ong A, Yeung DK-W, Yiu KK-L, Chu SH-T, Chan H-Y, Woo J, Chan FK-L, Chan HL-Y (2012) Hepatitis B virus infection and fatty liver in the general population. J Hepatol 56(3):533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.09.013
Tong S, Revill P (2016) Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J Hepatol 64(1Suppl):S4–S16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.01.027
Xia W, Shen Y, Xie H, Zheng S (2006) Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum in hepatitis B virus replication. Virus Res 121(2):116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2006.01.020
Patzer EJ, Nakamura GR, Simonsen CC, Levinson AD, Brands R (1986) Intracellular assembly and packaging of hepatitis B surface antigen particles occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol 58(3):884–892
Bruss V, Ganem D (1991) The role of envelope proteins in hepatitis B virus assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(3):1059–1063
Dorobantu C, Macovei A, Lazar C, Dwek RA, Zitzmann N, Branza-Nichita N (2011) Cholesterol depletion of hepatoma cells impairs hepatitis B virus envelopment by altering the topology of the large envelope protein. J Virol 85(24):13373–13383. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.05423-11
Lambert C, Prange R (2007) Posttranslational N-glycosylation of the hepatitis B virus large envelope protein. Virol J 4:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422x-4-45
Garcia PD, Ou JH, Rutter WJ, Walter P (1988) Targeting of the hepatitis B virus precore protein to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane: after signal peptide cleavage translocation can be aborted and the product released into the cytoplasm. J Cell Biol 106(4):1093–1104. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.106.4.1093
Wang J, Lee AS, Ou JH (1991) Proteolytic conversion of hepatitis B virus e antigen precursor to end product occurs in a postendoplasmic reticulum compartment. J Virol 65(9):5080–5083. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.65.9.5080-5083.1991
Lai E, Teodoro T, Volchuk A (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: signaling the unfolded protein response. Physiology 22(3):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00050.2006
Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334(6059):1081–1086. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1209038
Diehl JA, Fuchs SY, Koumenis C (2011) The cell biology of the unfolded protein response. Gastroenterology 141(1):38–41, e1–e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.05.018
Lebeaupin C, Vallée D, Hazari Y, Hetz C, Chevet E, Bailly-Maitre B (2018) Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 69(4):927–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.06.008
Ma Y, Yu J, Chan HLY, Chen Y-c, Wang H, Chen Y, Chan C-y, Go MYY, Tsai S-n, Ngai S-m, To K-f, Tong JHM, He Q-Y, Sung JJY, Kung H-f, Cheng CHK, He M-l (2009) Glucose-regulated protein 78 is an intracellular antiviral factor against hepatitis B virus. Mol Cell Proteomics 8(11):2582–2594. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M900180-MCP200
Huang KL, Lai YK, Lin CC, Chang JM (2009) Involvement of GRP78 in inhibition of HBV secretion by Boehmeria nivea extract in human HepG2 2.2.15 cells. J Viral Hepat 16(5):367–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01072.x
Shu W, Guo Z, Li L, Xiong Z, Wang Z, Yang Y, Li Y, He M, Gong R, Gao B (2019) Regulation of molecular chaperone GRP78 by HBV: control of viral replication and cell survival. Mol Cell Biol 40(3):e00475-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00475-19
Bucolo G, David H (1973) Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem 19(5):476–482
Wu L, Wang W, Zhang X, Zhao X, Yu G (2016) Anti-HBV activity and mechanism of marine-derived polyguluronate sulfate (PGS) in vitro. Carbohydr Polym 143:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.065
Zhang Z, Pan Q, Duan XY, Liu Q, Mo GY, Rao GR, Fan JG (2012) Fatty liver reduces hepatitis B virus replication in a genotype B hepatitis B virus transgenic mice model. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(12):1858–1864. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07268.x
Zhang RN, Pan Q, Zhang Z, Cao HX, Shen F, Fan JG (2015) Saturated fatty acid inhibits viral replication in chronic hepatitis B virus infection with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by toll-like receptor 4-mediated innate immune response. Hepat Mon 15(5):e27909. https://doi.org/10.5812/hepatmon.15(5)2015.27909
Yang W, Liu R, Xia C, Chen Y, Dong Z, Huang B, Li R, Li M, Xu C (2020) Effects of different fatty acids on BRL3A rat liver cell damage. J Cell Physiol 235(9):6246–6256. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29553
Yan D, Dou QL, Wang Z, Wei YY (2015) Establishment of a hepatocyte steatosis model using Chang liver cells. Genet Mol Res 14(4):15224–15232. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.November.25.10
Moon YA (2017) The SCAP/SREBP pathway: a mediator of hepatic steatosis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 32(1):6–10. https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.6
Xu Z, Jensen G, Yen TS (1997) Activation of hepatitis B virus S promoter by the viral large surface protein via induction of stress in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol 71(10):7387–7392. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.71.10.7387-7392.1997
Huang Z-M, Tan T, Yoshida H, Mori K, Ma Y, Yen TSB (2005) Activation of hepatitis B virus S promoter by a cell type-restricted IRE1-dependent pathway induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol 25(17):7522–7533. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.25.17.7522-7533.2005
Lazar C, Macovei A, Petrescu S, Branza-Nichita N (2012) Activation of ERAD pathway by human hepatitis B virus modulates viral and subviral particle production. PLoS One 7(3):e34169. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034169
Li X, Pan E, Zhu J, Xu L, Chen X, Li J, Liang L, Hu Y, Xia J, Chen J, Chen W, Hu J, Wang K, Tang N, Huang A (2018) Cisplatin enhances hepatitis B virus replication and PGC-1α expression through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sci Rep 8(1):3496. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21847-3
McClain SL, Clippinger AJ, Lizzano R, Bouchard MJ (2007) Hepatitis B virus replication is associated with an HBx-dependent mitochondrion-regulated increase in cytosolic calcium levels. J Virol 81(21):12061–12065. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00740-07
Bouchard MJ, Wang LH, Schneider RJ (2001) Calcium signaling by HBx protein in hepatitis B virus DNA replication. Science 294(5550):2376–2378. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.294.5550.2376
Sicari D, Delaunay-Moisan A, Combettes L, Chevet E, Igbaria A (2020) A guide to assessing endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis and stress in mammalian systems. FEBS J 287(1):27–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15107
Funding
This work was supported by the Funds of China National Natural Science Foundation Project (81160067/H0318, 81460124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL conceived and designed the study and critically revised the manuscript. QL, MM, HC, and GZ performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. JC, YY, YL, and FY participated in study design, study implementation, and manuscript revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have claimed no competing interests in this study.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Mu, M., Chen, H. et al. Hepatocyte steatosis inhibits hepatitis B virus secretion via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biochem 477, 2481–2491 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04143-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04143-z