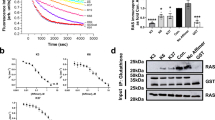
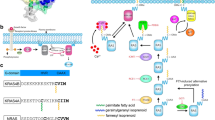
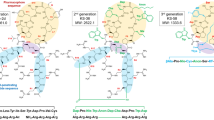
Abstract
Ras Proteins, play a pivotal role in the proliferation pathways, and Ras mutant forms are well-established cancer drivers. Ras mutations are found in about 30% of all human cancers widely known as challenging diseases to control and treat. The direct inhibition of Ras is challenging and makes Ras an “undruggable” target for many years. The important reason is, that Ras protein has a unique smooth surface and shows different dynamicity upon binding GDP and GTP. As a result, interfering peptides (IPs) targeting the Ras family protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are considered more likely to bind Ras effectively and inhibit the downstream signaling. In this review, we aimed to cover the recent approaches to design the peptides that target Ras family proteins, focusing on in silico methods. In this regard, the anti-cancer peptide development approaches including design and delivery strategies are discussed. Later, more specific methods regarding Ras-specific peptide design are presented. In conclusion, IPs are a promising group of cancer therapeutics to combat Ras mutant cancers. For future perspectives to have these peptides in clinical use, co-inhibition of other cancer targets as well as improving the pharmacokinetic features of peptides are suggested.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
There is no original data as this is a review article.
References
Asati V, Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK (2016) PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibitors as anticancer agents: structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur J Med Chem 109:314–341
Baek S et al (2012) Structure of the stapled p53 peptide bound to Mdm2. J Am Chem Soc 134(1):103–106
Bakail M, Ochsenbein F (2016) Targeting protein–protein interactions, a wide open field for drug design. C R Chim 19(1):19–27
Bird GH et al (2016) Biophysical determinants for cellular uptake of hydrocarbon-stapled peptide helices. Nat Chem Biol 12(10):845–852
Boohaker RJ et al (2018) Rational design and development of a peptide inhibitor for the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction. Cancer Lett 434:11–21
Bos JL (1989) Ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res 49(17):4682–4689
Bos JL, Rehmann H, Wittinghofer A (2007) GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell 129(5):865–877
Bruzzoni-Giovanelli H et al (2018) Interfering peptides targeting protein-protein interactions: the next generation of Drugs? Drug Discov Today 23(2):272–285
Bullock BN, Jochim AL, Arora PS (2011) Assessing helical protein interfaces for inhibitor design. J Am Chem Soc 133(36):14220–14223
Burns MC et al (2014) Approach for targeting Ras with small molecules that activate SOS-mediated nucleotide exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(9):3401–3406
Cao Q et al (2008) Evaluation of biodistribution and anti-tumor effect of a dimeric RGD peptide-paclitaxel conjugate in mice with Breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35(8):1489–1498
Chatterjee J et al (2008) N-methylation of peptides: a new perspective in medicinal chemistry. Acc Chem Res 41(10):1331–1342
Chatterjee J, Rechenmacher F, Kessler H (2013) N-methylation of peptides and proteins: an important element for modulating biological functions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(1):254–269
Cho KJ, van der Hoeven D, Hancock JF (2013) Inhibitors of K-Ras plasma membrane localization Enzymes, 33 Pt A: p. 249 – 65
Deng Y, Li J (2017) Rational optimization of Tumor suppressor-derived peptide inhibitor selectivity between Oncogene Tyrosine Kinases ErbB1 and ErbB2. Arch Pharm 350(12):1700181
Fairlie DP, Dantas de A, Araujo (2016) Rev Stapling Peptides Using Cysteine Crosslink Biopolymers 106(6):843–852
Ford B et al (2009) Characterization of a ras mutant with identical GDP-and GTP-bound structures. Biochemistry 48(48):11449–11457
Furet P et al (2019) Structure-based design of potent linear peptide inhibitors of the YAP-TEAD protein-protein interaction derived from the YAP omega-loop sequence. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29(16):2316–2319
Gabernet G et al (2019) In silico design and optimization of selective membranolytic anticancer peptides. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11
Green M, Loewenstein PM (1988) Autonomous functional domains of chemically synthesized human immunodeficiency virus tat trans-activator protein. Cell 55(6):1179–1188
Gunderwala AY et al (2019) Development of allosteric BRAF peptide inhibitors targeting the dimer interface of BRAF. ACS Chem Biol 14(7):1471–1480
Gupta UK, Mahanta S, Paul S (2013) Silico design of small peptide-based Hsp90 inhibitor: a novel anticancer agent. Med Hypotheses 81(5):853–861
Ho AL et al (2018) Preliminary results from a phase II trial of tipifarnib in squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) with HRAS mutations. Ann Oncol 29:viii373
Jing H et al (2016) Novel cell-penetrating peptide-loaded nanobubbles synergized with ultrasound irradiation enhance EGFR siRNA delivery for triple negative Breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 146:387–395
Kamagata K et al (2019) Rational design using sequence information only produces a peptide that binds to the intrinsically disordered region of p53 Scientific reports, 9(1): p. 1–10
Karnoub AE, Weinberg RA (2008) Ras oncogenes: split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(7):517–531
Kato K et al (1992) Isoprenoid addition to Ras protein is the critical modification for its membrane association and transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89(14):6403–6407
Kim YW, Grossmann TN, Verdine GL (2011) Synthesis of all-hydrocarbon stapled α-helical peptides by ring-closing olefin metathesis. Nat Protoc 6(6):761–771
Lelle M et al (2015) Octreotide-mediated tumor-targeted drug delivery via a cleavable doxorubicin-peptide conjugate. Mol Pharm 12(12):4290–4300
Li Z, Buck M (2019) Computational design of myristoylated cell-penetrating peptides targeting oncogenic K-Ras. G12D at the effector-binding membrane interface. J Chem Inf Model 60(1):306–315
Li HM et al (2017) De novo computational design for development of a peptide ligand oriented to VEGFR-3 with high affinity and long circulation. Mol Pharm 14(7):2236–2244
Lim KJ et al (2013) A cancer specific cell-penetrating peptide, BR2, for the efficient delivery of an scFv into cancer cells. PLoS ONE 8(6):e66084
Marqus S, Pirogova E, Piva TJ (2017) Evaluation of the use of therapeutic peptides for cancer treatment. J Biomed Sci 24(1):21
Matsson P et al (2016) Cell permeability beyond the rule of 5. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 101:42–61
Nakajima EC et al (2022) FDA approval Summary: Sotorasib for KRAS G12C-Mutated metastatic NSCLC. Clin Cancer Res 28(8):1482–1486
Nevola L, Giralt E (2015) Modulating protein-protein interactions: the potential of peptides. Chem Commun (Camb) 51(16):3302–3315
Nomura TK et al (2021) Specific inhibition of oncogenic RAS using cell-permeable RAS-binding domains. Cell Chem Biology 28(11):1581–1589e6
Novotny CJ et al (2017) Farnesyltransferase-mediated delivery of a covalent inhibitor overcomes alternative Prenylation to mislocalize K-Ras. ACS Chem Biol 12(7):1956–1962
Oliveira S et al (2007) Fusogenic peptides enhance endosomal Escape improving siRNA-induced silencing of oncogenes. Int J Pharm 331(2):211–214
Ostrem JM et al (2013) K-Ras(G12C) inhibitors allosterically control GTP affinity and effector interactions. Nature 503(7477):548–551
Papke B, Der CJ (2017) Drugging RAS: know the enemy. Science 355(6330):1158–1163
Patgiri A et al (2011) An orthosteric inhibitor of the ras-sos interaction. Nat Chem Biol 7(9):585–587
Qian Z, Dougherty PG, Pei D (2017) Targeting intracellular protein-protein interactions with cell-permeable cyclic peptides. Curr Opin Chem Biol 38:80–86
Regina A et al (2008) Antitumour activity of ANG1005, a conjugate between paclitaxel and the new brain delivery vector Angiopep-2. Br J Pharmacol 155(2):185–197
Sakamoto K et al (2017) K-Ras (G12D)-selective inhibitory peptides generated by random peptide T7 phage display technology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 484(3):605–611
Sakamoto K, Masutani T, Hirokawa T (2020) Generation of KS-58 as the first K-Ras (G12D)-inhibitory peptide presenting anti-cancer activity in vivo. Sci Rep 10(1):1–16
Samec T et al (2022) Peptide-based delivery of therapeutics in cancer treatment. Mater Today Bio 14:100248
Sang P et al (2019) Inhibition of β-catenin/B cell lymphoma 9 protein – protein interaction using α-helix–mimicking sulfono-γ-AApeptide inhibitors Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(22): p. 10757–10762
Sung H et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Tang S et al (2019) Structure-based Discovery of Novel CK2α-Binding cyclic peptides with anti-cancer activity. Mol Inf 38(3):e1800089
Trinh TB et al (2016) Discovery of a direct ras inhibitor by screening a Combinatorial Library of cell-permeable bicyclic peptides. ACS Comb Sci 18(1):75–85
Upadhyaya P et al (2014) Direct Ras inhibitors identified from a structurally rigidified bicyclic peptide library. Tetrahedron 70(42):7714–7720
Upadhyaya P et al (2015) Inhibition of Ras signaling by blocking Ras–effector interactions with cyclic peptides. Angew Chem Int Ed 54(26):7602–7606
Uprety D, Adjei AA (2020) KRAS: from undruggable to a druggable Cancer target. Cancer Treat Rev 89:102070
Vadevoo SMP et al (2023) Peptides as multifunctional players in cancer therapy. Exp Mol Med 55(6):1099–1109
Walensky LD, Bird GH (2014) Hydrocarbon-stapled peptides: principles, practice, and progress. J Med Chem 57(15):6275–6288
Weinberg RA (1996) How cancer arises. Sci Am 275(3):62–70
Whyte DB et al (1997) K- and N-Ras are geranylgeranylated in cells treated with farnesyl protein transferase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 272(22):14459–14464
Wu XL et al (2010) Tumor-targeting peptide conjugated pH-responsive micelles as a potential drug carrier for cancer therapy. Bioconjug Chem 21(2):208–213
Xu W et al (2018) P1c peptide decorated liposome targeting alphavbeta3-expressing Tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. RSC Adv 8(45):25575–25583
Xue S et al (2021) Cartilage-targeting peptide-modified dual-drug delivery nanoplatform with NIR laser response for osteoarthritis therapy. Bioact Mater 6(8):2372–2389
Yoo DY et al (2020) Covalent targeting of ras G12C by rationally designed peptidomimetics. ACS Chem Biol 15(6):1604–1612
Zeitouni D et al (2016) KRAS mutant Pancreatic cancer: no lone path to an effective treatment. Cancers 8(4):45
Zeng J et al (2001) Design of inhibitors of ras–raf interaction using a computational combinatorial algorithm. Protein Eng 14(1):39–45
Zenonos K, Kyprianou K (2013) RAS signaling pathways, mutations and their role in Colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 5(5):97
Zhang Z et al (2020) GTP-state-selective cyclic peptide ligands of K-Ras (G12D) block its interaction with Raf. ACS Cent Sci 6(10):1753–1761
Zhou P et al (2018) Disrupting the intramolecular interaction between proto-oncogene c-Src SH3 domain and its self-binding peptide PPII with rationally designed peptide ligands Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 46(6): p. 1122–1131
Zinatizadeh MR et al (2019) The role and function of ras-association domain family in Cancer: a review, vol 6. Genes & Diseases, pp 378–384. 4
Funding
This manuscript is supported by the grant of the National Institute for Medical Research Development (NIMAD), with grant number 972544.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have made a contribution to the concept or design of the article. P.M. and H.R.H. drafted the manuscript and interpret the relevant literature. M.S.H. and O.M revised the manuscript. E.M.A. conceptualize and draft the manuscript and interpret the relevant literature.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Motiei, P., Heidari, H.R., Hejazi, M.S. et al. A Review of the in Silico Design and Development Approaches of Ras-Specific Anticancer Therapeutics. Int J Pept Res Ther 30, 2 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-023-10578-3
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-023-10578-3