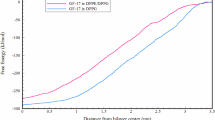
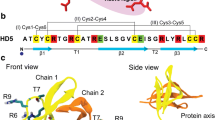
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a unique microorganism among the antibiotic-resistant microbial pathogens. Among the various therapeutic approaches, antimicrobial peptides are effective to combat this infection. The chimera C3 is a peptide derived from the human beta-defensins 2 and 3 that has previously displayed antibacterial activity against the Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. In this research, the antibacterial activity and the effect of a new genetically designed chimera C3 (i.e. chimera C3-3) on the bacterial membrane was assessed by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. To investigate the interactions of the peptide with the lipid bilayer model and their effects on each other, the characterizations e.g. Area Per Lipid (APL), density, deuterium order parameter, membrane thickness, Mean Square Displacement (MSD), Radial Distribution Function (RDF), hydrogen bonds (H-bond), root-mean-square-fluctuation (RMSF), bending modulus (KC) and free energy (ΔG) were compared between C3 and C3-3 peptides. Furthermore, the MD simulation of the pure membrane was also carried out. Finally, the comparison of the antibacterial effects showed that chimera C3-3 had the less antibacterial effect than the chimera C3 due to the N-terminal deletion of GII residues. Moreover, the results confirmed that the GII residue played the main role of an anchor in binding the membrane and deletion of anchor reduced the antibacterial activity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen WJ, Lemkul JA, Bevan DR (2009) GridMAT-MD: a grid-based membrane analysis tool for use with molecular dynamics. J Comput Chem 30:1952–1958
Amos S-BTA et al (2016) Antimicrobial peptide potency is facilitated by greater conformational flexibility when binding to gram-negative bacterial inner membranes. Sci Rep 6:37639. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37639
Appelt C, Eisenmenger F, Kuhne R, Schmieder P, Soderhall JA (2005) Interaction of the antimicrobial peptide cyclo(RRWWRF) with membranes by molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 89:2296–2306. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.105.063040
Arasteh S, Bagheri M (2017) Molecular dynamics simulation and analysis of the antimicrobial peptide-lipid bilayer interactions. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 1548:103–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6737-7_8
Arias M, Piga KB, Eric Hyndman M, Vogel HJ (2018) Improving the activity of trp-rich antimicrobial peptides by Arg/Lys substitutions and changing the length of cationic residues. Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8020019
Armas F et al (2019) Design, antimicrobial activity and mechanism of action of Arg-rich ultra-short cationic lipopeptides. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212447
Ashby M, Petkova A, Hilpert K (2014) Cationic antimicrobial peptides as potential new therapeutic agents in neonates and children: a review. Curr Opin Infect Dis 27:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1097/qco.0000000000000057
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, Gunsteren WFV, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.448118
Berglund NA, Piggot TJ, Jefferies D, Sessions RB, Bond PJ, Khalid S (2015) Interaction of the antimicrobial peptide polymyxin B1 with both membranes of E. coli: a molecular dynamics study. PLOS Comput Biol 11:e1004180. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004180
Best RB, Zhu X, Shim J, Lopes PE, Mittal J, Feig M, Mackerell AD Jr (2012) Optimization of the additive CHARMM all-atom protein force field targeting improved sampling of the backbone phi, psi and side-chain chi(1) and chi(2) dihedral angles. J Chem Theory Comput 8:3257–3273. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct300400x
Buchoux S (2017) FATSLiM: a fast and robust software to analyze MD simulations of membranes. Bioinformatics 33:133–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw563
Chang WK, Wimley WC, Searson PC, Hristova K, Merzlyakov M (2008) Characterization of antimicrobial peptide activity by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:2430–2436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.06.016
Cuendet MA, Gunsteren WFV (2007) On the calculation of velocity-dependent properties in molecular dynamics simulations using the leapfrog integration algorithm. J Chem Phys 127:184102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2779878
Dill KA, Bromberg S, Yue K, Fiebig KM, Yee DP, Thomas PD, Chan HS (1995) Principles of protein folding—a perspective from simple exact models. Protein Sci 4:561–602
Dings Ruud PM, Haseman Judith R, Mayo Kevin H (2008) Probing structure–activity relationships in bactericidal peptide βpep-25. Biochem J 414:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20080506
Dupuy FG, Pagano I, Andenoro K, Peralta MF, Elhady Y, Heinrich F, Tristram-Nagle AS (2018) Selective interaction of colistin with lipid model membranes. Biophys J 114:919–928
El Khoury M, Swain J, Sautrey G, Zimmermann L, Van Der Smissen P, Décout J-L, Mingeot-Leclercq M-P (2017) Targeting bacterial cardiolipin enriched microdomains: an antimicrobial strategy used by amphiphilic aminoglycoside antibiotics. Sci Rep 7:10697. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10543-3
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.470117
Harder J, Bartels J, Christophers E, Schröder J-M (2001) Isolation and characterization of human β-defensin-3, a novel human inducible peptide antibiotic. J Biol Chem 276:5707–5713. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008557200
Hess B (2008) P-LINCS: a parallel linear constraint solver for molecular simulation. J Chem Theor Comput 4:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct700200b
Hirt H, Gorr S-U (2013) Antimicrobial peptide GL13K is effective in reducing biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:4903–4910. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00311-13
Hoover WG (1985) Canonical dynamics: equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys Rev A 31:1695–1697. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.31.1695
Hoover DM, Wu Z, Tucker K, Lu W, Lubkowski J (2003) Antimicrobial characterization of human β-defensin 3 derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:2804–2809. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.47.9.2804-2809.2003
Jacobson K, Mouritsen OG, Anderson RG (2007) Lipid rafts: at a crossroad between cell biology and physics. Nat Cell Biol 9:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0107-7
Jafari M, Mehrnejad F, Doustdar F (2017) Insight into the interactions, residue snorkeling, and membrane disordering potency of a single antimicrobial peptide into different lipid bilayers. PLoS ONE 12:e0187216. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187216
Jing H, MA D (2013) CHARMM36 all-atom additive protein force field: validation based on comparison to NMR data. J Comput Chem 34:2135–2145. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23354
Jo S, Kim T, Im W (2007) Automated builder and database of protein/membrane complexes for molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS ONE 2:e880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000880
Jo S, Kim T, Iyer VG, Im W (2008) CHARMM-GUI: a web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J Comput Chem 29:1859–1865. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20945
Jo S, Lim JB, Klauda JB, Im W (2009) CHARMM-GUI membrane builder for mixed bilayers and its application to yeast membranes. Biophys J 97:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2009.04.013
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.445869
Jung S et al (2011) Human β-defensin 2 and β-defensin 3 chimeric peptides reveal the structural basis of the pathogen specificity of their parent molecules. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:954–960. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00872-10
Kapoor R, Wadman MW, Dohm MT, Czyzewski AM, Spormann AM, Barron AE (2011) Antimicrobial peptoids are effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:3054–3057. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.01516-10
Kenworthy A (2002) Peering inside lipid rafts and caveolae. Trends Biochem Sci 27:435–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(02)02178-3
Khan S, Vihinen M (2007) Spectrum of disease-causing mutations in protein secondary structures. BMC Struct Biol 7:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6807-7-56
Khandelia H, Ipsen JH, Mouritsen OG (2008) The impact of peptides on lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:1528–1536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.02.009
Klauda JB et al (2010) Update of the CHARMM all-atom additive force field for lipids: validation on six lipid types. J Phys Chem B 114:7830–7843. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp101759q
Kumari R, Kumar R (2014) Open Source Drug Discovery, C.; Lynn, A. G_Mmpbsa—a gromacs tool for high-throughput Mm-Pbsa calculations. J Chem Inf Model 54:1951–1962
Lee J et al (2016) CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive force field. J Chem Theory Comput 12:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00935
Lee J et al (2018) CHARMM-GUI membrane builder with glycolipids and lipopolysaccharides. Biophys J 114(3):344a
León-Calvijo MA, Leal-Castro AL, Almanzar-Reina GA, Rosas-Pérez JE, García-Castañeda JE, Rivera-Monroy ZJ (2015) Antibacterial activity of synthetic peptides derived from lactoferricin against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212. Int BioMed Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/453826
Li J et al (2012) Molecular dynamics simulations of a new branched antimicrobial peptide: a comparison of force fields. J Chem Phys 137:215101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4768899
Li Q, Yu H, Zhao X, Huang X (2015) Insight into the impact of environments on structure of chimera C3 of human beta-defensins 2 and 3 from molecular dynamics simulations. J Biomol Struct Dyn 33:1989–2002. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2014.985255
Lombardi L et al (2017) Antimicrobial peptides at work: interaction of myxinidin and its mutant WMR with lipid bilayers mimicking the P. aeruginosa and E. coli membranes. Sci Rep 7:44425. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44425
Lopez Cascales JJ, Garro A, Porasso RD, Enriz RD (2014) Dynamic action mechanism of small cationic antimicrobial peptides. Phys Chem Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP02537G
López Cascales JJ, Zenak S, García de la Torre J, Lezama OG, Garro A, Enriz RD (2018) Small cationic peptides: influence of charge on their antimicrobial activity. ACS Omega 3:5390–5398. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00293
Lund O, Nielsen M, Lundegaard C, Worning P (2002) CPHmodels 2.0: X3M a computer Program to extract 3D models. Abstract at the CASP5 conferenceA102
MacKerell AD et al (1998) All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J Phys Chem B 102:3586–3616. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp973084f
Maithri G, Manasa B, Vani SS, Narendra A, Harshita T (2016) Computational drug design and molecular dynamic studies—a review. Int J Biomed Data Min 6:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2090-4924.1000123
Mandal RS, Das S (2017) In silico approaches toward combating antibiotic resistance. In: Arora G, Sajid A, Kalia VC (eds) Drug resistance in bacteria, fungi, malaria, and cancer. Springer, Cham, pp 577–593
Michaelides EE (2008) Entropy, order and disorder. Open Thermodyn J 2:7–11
Mishra B, Wang G (2017) Individual and combined effects of engineered peptides and antibiotics on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofilms Pharm (Basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10030058
Nielsen M, Lundegaard C, Lund O, Petersen TN (2010) CPHmodels-3.0—remote homology modeling using structure guided sequence profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq535
Noguera-Salvà MA, Guardiola-Serrano F, Martin ML, Marcilla-Etxenike A, Bergo MO, Busquets X, Escribá PV (2017) Role of the C-terminal basic amino acids and the lipid anchor of the Gγ2 protein in membrane interactions and cell localization. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1859:1536–1547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.02.012
Nosé S (1984) A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J Chem Phys 81:511–519. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.447334
Nosé S, Klein ML (1983) Constant pressure molecular dynamics for molecular systems. Mol Phys 50:1055–1076. https://doi.org/10.1080/00268978300102851
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52:7182–7190. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.328693
Petkov P, Marinova R (2019) Computational study of solution behavior of magainin 2 monomers. J Biomol Struct Dyn 37:1231–1240. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2018.1454850
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Rahmanpour A, Ghahremanpour MM, Mehrnejad F, Moghaddam ME (2013) Interaction of Piscidin-1 with zwitterionic versus anionic membranes: a comparative molecular dynamics study. J Biomol Struct Dyn 31:1393–1403. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2012.737295
UCSF Resource for Biocomputing V, and Informatics is funded by the National Institutes of Health UCSF Chimera. UCSF Resource. https://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimera.
Sanchez-Gomez S, Ferrer-Espada R, Stewart PS, Pitts B, Lohner K, Martinez de Tejada G (2015) Antimicrobial activity of synthetic cationic peptides and lipopeptides derived from human lactoferricin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa planktonic cultures and biofilms. BMC Microbiol 15:137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-015-0473-x
Sawai MV et al (2001) The NMR structure of human â-Defensin-2 Reveals a Novel R -helical segment. Biochemistry 40:3810–3816
Schneider JJ, Unholzer A, Schaller M, Schäfer-Korting M, Korting HC (2005) Human defensins. J Mol Med 83:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-005-0657-1
Shelburne CE, Coulter WA, Olguin DA, Lantz MS, Lopatin DE (2005) Induction of β-Defensin resistance in the oral anaerobe porphyromonas gingivalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:183–187. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.49.1.183-187.2005
Silva PM, Gonçalves S, Santos NC (2014) Defensins: antifungal lessons from eukaryotes. Front Microbiol 5:1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00097
Silvius JR (1999) Lipid modifications of intracellular signal-transducing proteins. J Liposome Res 9:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3109/08982109909044489
Sneha P, George Priya Doss C (2016) Chapter seven—molecular dynamics: new frontier in personalized medicine. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 102:181–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apcsb.2015.09.004
Spudy B (2012) Identification of structural traits that increase the antimicrobial activity of a chimeric peptide of human β-defensins 2 and 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427:207–211
Talandashti R, Mahdiuni H, Jafari M, Mehrnejad F (2019) Molecular basis for membrane selectivity of antimicrobial peptide pleurocidin in the presence of different eukaryotic and prokaryotic model membranes. J Chem Inf Model 59:3262–3276. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00245
van der Spoel D et al. (2010a) Gromacs User Manual version 4.5.4
van der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, van Buuren AR, Apol E, PJ Meulenhoff ea (2010b) Gromacs User Manual version 4.5.4.
Vanommeslaeghe K et al (2010) CHARMM general force field: a force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. J Comput Chem 31:671–690. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21367
Wu EL et al (2014) CHARMM-GUI Membrane builder toward realistic biological membrane simulations. J Comput Chem 35:1997–2004. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23702
Wu W, Jin Y, Bai F, Jin S (2015) Chapter 41—Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In: Tang Y-W, Sussman M, Liu D, Poxton I, Schwartzman J (eds) Molecular medical microbiology, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Boston, pp 753–767
Yang H, Huang Z, Zhang Y (2018) Effect of C60 on the phase transition behavior of a lipid bilayer under high pressure. RSC Adv 8:655–661. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA09514G
Zeiske T, Stafford KA, Friesner RA, Palmer AG 3rd (2013) Starting-structure dependence of nanosecond timescale intersubstate transitions and reproducibility of MD-derived order parameters. Proteins 81:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.24209
Zhang L, Dhillon P, Yan H, Farmer S, Hancock RE (2000) Interactions of bacterial cationic peptide antibiotics with outer and cytoplasmic membranes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:3317–3321
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Shahed University for support of this work. We also thank Mr. Reza Talandashti and Dr. Ammar Mohseni for their cooperation. The authors are also grateful to Sana Alavi for re-reading and language/editing assistance. We also appreciate the manufacturers and developers of Gromacs, Chimera, VMD, Fatslime and Gridmat Software. Some molecular graphics and analyses were performed by the UCSF Chimera package. Chimera is developed by the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California, San Francisco (supported by NIGMS P41-GM103311). Finally, we would like to thank all the people who have direct or indirect involvement in this work and their names have probably been forgotten.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghafari, M.D., Rasooli, I., Khajeh, K. et al. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Human Beta-defensins 2 and 3 Chimeric Peptides with the Cell Membrane Model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Pept Res Ther 26, 2039–2056 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-10000-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-10000-x