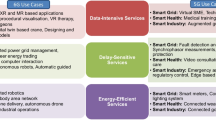
Abstract
Smart city enhances the intelligence and sustainability of the city assets through advanced and diversified applications characterised by specific Quality of Service requirements. To realise the stringent requirements of these applications, multi-connectivity (MC) emerged as a potential solution that ensures seamless mobility, high reliability and enhanced data rates. However, the smart city verticals driven by the energy-constrained IoT devices experience an energy optimisation challenge in the MC configured environment. Recently, significant research has been reported in the direction of MC but they are incapacitated in terms of enhancing energy efficiency. To address the aforementioned issue, an intelligent framework based on software-defined wireless networking and edge computing has been proposed. The proposed framework leverages the synergetic integration of Double Deep Reinforcement Learning and Matching Game Theory to attain energy-efficient multi-connectivity association policy. In addition to this, the proposed approach defines the preference functions to guarantee service provisioning while respecting the radio access technologies constraints. The analytical results validated through the rigorous simulation exhibited an improvement of 45% in the overall energy efficiency. Furthermore, the proposed association scheme outperformed the other existing schemes by 12%, 27%, and 82% in terms of fairness, robustness and system satisfaction degree respectively.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This manuscript has no associated data file.
References
UN.org: 68% of the world population projected to live in urban areas by 2050, says UN. https://www.un.org/development/desa/en/news/population/2018-revision-of-world-urbanization-prospects.html (2018). Accessed 8 June 2021
Shamsuzzoha, A., Nieminen, J., Piya, S., Rutledge, K.: Smart city for sustainable environment: a comparison of participatory strategies from Helsinki, Singapore and London. Cities 114, 103194 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2021.103194
Kirimtat, A., Krejca, O., Kertesz, A., Tasgetiren, M.F.: Future trends and current state of smart city concepts: a survey. IEEE Access. 8, 86448–86467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992441
Yaqoob, I., Hashem, I.A.T., Mehmood, Y., Gani, A., Mokhtar, S., Gzani, S.: Enabling communication technologies for smart cities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 55(1), 112–120 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600232CM
Ahuja, K., Khosla, A.: Network selection criterion for ubiquitous communication provisioning in smart cities for smart energy system. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 127, 82–91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.11.011
Sandoval, R.M., Canovas-Carrasco, S., Garcia-Sanchez, A.J., Garcia-Haro, J.: Smart usage of multiple RAT in IoT-oriented 5G networks: a reinforcement learning approach. In: Proceedings of 2018 ITU kaleidoscope: machine learning for a 5G Future (ITU K), pp. 1–8. IEEE, Santa Fe (2018)
Sandoval, R.M., Canovas-Carrasco, S., Garcia-Sanchez, A.J., Garcia-Haro, J.: A reinforcement learning-based framework for the exploitation of multiple rats in the IoT. IEEE Access. 7, 123341–123354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2938084
Habbal, A., Goudar, S.I., Hassan, S.: A context-aware radio access technology selection mechanism in 5G mobile network for smart city applications. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 135, 97–107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2019.02.019
Ahuja, K., Khosla, A.: A novel framework for data acquisition and ubiquitous communication provisioning in smart cities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 101, 785–803 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.07.029
Wang, X., Li, J., Wang, L., Yang, C., Han, Z.: Intelligent user-centric network selection: a model-driven reinforcement learning framework. IEEE Access. 7, 21645–21661 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2898205
Ding, H., Zhao, F., Tian, J., Li, D., Zhang, H.: A deep reinforcement learning for user association and power control in heterogeneous networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 102, 102069–102087 (2019)
Arabi, S., Hammouti, H., Sabir, E., Elbiaze, H., Sadik, M.: RAT association for autonomic IoT systems. IEEE Netw. 33(6), 116–123 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2019.1800513
Arabi, S., Hammouti, Hel., Sabir, E., Elbiaze, H., Sadik, M.: Lightweight energy-cost-efficient RAT association for Internet of Things. In: the proceedings of 4th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), pp. 332–337 IEEE, Singapore (2018).https://doi.org/10.1109/WF-IoT.2018.8355135
Hsieh, C.-K., Chan, K.-L., Chien, F.-T.: Energy-efficient power allocation and user association in heterogeneous networks with deep reinforcement learning. Appl. Sci. 11(9), 4135–4154 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094135
Ding, H., Zhang, H., Tian, J., Xu, S., Yuan, D.: Energy-efficient user association and power control for dense heterogeneous networks. In: Proceedings of international conference on computing, networking and communications (ICNC), pp. 741–746. IEEE, Maui (2018)
Tayyab, M., Koudouridis, G.P., Gelabert, X., Jantti, R.: Uplink reference signals for energy-efficient handover. IEEE Access. 8, 163060–163076 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3020618
Alsaeedy, A.A.R., Chong, E.K.P.: Mobility management for 5G IoT devices: improving power consumption with lightweight signaling overhead. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(5), 8237–8247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2920628
Zhang, H., Huang, S., Jiang, C., Long, K., Leung, V.C.M., Poor, H.V.: Energy-efficient user association and power allocation in millimeter-wave-based ultra dense networks with energy harvesting base stations. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 35(9), 1936–1947 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2017.2720898
Ghatak, G., Sharma, Y., Zaid, K., Rahman, A.U.: Elastic multi-connectivity in 5G networks. Phys. Commun. 43, 101176–101210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2020.101176
Galinina, O., Andreev, S., Komarov, M., Maltseva, S.: Leveraging heterogeneous device connectivity in a converged 5G-IoT ecosystem. Comput. Netw. 128, 123–132 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2017.04.051
Lee, H., Vahid, S., Moessner, K.: Machine Learning Based RATs Selection Supporting Multi-connectivity for Reliability (Invited Paper). In: Kliks A. et al. (eds) Cognitive Radio-Oriented Wireless Networks. CrownCom 2019. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, pp. 31–41. Springer, Cham (2019)
Giordani, M., Mezzavilla, M., Rangan, S., Zorzi, M.: An efficient uplink multi-connectivity scheme for 5G millimeter-wave control plane applications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 17(10), 6806–6821 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/twc.2018.2864650
Wang, D., Wang, Y., Dong, S., Huang, G., Liu, J., Gao, W.: Exploiting dual connectivity for handover management in heterogeneous aeronautical network. IEEE Access. 7, 62938–62949 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2916920
Khodapanah, B., Hobler, T., Yuncu, B., Barreto, A.N., Simsek, M., Fettweis, G.: Coexistence management for URLLC in campus networks via deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), pp. 1–6. IEEE, Seoul (2020)
Kumar, V., Tyagi, N.: An integrated-multi-RAT framework for multipath-computing in heterogeneous-wireless network. J. Inf. Telecommun. 5(3), 350–374 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/24751839.2021.1871819
Malche, T., Maheshwary, P., Kumar, R.: Environmental monitoring system for smart city based on secure internet of things (IoT) architecture. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 107, 2143–2172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06376-0
Kalajdjieski, J., Stojkoska, B.R., Trivodaliev, K.: IoT based framework for air pollution monitoring in smart cities. In: Proceedings of 28th telecommunications forum (TELFOR), pp. 1–4. IEEE, Belgrade (2020)
Filho, G.P.R., et al.: Enhancing intelligence in traffic management systems to aid in vehicle traffic congestion problems in smart cities. Ad Hoc Netw. 107, 102265–102295 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2020.102265
Sarrab, M., Pulparambil, S., Awadalla, M.: Development of an IoT based real-time traffic monitoring system for city governance. Glob. Trans. 2, 230–245 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.glt.2020.09.004
Singh, S.K., Pan, Y., Park, J.H.: Blockchain-enabled secure framework for energy-efficient smart parking in sustainable city environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 76, 103364 (2022)
Avancini, D.B., Rodrigues, J.J.P.C., Ricardo, A.L.R., Das, A.K., Kozlov, S., Solic, P.: A new IoT-based smart energy meter for smart grids. Int. J. Energy Res. 45, 189–201 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5177
Wang, Y., Chen, Q., Hong, T., Kang, C.: Review of smart meter data analytics: applications, methodologies, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 10(3), 3125–3148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2018.2818167
He, S., Zeng, W., Xie, K., Yang, H., Lai, M., Su, X.: PPNC: privacy preserving scheme for random linear network coding in smart grid. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 11, 1510–1532 (2017)
Varga, N., Piri, E., Bokor, L.: Network-assisted smart access point selection for pervasive real-time mHealth applications. Proc. Comput. Sci. 63, 317–324 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.08.349
Neustadter, D.: Unleash the mobile IoT with secure connectivity powered by integrated SIM. https://www.synopsys.com/designware-ip/technical-bulletin/secure-connectivity-integrated-sim-isim.html (2021). Accessed 26 July 2021
Manjeshwar, A.N., Roy, A., Jha, P., Karandikar.: A control and management of multiple RATs in wireless networks: an SDN approach. In: Proceedings of the 2nd 5G World Forum (5GWF). IEEE, Dresden, pp. 596–601 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/5GWF.2019.8911703
Liberg, O., Sundberg, M., Wang, E., Bergman, J., Sachs, J.: Cellular Internet of Things: Technologies, Standards and Performance. Academic Press, Cambridge (2017)
Khan, L.U., Yaqoob, I., Tran, N.H., Kazmi, S.M.A., Dang, T.N., Hong, C.S.: Edge computing enabled smart cities: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(10), 10200–10232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2987070
Xu, F., Ye, H., Yang, F., Zhao, C.: Software defined mission-critical wireless sensor network: architecture and edge offloading strategy. IEEE Access. 7, 10383–10391 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2890854
Priya, B., Malhotra, J.: QAAs: QoS provisioned artificial intelligence framework for AP selection in next-generation wireless networks. Telecommun. Syst. 76(2), 233–249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-020-00710-9
Gu, K., Wu, N., Yin, B., Jia, W.: Secure data query framework for cloud and fog computing. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 17(1), 332–345 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSM.2019.2941869
Singh, S.K., Park, J.H.: TaLWaR: blockchain-based trust management scheme for smart enterprises with augmented intelligence. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 19(1), 626–634 (2023)
Poirot, V., Ericson, M., Nordberg, M., Andersson, K.: Energy-efficient multi-connectivity algorithms for ultra-dense 5G networks. Wirel. Netw. 26, 2207–2222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02056-w
He, L., Jiang, D., Wei, C.: A QoE-based dynamic energy-efficient network selection algorithm. Wirel. Netw. 27, 3585–3595 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02231-z
Zhou, T., Qin, D., Nie, X., et al.: Coalitional game-based user association integrated with open loop power control for green communications in uplink HCNs. Wirel. Pers. Commun. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08602-0
Xu, X., Huang, Q., Yin, X., Abbasi, M., Khosravi, M.R., Qi, L.: Intelligent offloading for collaborative smart city services in edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(9), 7919–7927 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3000871
Zhang, Z., Li, C., Peng, S., et al.: A new task offloading algorithm in edge computing. J Wirel. Commun. Netw. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-021-01895-6
Qin, Z., Cheng, Z., Lin, C., Lu, Z., Wang, Z.: Optimal workload allocation for edge computing network using application prediction. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5520455
Alamu, O., Gbenga-Ilori, A., Adelabu, M., Imoize, A., Ladipo, O.: Energy efficiency techniques in ultra-dense wireless heterogeneous networks: an overview and outlook. Eng. Sci. Technol. 23(6), 1308–1326 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2020.05.001
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998)
Francois-Lavet, V., Henderson, P., Islam, R., Bellemare, M.G., Pineau, J.: An introduction to deep reinforcement learning. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 11(3–4), 219–354 (2018)
Arulkumaran, K., Deisenroth, M.P., Brundage, M., Bharath, A.A.: Deep reinforcement learning: a brief survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 34(6), 26–38 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2017.2743240
Hasselt, H.V., Guez, A., Silver, D.: Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning . In: Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 2094–2100. Phoneix (2016)
Mollel, M.S., Abubakar, A.I., Ozturk, M., Kaijage, S., Kisangiri, M., Zoha, A., Abbasi, Q.H.: Intelligent handover decision scheme using double deep reinforcement learning. Phys. Commun. 42, 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2020.101133
Zhao, N., Liang, Y.C., Niyato, D., Pei, Y., Wu, M., Jiang, Y.: Deep reinforcement learning for user association and resource allocation in heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 18(11), 5141–5152 (2019)
Bhattacharya, R., et al.: QFlow: a reinforcement learning approach to high QoE video streaming over wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the twentieth ACM international symposium on mobile ad hoc networking and computing, pp. 251–260. ACM, Catania (2019)
Roth, A.E.: A natural experiment in the organization of entry-level labor markets: regional markets for new physicians and surgeons in the United Kingdom. Am. Econ. Rev. 81(3), 415–440 (1991). https://doi.org/10.2307/2006511
Hoessler, T., Schulz, P., Jorswieck, E.A., Simsek, M., Fettweis, G.P.: Stable matching for wireless URLLC in multi-cellular, multi-user systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68(8), 5228–5241 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcomm.2020.2995150
Roth, A.E.: Deferred acceptance algorithms: history, theory, practice, and open questions. Int. J. Game Theory 36, 537–569 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00182-008-0117-6
Martinez, R., Masso, J., Neme, A., Oviedo, J.: An algorithm to compute the full set of many-to-many stable matchings. Math. Soc. Sci. 47(2), 187–210 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mathsocsci.2003.07.002
Chowdhury, S.: Matching theory for cognitive radio networks: an overview. ICT Express. 5(1), 12–15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2018.01.008
Zhang, Q., Liang, Y.-C., Poor, H.V.: Intelligent user association for symbiotic radio networks using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 19(7), 4535–4548 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2020.2984758
Zhang, Q., Lin, M., Yang, L.T., Chen, Z., Khan, S.U., Li, P.: A double deep Q-learning model for energy-efficient edge scheduling. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 12(5), 739–749 (2018)
Zhou, Y., Fadlullah, Z.M., Mao, B., Kato, N.: A deep-learning-based radio resource assignment technique for 5G ultra dense networks. IEEE Netw. 32(6), 28–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2018.1800085
Shang, F., Zhou, D., He, D.: An admission control algorithm based on matching game and differentiated service in wireless mesh networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 32, 2945–2962 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3751-3
Priya, B., Malhotra, J.: An Intelligent User-RAT association for 5G enabled Smart Grid. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computing, power and communication technologies (GUCON). IEEE, Noida, pp. 300–304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/GUCON48875.2020.9231264
Nguyen, D.D., Nguyen, H.X., White, L.B.: Evaluating performance of RAT selection algorithms for 5G HetNets. IEEE Access. 6, 61212–61222 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2875469
Du, Z., Jiang, B., Wu, Q., Xu, Y., Xu, K.: Exploiting User Demand Diversity: QoE Game and MARL Based Network Selection. In: Du, Z. (ed.) Towards User-Centric Intelligent Network Selection in 5G Heterogeneous Wireless Networks, pp. 101–130. Springer, Singapore (2020)
Matlab: Deep Learning Toolbox Design, train, and analyze deep learning networks. https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html (2021). Accessed 8 March 2021
Valiveti, H.B., Polipalli, T.R.: Hierarchy-based knapsack approach for network selection in HetNets. Int. J. Comput. Aided Eng. Technol. 10(5), 599–608 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1504/ijcaet.2018.094340
Acknowledgements
Author would like to thank University Grant Commission, New Delhi for Junior Research Fellowship.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, simulation and analysis were performed by BP. The first draft of the manuscript was written by BP and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Priya, B., Malhotra, J. Intelligent Multi-connectivity Based Energy-Efficient Framework for Smart City. J Netw Syst Manage 31, 48 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-023-09740-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-023-09740-5