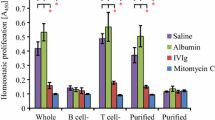
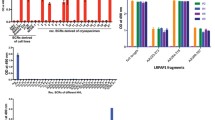
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) has been used to treat autoimmune diseases and lymphoid malignancies with some therapeutic effect. In both these pathological conditions, there is an overproduction of BAFF (for “B-cell-activating factor of the TNF family”), and APRIL (for “a proliferation-inducing ligand”). The presence of antibodies (Abs) with BAFF and APRIL specificities in IVIg preparations was investigated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and Western Blot analysis. Apoptosis was measured by the annexin-V binding method, and confirmed using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling technique. Nonglycosylated recombinant BAFF, glycosylated affinity-purified BAFF, and recombinant APRIL (but not TNFα), were recognized by certain IgG in IVIg, and their F(ab′)2 fragments. Steric hindrance prevented the antiapoptotic effects of BAFF on B-lymphocytes. This work documents the presence of anti-BAFF and anti-APRIL Abs in IVIg. These can functionally neutralize the role of BAFF in B-cell survival. These anti-BAFF IgG might amend deleterious effects of BAFF in B-cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kazatchkine MD, Kaveri SV: Immunomodulation of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases with intravenous immune globulin. N Engl J Med 345:747–755, 2001
Orange JS, Hossny EM, Weiler CR, Ballow M, Berger M, Bonilla FA, et al.: Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in human disease: A review of evidence by members of the Primary Immunodeficiency Committee of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117(Suppl):S525–S553, 2006
Toubi E, Kessel A, Shoenfeld Y: High-dose intravenous immunoglobulins: An option in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol 66:395–402, 2005
Levy Y, Amital H, Langevitz P, Nacci F, Righi A, Conforti L, et al.: Intravenous immunoglobulin modulates cutaneous involvement and reduces skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: An open-label study. Arthritis Rheum 50:1005–1007, 2004
Achiron A, Kishner I, Sarova-Pinhas I, Raz H, Faibel M, Stern Y, et al.: Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment following the first demyelinating event suggestive of multiple sclerosis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Neurol 61:1515–1520, 2004
Chapel H, Dicato M, Gamm H, Brennan V, Ries F, Bunch C, et al.: Immunoglobulin replacement in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A comparison of two dose regimes. Br J Haematol 88:209–212, 1994
Reed JC: Molecular biology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Oncol 25:11–18, 1995
Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 352:804–815, 2005
Sapir T, Shoenfeld Y: Facing the enigma of immunomodulatory effects of intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 29:185–199, 2005
Youinou P, Jamin C, Pers JO, Berthou C, Saraux A, Renaudineau Y: B lymphocytes are required for development and treatment of autoimmune diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci 1050:19–33, 2005
Youinou P, Daridon C, Steinfeld S, Pers JO: A case for B-cells in the pathogenesis of Sjögren's syndrome. Trends Immunol (in press), 2007
Ollila J, Vihinen M: B cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:518–523, 2005
Schneider P, MacKay F, Steiner V, Hofmann K, Bodmer JL, Holler N, et al.: BAFF, a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates B cell growth. J Exp Med 189:1747–1756, 1999
Moore PA, Belvedere O, Orr A, Pieri K, LaFleur DW, Feng P, et al.: BLyS: Member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science 285:260–263, 1999
Shu HB, Hu WH, Johnson H: TALL-1 is a novel member of the TNF family that is down-regulated by mitogens. J Leukoc Biol 65:680–683, 1999
Mukhopadhyay A, Ni J, Zhai Y, Yu GL, Aggarwal BB: Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine, THANK, a TNF homologue that activates apoptosis, nuclear factor-kappaB, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem 274:15978–15981, 1999
Thien M, Phan TG, Gardam S, Amesbury M, Basten A, Mackay F, et al.: Excess BAFF rescues self-reactive B cells from peripheral deletion and allows them to enter forbidden follicular and marginal zone niches. Immunity 20:785–798, 2004
Novak AJ, Bram RJ, Kay NE, Jelinek DF: Aberrant expression of B lymphocyte stimulator by B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: A mechanism for survival. Blood 100:2973–2979, 2002
Krumbholz M, Theil D, Derfuss T, Rosenwald A, Schrader F, Monoranu CM, et al.: BAFF is produced by astrocytes and up-regulated in multiple sclerosis lesions and primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Exp Med 201:195–200, 2005
Hahne M, Kataoka T, Schroter M, Hofmann K, Irmler M, Bodmer JL, et al.: APRIL, a new ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates tumor cell growth. J Exp Med 188:1185–1190, 1998
Zhang J, Roschke V, Baker KP, Wang Z, Alarcon GS, Fessler BJ, et al.: Cutting edge: A role for B lymphocyte stimulator in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 166:6–10, 2001
Matsushita T, Hasegawa M, Yanaba K, Kodera M, Takehara K, Sato S: Elevated serum BAFF levels in patients with systemic sclerosis: Enhanced BAFF signaling in systemic sclerosis B lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum 54:192–201, 2006
Thangarajh M, Gomes A, Masterman T, Hillert J, Hjelmstrom P: Expression of B-cell-activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF) and its receptors in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 152:183–190, 2004
Shoenfeld Y, Krause I: IVIg for autoimmune, fibrosis, and malignant conditions: Our experience with 200 patients. J Clin Immunol 24:107–114, 2004
Nardelli B, Belvedere O, Roschke V, Moore PA, Olsen HS, Migone TS, et al.: Synthesis and release of B-lymphocyte stimulator from myeloid cells. Blood 97:198–204, 2001
Pers JO, Devauchelle V, Bendaoud B, Saraux A, Jamin C, Youinou P: BLyS overexpression is associated with autoantibody production in autoimmune diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci 1050:34–39, 2005
d’Arbonneau F, Pers JO, Devauchelle V, Pennec Y, Saraux A, Youinou P: BAFF-induced changes in B cell antigen receptor-containing lipid rafts in Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 54:115–126, 2006
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CP, Kuijten GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST, van Oers MH: Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 84:1415–1420, 1999
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA: Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501, 1992
Karpusas M, Cachero TG, Qian F, Boriack-Sjodin A, Mullen C, Strauch K, et al.: Crystal structure of extracellular human BAFF, a TNF family member that stimulates B lymphocytes. J Mol Biol 315:1145–1154, 2002
Cao P, Mei JL, Diao ZY, Zhang S: Expression, refolding and characterization of human soluble BAFF synthesized in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 41:199–206, 2005
Kurlander RJ, Hall J: Comparison of intravenous gamma globulin and a monoclonal anti-Fc receptor antibody as inhibitors of immune clearance in vivo in mice. J Clin Invest 77:2010–2018, 1986
Bendtzen K, Svenson M, Hansen M: Autoantibodies to cytokines in IVIG. J Rheumatol 20:2176–2177, 1993
Rossi F, Kazatchkine MD: Antiidiotypes against autoantibodies in pooled normal human polyspecific Ig. J Immunol 143:4104–4109, 1989
De Grandmont MJ, Racine C, Roy A, Lemieux R, Neron S: Intravenous immunoglobulins induce the in vitro differentiation of human B lymphocytes and the secretion of IgG. Blood 101:3065–3073, 2003
Prasad NK, Papoff G, Zeuner A, Bonnin E, Kazatchkine MD, Ruberti G, et al.: Therapeutic preparations of normal polyspecific IgG (IVIg) induce apoptosis in human lymphocytes and monocytes: A novel mechanism of action of IVIg involving the Fas apoptotic pathway. J Immunol 161:3781–3790, 1998
Rossi F, Sultan Y, Kazatchkine MD: Anti-idiotypes against autoantibodies and alloantibodies to VIIIC (anti-haemophilic factor) are present in therapeutic polyspecific normal immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol 74:311–316, 1988
Miletic VD, Hester CG, Frank MM: Regulation of complement activity by immunoglobulin. I. Effect of immunoglobulin isotype on C4 uptake on antibody-sensitized sheep erythrocytes and solid phase immune complexes. J Immunol 156:749–757, 1996
Leusch HG, Sitzler G, Markos-Pusztai S: Failure to demonstrate TNF alpha-specific autoantibodies in human sera by ELISA and Western Blot. J Immunol Methods 139:145–147, 1991
Swenson ER, Robertson HT, Hlastala MP: Effects of carbonic anhydrase inhibition on ventilation-perfusion matching in the dog lung. J Clin Invest 92:702–709, 1993
Avrameas S: Natural autoantibodies: from “horror autotoxicus” to “gnothi seauton.” Immunol Today 12:154–159, 1991
Hansen MB, Svenson M, Abell K, Yasukawa K, Diamant M, Bendtzen K: Influence of interleukin-6 (IL-6) autoantibodies on IL-6 binding to cellular receptors. Eur J Immunol 25:348–354, 1995
Sundblad A, Marcos M, Huetz F, Freitas A, Heusser C, Portnoi D, et al.: Normal serum immunoglobulins influence the numbers of bone marrow pre-B and B cells. Eur J Immunol;21:1155–1161, 1991
Roschke V, Sosnovtseva S, Ward CD, Hong JS, Smith R, Albert V, et al.: BLyS and APRIL form biologically active heterotrimers that are expressed in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic diseases. J Immunol 169:4314–4321, 2002
Bröker BM, Klajman A, Youinou P, Jouquan J, Worman CP, Murphy J, et al.: Chronic lymphocytic leukemic (CLL) cells secrete multispecific autoantibodies. J Autoimmun 1:469–481, 1988
Collins CE, Gavin AL, Migone TS, Hilbert DM, Nemazee D, Stohl W. B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) isoforms in systemic lupus erythematosus: Disease activity correlates better with blood leukocyte BLyS mRNA levels than with plasma BLyS protein levels. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R6, 2006
Kern C, Cornuel JF, Billard C, Tang R, Rouillard D, Stenou V, et al.: Involvement of BAFF and APRIL in the resistance to apoptosis of B-CLL through an autocrine pathway. Blood 103:679–688, 2004
Kalled SL: BAFF: a novel therapeutic target for autoimmunity. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3:1005–1011, 2002
Daridon C, Youinou P, Pers JO: BAFF, APRIL, TWE-PRIL: Who's who? Autoimmun Rev (in press), 2007
Kalled SL, Ambrose C, Hou YM: The biochemistry and biology of BAFF, APRIL and their receptors. Curr Dir Autoimmun 8:206–242, 2005
Krause I, Blank M, Sherer Y, Gilburd B, Kvapil F, Shoenfeld Y: Induction of oral tolerance in experimental antiphospholipid syndrome by feeding with polyclonal immunoglobulins. Eur J Immunol 32:3414–3424, 2002
Shoenfeld Y, Rauova L, Gilburd B, Kvapil F, Goldberg I, Kopolovic J, Rovensky J, Blank M. Efficacy of IVIG affinity-purified anti-double-stranded DNA anti-idiotypic antibodies in the treatment of an experimental murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunol 14:1303–1311, 2002
Fu L, Lin-Lee YC, Pham LV, Tamayo A, Yoshimura L, Ford RJ: Constitutive NF-kappaB and NFAT activation leads to stimulation of the BLyS survival pathway in aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Blood 107:4540–4548, 2006
Lamoureux J, Aubin E, Lemieux R: Autoantibodies purified from therapeutic preparations of intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) induce the formation of autoimmune complexes in normal human serum: A role in the in vivo mechanisms of action of IVIg? Int Immunol 16:929–936, 2004
Ware CF: APRIL and BAFF connect autoimmunity and cancer. J Exp Med 192:F35–F37, 2000
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Cindy Séné and Simone Forest for their help with editing of this manuscript. Thanks are also due to Professor Peter M. Lydyard (London, UK) for critical reading of the text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le pottier, L., Bendaoud, B., Dueymes, M. et al. BAFF, a New Target for Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Autoimmunity and Cancer. J Clin Immunol 27, 257–265 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9082-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9082-2