Abstract
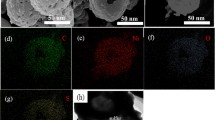
Hollow amorphous CoS was synthesized via a sulfidation of zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67), which possessed the characters of physical entrapment and chemical interaction between sulfur species. The prepared hollow amorphous CoS possessed high initial capacity of 1276 mAh·g−1 at 0.2 C and reversible capacity of 812 mAh·g−1 after 120 cycles, which was better than common CoS nanoparticles. What's more, it still delivered 606 mAh·g−1 during 200 cycles at 1 C with an average coulombic efficiency of about 98.2%. These above results indicated that the hollow amorphous CoS possessed great potential as the cathode of high-performance Li–S battery.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
A. Manthiram, Y. Fu, Y.-S. Su, Challenges and prospects of lithium–sulfur batteries. Acc. Chem. Res. 46(5), 1125–1134 (2002)
P.G. Bruce, S.A. Freunberger, L.J. Hardwick, Li-O2 and Li–S batteries with high energy storage. Nat. Mater. 11(1), 19–29 (2012)
Z.W. Seh, Y. Sun, Q. Zhang, Designing high-energy lithium–sulfur batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45(20), 5605–5634 (2016)
J. Hassoun, B. Scrosati, A high-performance polymer tin sulfur lithium ion battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49(13), 2371–2374 (2010)
G. Zhou, D.W. Wang, F. Li, A flexible nanostructured sulphur–carbon nanotube cathode with high rate performance for Li–S batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 5(10), 8901–8906 (2012)
H.J. Peng, Q. Zhang, Designing host materials for sulfur cathodes: from physical confinement to surface chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54(38), 11018–11020 (2015)
L. Xiao, Y. Cao, J. Xiao, A soft approach to encapsulate sulfur: polyaniline nanotubes for lithium–sulfur batteries with long cycle life. Adv. Mater. 24(9), 1176–1181 (2012)
M. Yu, J. Ma, H. Song, Atomic layer deposited TiO2 on a nitrogen-doped graphene/sulfur electrode for high performance lithium–sulfur batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 9(4), 1495–1503 (2016)
G. Zhou, L. Li, D.W. Wang, A flexible sulfur–graphene–polypropylene separator integrated electrode for advanced Li–S batteries. Adv. Mater. Technol. 27(4), 641–647 (2015)
R. Singhal, S.H. Chung, A. Manthiram, A free-standing carbon nanofiber interlayer for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(8), 4530–4538 (2015)
L. Suo, Y.S. Hu, H. Li, A new class of solvent-in-salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries. Nat. Commun. 4, 1481–1481 (2012)
M.L. Gordin, F. Dai, S. Chen, Bis (2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl) ether as an electrolyte co-solvent for mitigating self-discharge in lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(11), 8006–8010 (2014)
W. Xu, J. Wang, F. Ding, Lithium metal anodes for rechargeable batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 7(2), 513–537 (2014)
Z. Lin, Z. Liu, W. Fu, Phosphorous pentasulfide as a novel additive for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23(8), 1064–1069 (2013)
M.J. Lacey, F. Jeschull, K. Edström, Functional, water-soluble binders for improved capacity and stability of lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources 264, 8–14 (2014)
S.E. Cheon, J.H. Cho, K.S. Ko, Structural factors of sulfur cathodes with poly (ethylene oxide) binder for performance of rechargeable lithium sulfur batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149(11), A1437–A1441 (2002)
H.B. Zhang, C. Wu, Yuan, Confining sulfur in double-shelled hollow carbon spheres for lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 124(38), 9730–9733 (2012)
S. Moon, Y.H. Jung, W.K. Jung, Encapsulated monoclinic sulfur for stable cycling of Li–S rechargeable batteries. Adv. Mater. 25(45), 6547–6553 (2013)
Z. Li, H.B. Wu, X.W.D. Lou, Rational designs and engineering of hollow micro-/nanostructures as sulfur hosts for advanced lithium–sulfur batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 9(10), 3061–3070 (2016)
W. Zhou, X. Xiao, M. Cai, Polydopamine-coated, nitrogen-doped, hollow carbon–sulfur double-layered core–shell structure for improving lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 14(9), 5250–5256 (2014)
Y. Xie, L. Fang, H. Cheng, Biological cell derived N-doped hollow porous carbon microspheres for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(40), 15612–15620 (2016)
X. Li, Y. Lu, Z. Hou, SnS2-compared to SnO2-stabilized S/C composites toward high-performance lithium sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(30), 19550–19557 (2016)
Z.F. Huang, J. Song, K. Li, Hollow cobalt-based bimetallic sulfide polyhedra for efficient all-pH-value electrochemical and photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(4), 1359–1365 (2016)
R. Wu, X. Qian, K. Zhou, Porous spinel ZnxCo3−xO4 hollow polyhedra templated for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 8(6), 6297–6303 (2014)
R. Wu, D.P. Wang, X. Rui, In situ formation of hollow hybrids composed of cobalt sulfides embedded within porous carbon polyhedra/carbon nanotubes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 27(19), 3038–3044 (2015)
N.L. Torad, R.R. Salunkhe, Y. Li, Electric double-layer capacitors based on highly graphitized nanoporous carbons derived from ZIF-67. Chem. Eur. J. 20(26), 7895–7900 (2014)
Z. Liu, X. Zheng, S. Luo, High performance Li–S battery based on amorphous NiS2 as the host material for the S cathode. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(35), 13395–13399 (2016)
J. Zhou, N. Lin, W. Long Cai, Synthesis of S/CoS2 nanoparticles-embedded N-doped carbon polyhedrons from polyhedrons ZIF-67 and their properties in lithium–sulfur batteries. Electrochim. Acta 218, 243–251 (2016)
H. Hu, B.Y. Guan, X.W.D. Lou, Construction of complex CoS hollow structures with enhanced electrochemical properties for hybrid supercapacitors. Chem 1(1), 102–113 (2016)
G.F. Khudorozhko, I.P. Asanov, L.N. Mazalov, The study of electronic structure of molybdenum and tungsten trisulfides and their lithium intercalates by X-ray electron and X-ray emission and absorption spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 68, 199–209 (1994)
T. Lei, W. Chen, J. Huang, Multi-functional layered WS2 nanosheets for enhancing the performance of lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 7(4), 1601843–1601847 (2017)
J. Liu, Y. Xing, X. Liu, Hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of nanoplate-assembled hierarchical structured Co1−xS microrods. Mater. Charact. 67, 112–118 (2012)
Q. Liu, J. Zhang, A general and controllable synthesis of ComSn (Co9S8, Co3S4, and Co1−xS) hierarchical microspheres with homogeneous phases. CrystEngComm 15(25), 5087–5092 (2013)
X. Gu, C. Lai, F. Liu, A conductive interwoven bamboo carbon fiber membrane for Li–S batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(18), 9502–9509 (2015)
D.H. Han, B.S. Kim, S.J. Choi, Time-resolved in situ spectroelectrochemical study on reduction of sulfur in N, N′-dimethylformamide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151(9), E283–E290 (2004)
Y. Zu, A. Fu, Manthiram, Highly reversible Li/dissolved polysulfide batteries with binder-free carbon nanofiber electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 1(35), 10362–10367 (2013)
H. Li, X. Yang, X. Wang, Dense integration of graphene and sulfur through the soft approach for compact lithium/sulfur battery cathode. Nano Energy 12, 468–475 (2015)
S.Y. Zheng, Y. Wen, Y.J. Zhu, In situ sulfur reduction and intercalation of graphite oxides for Li–S battery cathodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 482–491 (2014)
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52003239), the Science Foundation of Yancheng Institute of Technology (No. xjr2019031), the Science Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (ZSTU) (Nos. 11152932612005 and 11150131722006), and Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2021C01074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY: Investigation, Data curation, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing—review and editing. YY, XG, and ZL: Formal analysis and discussion. SL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Supervision, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Zhang, L., Yan, Y. et al. Hollow amorphous CoS to reversible storage sulfur as cathode of Li–S battery. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 20479–20486 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08862-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08862-x