Abstract
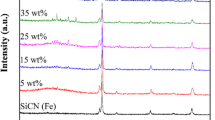
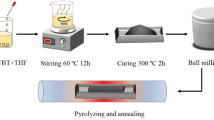
Polymer-derived SiCN ceramics containing cobalt was prepared with SiCN ceramics as matrix and cobalt nanoparticles as doping phase. Phase composition, Raman analysis, electromagnetic parameters and microwave absorption properties of SiCN ceramics with different cobalt content pyrolyzed at 1100 ℃ and cobalt content of 2 wt% but different pyrolysis temperature were carried out. The microstructures and magnetic properties of SiCN ceramics with cobalt content of 2 wt% and pyrolysis temperature of 900 ℃ were analyzed. The results show that some cobalt particles can react with carbon to form magnetic Co3C particles, which is one of the reasons for the magnetism of the sample. The good dielectric property of SiCN ceramics matches the magnetic property, which makes the material have excellent microwave absorption property. When the cobalt content is 2 wt% and the pyrolysis temperature is 900 ℃, the sample has the best microwave absorption performance. The minimum RL reaches − 10.9 at about 15 GHz, and the effective absorption bandwidth (RL < − 10 dB) is 3.3 GHz with a thickness of 3 mm. When the thickness became 6 mm, the minimum RL of the sample can reach − 11.8 dB and the effective absorption bandwidth (RL < − 10 dB) is 4.2 GHz, showing the excellent microwave absorption performance of materials we obtained.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Balci, E.O. Polat, N. Kakenov et al., Graphene-enabled electrically switchable radar-absorbing surfaces. Nat. Commun. 6, 6628 (2015)
L. Long, W. Zhou, P. Xiao et al., Microwave absorption properties of SiO2 doped furan resin derived carbon particles. J. Mater. Sci. 30(4), 3359–3364 (2019)
Z. Teng, S. Zeng, W. Feng et al., Facile synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Fe-Fe3C@C composites. J. Mater. Sci. 30(15), 14573–14579 (2019)
S.M. Abbas, R. Chatterjee, A.K. Dixit et al., Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of (Co2+–Si4+) substituted barium hexaferrites and its polymer composite. J. Appl. Phys. 101(7), 074105 (2007)
Z. Chen, C. Xu, C. Ma et al., Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 25(9), 1296–1300 (2013)
C.Y. Lee, H.G. Song, K.S. Jang et al., Electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency of polyaniline mixtures and multilayer films. Synth. Met. 102(1–3), 1346–1349 (1999)
B. Wen, Reduced graphene oxides light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 26(21), 3484–3489 (2014)
M.S. Cao, W.L. Song, Z.L. Hou et al., The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 48(3), 788–796 (2010)
X.L. Shi, M.S. Cao, J. Yuan et al., Dual nonlinear dielectric resonance and nesting microwave absorption peaks of hollow cobalt nanochains composites with negative permeability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(16), 163108 (2009)
P. Meng, K. Xiong, L. Wang et al., Tunable complex permeability and enhanced microwave absorption properties of BaNixCo1–xTiFe10O19. J. Alloys Compd. 628, 75–80 (2015)
M.S. Cao, J. Yang, W.L. Song et al., Ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube vs polyaniline/ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube multiheterostructures for highly effective microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4(12), 6949–6956 (2012)
H. Yang, M. Cao, Y. Li et al., Enhanced dielectric properties and excellent microwave absorption of SiC powders driven with NiO nanorings. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2(3), 214–219 (2014)
W. Wang, M. Cao, Ni3Sn2 alloy nanocrystals encapsulated within electrospun carbon nanofibers for enhanced microwave absorption performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 177, 198–205 (2016)
W.Q. Cao, X.X. Wang, J. Yuan et al., Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 3(38), 10017–10022 (2015)
B. Wen, M.S. Cao, Z.L. Hou et al., Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 65, 124–139 (2013)
S.I. Andronenko, A. Leo, I. Stiharu et al., EPR/FMR investigation of Mn-doped SiCN ceramics. Appl. Magn. Reson. 39(4), 347–356 (2010)
C. Zhou, L. Yang, H. Geng et al., Preparation of Si–C–N–Fe magnetic ceramic derived from iron-modified polysilazane. Ceram. Int. 38(8), 6815–6822 (2012)
Y. Liu, Y. Feng, H. Gong et al., Microwave absorbing performance of polymer-derived SiCN (Ni) ceramics prepared from different nickel sources. J. Alloys Compd. 749, 620–627 (2018)
X. Guo, Y. Feng, Y. Liu et al., Cross-linking behavior and dielectric properties of SiCN precursor. Ceram. Int. 43(18), 16866–16871 (2017)
P. Colombo, R. Riedel, G.D. Sorarù et al., Historical review of the development of polymer derived ceramics (PDCs), Polymer Dervied Ceramics: From Nanostructure to Apllications (DEStech Publictions Inc., Lancaster, 2009), pp. 1–12
S.J. Byun, H. Lim, G.Y. Shin et al., Graphenes converted from polymers. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(5), 493–497 (2011)
P. Colombo, G. Mera, R. Riedel et al., Polymer-derived ceramics: 40 years of research and innovation in advanced ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(7), 1805–1837 (2010)
L. Dong-Duk, L. Suk-Joong, D.N. Kang, Mechanism of Grain Growth and α-β’Transformation During Liquid-Phase Sintering of β′-Sialon (Ceramic Society, Pittsburgh, 1988)
W. Verbeek, Production of shaped articles of homogeneous mixtures of silicon carbide and nitride: U.S. Patent 3,853,567. 1974-12-10
K.R. Lai, T.Y. Tien, Kinetics of β-Si3N4 grain growth in Si3N4 ceramics sintered under high nitrogen pressure. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76(1), 91–96 (1993)
X. Wang, M. Yu, W. Zhang et al., Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of graphene/nickel composite materials. Appl. Phys. A 118(3), 1053–1058 (2015)
M. Qin, D. Lan, G. Wu et al., Sodium citrate assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nickel cobaltate absorbers with tunable morphology and complex dielectric parameters toward efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 144480 (2019)
A. Afzali, V. Mottaghitalab, S.S.S. Afghahi et al., Electromagnetic properties of absorber fabric coated with BaFe12O19/MWCNTs/PANi nanocomposite in X and Ku bands frequency. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 442, 224–230 (2017)
Y.H. Zou, H.B. Liu, L. Yang et al., The influence of temperature on magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Fe/graphite oxide nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302(2), 343–347 (2006)
Y. Lu, Y. Wang, H. Li et al., MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(24), 13604–13611 (2015)
H. Liang, J. Liu, Y. Zhang et al., Ultra-thin broccoli-like SCFs@TiO2 one-dimensional electromagnetic wave absorbing material. Composites B 178, 107507 (2019)
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, X. Zhao et al., Insights into size-dominant magnetic microwave absorption properties of CoNi microflowers via off-axis electron holography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(7), 4233–4240 (2015)
Q. Su, J. Li, G. Zhong et al., In situ synthesis of iron/nickel sulfide nanostructures-filled carbon nanotubes and their electromagnetic and microwave-absorbing properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(5), 1838–1842 (2011)
G. Li, T. Xie, S. Yang et al., Microwave absorption enhancement of porous carbon fibers compared with carbon nanofibers. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(16), 9196–9201 (2012)
C. Yan, X. Cheng, Y. Zhang et al., Ferromagnetism and microwave electromagnetism of iron-doped titanium nitride nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(49), 26006–26012 (2012)
Y.J. Chen, F. Zhang, G. Zhao et al., Synthesis, multi-nonlinear dielectric resonance, and excellent electromagnetic absorption characteristics of Fe3O4/ZnO core/shell nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(20), 9239–9244 (2010)
J. Liu, H. Liang, Y. Zhang et al., Facile synthesis of ellipsoid-like MgCo2O4/Co3O4 composites for strong wideband microwave absorption application. Composites B 176, 107240 (2019)
F. Yu, H. Deng, Q. Zhang, et al, Anisotropic multilayer conductive networks in carbon nanotubes filled polyethylene/polypropylene blends obtained through high speed thin wall injection molding. Polymer 54(23), 6425–6436 (2013)
D. Lan, M. Qin, J. Liu et al., Novel binary cobalt nickel oxide hollowed-out spheres for electromagnetic absorption applications. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 122797 (2020)
M. Cao, X. Wang, W. Cao et al., Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 14(29), 1800987 (2018)
H.J. Yang, W.Q. Cao, D.Q. Zhang et al., NiO hierarchical nanorings on SiC: enhancing relaxation to tune microwave absorption at elevated temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(13), 7073–7077 (2015)
M. Wu, Y.D. Zhang, S. Hui, et al, Microwave magnetic properties of Co50/(SiO2)50 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80(23), 4404–4406 (2002)
H. Wu, D. Lan, B. Li et al., High-entropy alloy@air@Ni–NiO core-shell microspheres for electromagnetic absorption applications. Composites B 179, 107524 (2019)
H. Nikmanesh, M. Moradi, G.H. Bordbar et al., Effect of multi dopant barium hexaferrite nanoparticles on the structural, magnetic, and X-Ku bands microwave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 708, 99–107 (2017)
S. Chang, S. Kangning, C. Pengfei, Microwave absorption properties of Ce-substituted M-type barium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(5), 802–805 (2012)
Z. Zhang, X. Liu, X. Wang et al., Effect of Nd–Co substitution on magnetic and microwave absorption properties of SrFe12O19 hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 525, 114–119 (2012)
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B. Fan et al., Facile preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of core–shell composite spheres composited of Ni cores and TiO2 shells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(14), 8802–8810 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 51572154).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Lin, X., Ashfaq, M.Z. et al. Microwave absorption properties of SiCN ceramics doped with cobalt nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 3803–3816 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02912-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02912-y