Abstract
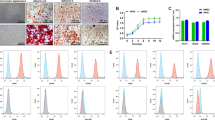
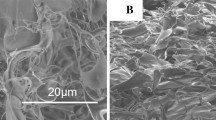
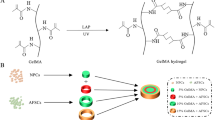
The stem cell-based therapeutic approaches for intervertebral disc regeneration are thought to have promising attention in the treatment of degenerative disc disease, which is closely related to lower back pain. In this study, we developed a Gefitinib small molecules-crosslinked blended chitosan/collagen type 1 biopolymeric hydrogel (Ge-CS/COL-I) that can be injected and exhibit better in-situ processability than bare hydrogels, while conserving the ability to direct differentiation of nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs). The blended injectable hydrogel was explored as a cell carrier and scaffold for nucleus pulposus (NP) tissue engineering because of its biocompatibility, adaptable qualities, and microporous architecture. The prepared hydrogel system might be delivered effectively using a minimally invasive method, and its mechanical properties could be tailored to match the rigidity of the native human nucleus pulposus, according to oscillatory rheology ability. The most of the cellular components were eliminated, although the extracellular matrix and microstructure were substantially retained, according to histopathological and DAPI staining observations using fluorescence microscopic method. The ability of NPMSCs-loaded hydrogel to regenerate degenerated NP in a rat model was investigated in vivo. The findings indicate that NPMSC could cause differentiation in blended hydrogel in vivo and were greatly biocompatible. At eight weeks following injection, the disc height index and MRI index of NPMSCs-loaded hydrogel groups have both been noticeably higher than those of the other control groups. After eight weeks, immunofluorescence and histological staining revealed that the NPMSCs-loaded hydrogel had also partially repaired the structure and ECM content of the degraded NP. Combined, our results demonstrate that a hydrogel system has a great deal of potential for NPMSC administration for promoting IVD regeneration in the rat model.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data and code availability
Not applicable.
References
Vadalà G, Russo F, Ambrosio L, Loppini M, Denaro V (2016) Stem cells sources for intervertebral disc regeneration. World J Stem Cells 8:185–201. https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i5.185
Khandaker M, Riahanizad S (2017) Evaluation of electrospun nanofiber-Anchored silicone for the degenerative intervertebral disc. J Healthc Eng 2017:5283846. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5283846
Li C, Chen J, Lv Y, Liu Y, Guo Q, Wang J et al (2022) Recent progress in electrospun nanofiber-based degenerated intervertebral disc repair. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 8:16–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00970
Uysal O, Arslan E, Gulseren G, Kilinc MC, Dogan I, Ozalp H et al (2019) Collagen peptide presenting nanofibrous scaffold for intervertebral disc regeneration. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2:1686–1695. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.9b00062
Melrose J (2016) Strategies in regenerative medicine for intervertebral disc repair using mesenchymal stem cells and bioscaffolds. Regen Med 11:705–724. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2016-0069
Sampara P, Banala RR, Vemuri SK, Av GR, Gpv S (2018) Understanding the molecular biology of intervertebral disc degeneration and potential gene therapy strategies for regeneration: a review. Gene Ther 25:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-018-0004-0
Peng Y, Huang D, Liu S, Li J, Qing X, Shao Z (2020) Biomaterials-induced stem cells specific differentiation into intervertebral disc lineage cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00056
Gullbrand SE, Schaer TP, Agarwal P, Bendigo JR, Dodge GR, Chen W et al (2017) Translation of an injectable triple-interpenetrating-network hydrogel for intervertebral disc regeneration in a goat model. Acta Biomater 60:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2017.07.025
Wang F, Nan LP, Zhou SF, Liu Y, Wang ZY, Wang JC et al (2019) Injectable hydrogel combined with nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of degenerative intervertebral disc in rats. Stem Cells Int 2019:8496025. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8496025
Brown C, McKee C, Bakshi S, Walker K, Hakman E, Halassy S et al (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells: cell therapy and regeneration potential. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 13:1738–1755. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2914
Richardson SM, Hughes N, Hunt JA, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA (2008) Human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to NP-like cells in chitosan-glycerophosphate hydrogels. Biomaterials 29:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.09.018
Li X, Wu A, Han C, Chen C, Zhou T, Zhang K et al (2019) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional co-culture attenuate degeneration of nucleus pulposus cells. Aging (Albany NY) 11:9167–9187. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102390
Hu A, Xing R, Jiang L, Li Z, Liu P, Wang H et al (2020) Thermosensitive hydrogels loaded with human-induced pluripotent stem cells overexpressing growth differentiation factor-5 ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. J Biomed Mater Res-Part B Appl Biomater 108:2005–2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.34541
Liu S, Zhou J, Zhang X, Liu Y, Chen J, Hu B et al (2016) Strategies to optimize adult stem cell therapy for tissue regeneration. Int J Mol Sci 17:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060982
Migliorini F, Rath B, Tingart M, Baroncini A, Quack V, Eschweiler J (2019) Autogenic mesenchymal stem cells for intervertebral disc regeneration. Int Orthop 43:1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4218-y
Thorpe AA, Boyes VL, Sammon C, Le Maitre CL (2016) Thermally triggered injectable hydrogel, which induces mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to nucleus pulposus cells: potential for regeneration of the intervertebral disc. Acta Biomater 36:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.03.029
Vadalà G, Ambrosio L, Russo F, Papalia R, Denaro V (2019) Interaction between mesenchymal stem cells and intervertebral disc microenvironment: from cell therapy to tissue engineering. Stem Cells Int 2019:2376172. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2376172
Eivazzadeh-Keihan R, Khalili F, Aliabadi HAM, Maleki A, Madanchi H, Ziabari EZ et al (2020) Alginate hydrogel-polyvinyl alcohol/silk fibroin/magnesium hydroxide nanorods: a novel scaffold with biological and antibacterial activity and improved mechanical properties. Int J Biol Macromol 162:1959–1971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.090
Ghorbani F, Li D, Ni S, Zhou Y, Yu B (2020) 3D printing of acellular scaffolds for bone defect regeneration: a review. Mater Today Commun 22:100979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.100979
Kluczka J, Dudek G, Kazek-Kęsik A, Gnus M (2019) Chitosan hydrogel beads supported with ceria for boron removal. Int J Mol Sci 20:1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071567
Deng A, Kang X, Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang S (2017) Enhanced gelation of chitosan/β-sodium glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel with sodium bicarbonate and biocompatibility evaluated. Mater Sci Eng C 78:1147–1154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.04.109
Liu J, Yang B, Li M, Li J, Wan Y (2020) Enhanced dual network hydrogels consisting of thiolated chitosan and silk fibroin for cartilage tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym 227:115335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115335
Zhao YZ, Jiang X, Xiao J, Lin Q, Yu WZ, Tian FR et al (2016) Using NGF heparin-poloxamer thermosensitive hydrogels to enhance the nerve regeneration for spinal cord injury. Acta Biomater 29:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.10.014
Zhao Y, Zhu B, Xu H, Du F, Lei F, Tan X et al (2020) Temperature-induced structural changes of biocompatible crystallizable rosin polymer in solution and hydrogel. J Mol Liq 320:114512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114512
Li T, Song X, Weng C, Wang X, Gu L, Gong X et al (2019) Silk fibroin/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel with tunable biomechanical properties has application potential as cartilage scaffold. Int J Biol Macromol 137:382–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.245
Tan W, Krishnaraj R, Desai TA (2001) Evaluation of nanostructured composite collagen-Chitosan matrices for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng 7:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1089/107632701300062831
Pupkaite J, Rosenquist J, Hilborn J, Samanta A (2019) Injectable shape-holding collagen hydrogel for cell encapsulation and delivery cross-linked using thiol-michael addition click reaction. Biomacromol 20:3475–3484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00769
Deepthi S, Nivedhitha Sundaram M, Deepti Kadavan J, Jayakumar R (2016) Layered chitosan-collagen hydrogel/aligned PLLA nanofiber construct for flexor tendon regeneration. Carbohydr Polym 153:492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.124
Moreira CDF, Carvalho SM, Mansur HS, Pereira MM (2016) Thermogelling chitosan-collagen-bioactive glass nanoparticle hybrids as potential injectable systems for tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 58:1207–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.09.075
Bhardwaj N, Nguyen QT, Chen AC, Kaplan DL, Sah RL, Kundu SC (2011) Potential of 3-D tissue constructs engineered from bovine chondrocytes/silk fibroin-chitosan for in vitro cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 32:5773–5781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.04.061
Filion D, Lavertu M, Buschmann MD (2007) Ionization and solubility of chitosan solutions related to thermosensitive chitosan/glycerol-phosphate systems. Biomacromol 8:3224–3234. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm700520m
Cheng Y-H, Chen Y-C, Yang S-H, Yang K-C, Wu S-C, Su W-Y et al (2010) Thermosensitive chitosan–Gelatin–glycerol phosphate hydrogels as a cell carrier for nucleus pulposus. TISSUE Eng Part A 16:695–703
Dang JM, Sun DDN, Shin-Ya Y, Sieber AN, Kostuik JP, Leong KW (2006) Temperature-responsive hydroxybutyl chitosan for the culture of mesenchymal stem cells and intervertebral disk cells. Biomaterials 27:406–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.07.033
Pan Z, Sun H, Xie B, Xia D, Zhang X, Yu D et al (2018) Therapeutic effects of gefitinib-encapsulated thermosensitive injectable hydrogel in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomaterials 160:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.01.016
Sun B, Lian M, Han Y, Mo X, Jiang W, Qiao Z et al (2021) A 3D-Bioprinted dual growth factor-releasing intervertebral disc scaffold induces nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus reconstruction. Bioact Mater 6:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.06.022
Xia K, Zhu J, Hua J, Gong Z, Yu C, Zhou X et al (2019) Intradiscal injection of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived nucleus pulposus-like cell-seeded polymeric microspheres promotes rat disc regeneration. Stem Cells Int 2019:6806540. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6806540
Nagae M, Ikeda T, Mikami Y, Hase H, Ozawa H, Matsuda KI et al (2007) Intervertebral disc regeneration using platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres. Tissue Eng 13:147–158. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.2006.0042
Alinejad Y, Adoungotchodo A, Grant MP, Epure LM, Antoniou J, Mwale F et al (2019) Injectable chitosan hydrogels with enhanced mechanical properties for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Tissue Eng-Part A 25:303–313. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2018.0170
Feng G, Zhang Z, Dang M, Zhang X, Doleyres Y, Song Y et al (2017) Injectable nanofibrous spongy microspheres for NR4A1 plasmid DNA transfection to reverse fibrotic degeneration and support disc regeneration. Biomaterials 131:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.03.029
Liu Y, Li Y, Huang ZN, Wang ZY, Nan LP, Wang F et al (2019) The effect of intervertebral disc degenerative change on biological characteristics of nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cell: an in vitro study in rats. Connect Tissue Res 60:376–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/03008207.2019.1570168
Jia J, Wang SZ, Ma LY, Yu JB, Guo YD, Wang C (2018) The differential effects of leukocyte-containing and pure platelet-rich plasma on nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells: implications for the clinical treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Stem Cells Int 2018:7162084. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7162084
Wan S, Borland S, Richardson SM, Merry CLR, Saiani A, Gough JE (2016) Self-assembling peptide hydrogel for intervertebral disc tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 46:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.09.033
Lai A, Gansau J, Gullbrand SE, Crowley J, Cunha C, Dudli S et al (2021) Development of a standardized histopathology scoring system for intervertebral disc degeneration in rat models: an initiative of the ORS spine section. JOR Spine 4:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsp2.1150
Bouhsina N, Decante C, Hardel JB, Rouleau D, Abadie J, Hamel A et al (2022) Comparison of MRI T1, T2, and T2* mapping with histology for assessment of intervertebral disc degeneration in an ovine model. Sci Rep 12:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09348-w
Ng TT, Mak KHM, Popp C, Ng RK (2020) Murine mesenchymal stromal cells retain biased differentiation plasticity towards their tissue of origin. Cells 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030756
Borghese C, Cattaruzza L, Pivetta E, Normanno N, De Luca A, Mazzucato M et al (2013) Gefitinib inhibits the cross-talk between mesenchymal stem cells and prostate cancer cells leading to tumor cell proliferation and inhibition of docetaxel activity. J Cell Biochem 114:1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24456
Liu S, Liang H, Lee SM, Li Z, Zhang J, Fei Q (2017) Isolation and identification of stem cells from degenerated human intervertebral discs and their migration characteristics. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 49:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmw121
Wu H, Zeng X, Yu J, Shang Y, Tu M, Cheang LH et al (2017) Comparison of nucleus pulposus stem/progenitor cells isolated from degenerated intervertebral discs with umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res 361:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.10.034
Friedmann A, Baertel A, Schmitt C, Ludtka C, Milosevic J, Meisel HJ et al (2021) Intervertebral disc regeneration injection of a cell-loaded collagen hydrogel in a sheep model. Int J Mol Sci 22:4248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084248
Kumar D, Lyness A, Gerges I, Lenardi C, Forsyth NR, Liu Y (2016) Stem cell delivery with polymer hydrogel for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: From 3D culture to design of the delivery device for minimally invasive therapy. Cell Transplant 25:2213–2220. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368916X692618
Ding J, Zhang R, Li H, Ji Q, Cheng X, Thorne RF, Hondermarck H, Liu X, Shen C (2021) ASIC1 and ASIC3 mediate cellular senescence of human nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells during intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging 13(7):10703–10723. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202850
Liu J, Tao H, Wang H, Dong F, Zhang R, Li J et al (2017) Biological behavior of human nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells in response to changes in the acidic environment during intervertebral disc degeneration. Stem Cells Dev 26:901–911. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2016.0314
Tsaryk R, Gloria A, Russo T, Anspach L, De Santis R, Ghanaati S et al (2015) Collagen-low molecular weight hyaluronic acid semi-interpenetrating network loaded with gelatin microspheres for cell and growth factor delivery for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Acta Biomater 20:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.03.041
Tellegen AR, Rudnik-Jansen I, Beukers M, Miranda-Bedate A, Bach FC, de Jong W et al (2018) Intradiscal delivery of celecoxib-loaded microspheres restores intervertebral disc integrity in a preclinical canine model. J Control Release 286:439–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.08.019
Frith JE, Cameron AR, Menzies DJ, Ghosh P, Whitehead DL, Gronthos S et al (2013) An injectable hydrogel incorporating mesenchymal precursor cells and pentosan polysulphate for intervertebral disc regeneration. Biomaterials 34:9430–9440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.072
Liang CZ, Li H, Tao YQ, Peng LH, Gao JQ, Wu JJ et al (2013) Dual release of dexamethasone and TGF-β3 from polymeric microspheres for stem cell matrix accumulation in a rat disc degeneration model. Acta Biomater 9:9423–9433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2013.08.019
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Key Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Provincial Department of Education (No. KJ2021A0802), PR China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GX and KZ–Conception and experimental design; YY and PZ–Experimental analyses and carrying out measurements; ZB–Formal analysis and results interpretations; CZ*–Supervision and manuscript composition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflict of interest for the present investigation.
Ethical approval
The US National Institutes of Health's Laboratory Animals published protocol followed to conduct experiments of animal care and use. The laboratory Animal Management and Ethics Committee of Bengbu Medical College (Ethical number:2022-0294) provided consent approval to all animal experiments.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Annela M. Seddon.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Zhu, K., Ye, Y. et al. Systemic therapeutic investigation of transplanting nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells embedded on Gefitinib-chitosan/collagen blended injectable hydrogels to the intervertebral disc regeneration treatment using a rat model. J Mater Sci 58, 14480–14499 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08918-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08918-1