Abstract
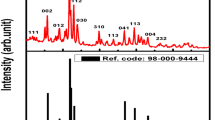
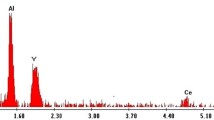
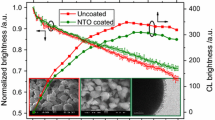
In this paper, we have proved the possibility of improving the emissive properties of cerium, Ce3+, activated yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG:Ce) phosphor both by internally modifying the lattice parameters as a result of adding a codopant and by external silanization of the phosphor particle's surface. The addition of codopant in the form of gadolinium, Gd3+, ions was performed using the method of concomitant precipitation of metal cations. The silanization of phosphor was achieved by activating the surface and cross-linking of the (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane molecules. By FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction, we have assessed the influence of internal and external modifications on the structure of phosphor. At the same time, the optical properties using fluorescence spectroscopy were evaluated. The analysis of modified phosphor samples confirmed the improvement of the emissive properties of YAG:Ce and the possibility of manufacturing the white light-emitting devices with a high-efficiency degree as a result of the bathochromic shift, increasing the emission intensity and of the quantum yield. By linking organic compounds with amine terminal groups at YAG:Ce surface, it creates the premises for covalently linking biomolecules, expanding the range of applicability of these fluorescent materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen Y, Moomy R, Eggert RG (2020) China’s public policies toward rare earths, 1975–2018. Miner Econ 33:127–151
Zhang K, Kleitb AN, Nietoc A (2017) An economics strategy for criticality—application to rare earth element Yttrium in new lighting technology and its sustainable availability. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 77:899–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.127
Borlaf M, Frankowska M, Kubiak WW, Graule T (2018) Strong photoluminescence emission at low dopant amount in YAG: Ce and YAG: Eu phosphors. Mater Res Bull 100:413–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.01.005
Palmero P, Traverso R (2014) Co-precipitation of YAG powders for transparent materials: effect of the synthesis parameters on processing and microstructure. Materials 7:7145–7156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7107145
Ţucureanu V, Romaniţan C, Tudor IA, Ţucureanu C, Popescu MA, Matei A (2020) Effect of process parameters on YAG: Ce phosphor properties obtained by co-precipitation method. Ceram Int 46:23802–23812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.156
Jain A, Sengar P, Hirata GA (2018) Rare-earth-doped Y3Al5O12 (YAG) nanophosphors: synthesis, surface functionalization, and applications in thermoluminescence dosimetry and nanomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:303002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aaca49
Sasaki Y, Takeshita S, Isobe T (2016) Preparation, photoluminescence, and photostability of transparent composite films of glycothermally synthesized YAG:Ce3+nanoparticles for White LED. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 5(1):R3049–R3054. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0061601jss
Qiu Q, Huang M, Zheng W, Xuan C, Wan Y, Zhang B, Luo Z, Lv W (2017) Impact of molar ratio of total metal ions to precipitant on YAG:Ce nanophosphors synthesized by reverse titration coprecipitation. Ceram Int l43:8730-8734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.04.004
Koizumi H, Watabe J, Sugiyama S, Hirabayashi H, Tokuno Y, Wada H, Homma T (2018) Properties of Ce3+-doped Y3Al5O12 phosphor nanoparticles formed by laser ablation in liquid. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 7(6):R63–R69. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0031806jss
Kim Y, Shim KB, Wu M, Jung HK (2017) Monodispersed spherical YAG:Ce3+ phosphor particles by one-pot synthesis. J Alloy Compd 693:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.09.129
Borlaf M, Kubrin R, Aseev V, Petrov AY, Nikonorov N, Graule T (2017) Deep submicrometer YAG:Ce phosphor particles with high photoluminescent quantum yield prepared by flame spray synthesis. J Am Ceram Soc 2017:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.14905
Jain A, González CAE, Tejeda EM, Durán A, Contreras OE, Hirata GA (2017) Covering the optical spectrum through different rare-earth ion-doping of YAG nanospheres produced by rapid microwave synthesis. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.127
Chen YC, Nien YT (2016) Microstructure and photoluminescence properties of laser sintered YAG:Ce phosphor ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.07.032
Tsuruoka N, Sasagawa T, Yodo T, Yoshimoto M, Odawara O, Wadal H (2016) Facile preparation of YAG:Ce nanoparticles by laser irradiation in water and their optical properties. Springer Plus 5:325. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-1958-2
Tucureanu V, Matei A, Avram AM (2015) Synthesis and characterization of YAG:Ce phosphors for white LEDs. Opto-Electron Rev 23(4):239–251. https://doi.org/10.1515/oere-2015-0038
Upasani M, Butey B (2015) Doping effect of Mg on photoluminescence properties of YAG:Ce phosphor. Int Res J Eng Technol 2(3):2360–2363
Pan Y, Wu M, Su Q (2004) Tailored photoluminescence of YAG:Ce phosphor through various methods. J Phys Chem Solids 65:845–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2003.08.018
Ayvacikli M, Canimoglu A, Muresan LE, Barbu-Tudoran L, Garcia Guinea J, Karabulut Y, Jorge A, Karali T, Can N (2016) Structural and luminescence effects of Ga co-doping on Ce-doped yttrium aluminate-based phosphors. J Alloy Compd 666:447–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.01.113
Sengar P, Hirata GA, Farias MH, Castillón F (2016) Morphological optimization and (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxy silane surface modification of Y3Al5O12:Pr nanoscintillator for biomedical applications. Mater Res Bull 77:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.01.045
Skaudzius R, Juestel T, Kareiva A (2016) Luminescence properties of Ln3+-doped (Ce3+, Eu3+, Tb3+ or Er3+) mixede metals Y3(Al, In)5O12 and Y3Al4.75Cr0.25O12 garnets synthesized by sol-gel method. Mater Chem Phys 170:229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.12.043
Yadav PJ, Meshram ND, Joshi CP, Moharil SV (2018) Phosphor converted white led with improved CRI. J Appl Math Phys 6:657–662. https://doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2018.64058
Canimoglu A, Karabulut Y, Ayvacikli M, Muresan LE, Perhaita I, Barbu-Tudoran L, Guinea JG, Karali T, Can N (2016) Optical spectroscopy of the Ce-doped multicomponent garnets. Appl Radiat Isotopes 114:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2016.05.021
Peng D, Cheng J, Liming S, Qi Q, Guobiao G, Xiaoyan Z, Ningzhong B (2017) Photoluminescence properties of YAG:Ce3+, Pr3+ nano-sized phosphors synthesized by a modified co-precipitation method. J Rare Earth 35(4):341–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(17)60917-7
Zeng P, Wei X, Zhou S, Yin M, Chen Y (2016) Evaluation of critical distances for energy transfer between Pr3+ and Ce3+ in yttrium aluminium garnet. J Appl Phys 120:0931. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4962018
Tang L, Ye H, Xiao D (2018) Photo-induced luminescence degradation in Ce, Yb co-doped yttrium aluminum garnet phosphors. Appl Opt 57(26):7627–7632. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.007627
Schiopu V, Matei A, Dinescu A, Danila M, Cernica I (2012) Ce, Gd codoped YAG nanopowder for white light emitting device. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12(11):8836–8840. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2012.6829
Ţucureanu V, Matei A, Mihalache I, Danila M, Popescu M, Bita B (2015) Synthesis and characterization of YAG:Ce, Gd and YAG:Ce, Gd/PMMA nanocomposites for optoelectronic applications. J Mater Sci 50(4):1883–1890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8751-9
Yang C, Gu G, Zhao X, Liang X, Xiang W (2016) The growth and luminescence properties of Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ single crystal by doping Gd3+ for W-LEDs. Mater Lett 170:58–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.02.001
Hong WT, Lee JH, Son JW, Lee Z, Park HJ, Kim HS, Lee JS, Yang HK (2016) Color rendering improvement of the YAG:Ce3+ phosphors by co-doping with Gd3+ ions. Ceram Int 42:2204–2208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.010
Korir PC, Dejene FB (2019) The effect of oxygen pressure on the structural and photoluminescence properties of pulsed laser deposited (Y-Gd)3Al5O12:Ce3+ thin films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:3257–3267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00598-x
Gong M, Xiang W, Liang X, Zhong J, Chen D, Huang J, Gu G, Yang C, Xiang R (2015) Growth and characterization of air annealing Tb-doped YAG:Ce single crystal for white-light-emitting diode. J Alloy Compd 639:611–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.03.162
Zhao Y, Xu H, Zhang X, Zhu G, Yan D, Ling Q, Chen M, Yu A (2016) Optical performances of YAG:Re3+ (Re = Ce, Eu) phosphor films with co-doping Tb3+ as energy-transfer sensitizer. J Am Ceram Soc 99(3):756–759. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.14098
Zhou X, Luo X, Wu B, Jiang S, Li L, Luo X, Pang Y (2018) The broad emission at 785 nm in YAG:Ce3+, Cr3+ phosphor. Spectrochim Acta Part A 190:76–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.09.011
Yang Y, Li J, Liu B, Zhang Y, Lv X, Wei L, Wang X, Xu J, Yu H, Hu Y, Zhang H, Ma L, Wang J (2017) Synthesis and luminescent properties of Eu3+, Eu3+/Bi3+ and Gd3+ codoped YAG:Ce3+ phosphors and their potential applications in warm white light-emitting diodes. Chem Phys Lett 685:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2017.07.042
Oliva J, De la Rosa E, Diaz-Torres LA, Torres A, Salas P, Meza O (2014) White light generation from YAG/YAM:Ce3+,Pr3+,Cr3+ nanophosphors mixed with a blue dye under 340 nm excitation. J Lumin, 154:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.04.018
Ma R, Ma C, Zhang J, Long J, Wen Z, Yuan X, Cao Y (2017) Energy transfer properties and enhanced color rendering index of chromaticity tunable green-yellow-red-emitting Y3Al5O12:Ce3+, Cr3+ phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Opt Mater Express 7(2):454–467. https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.7.000454
He X, Liu X, You C, Zhang Y, Li R, Yu R (2016) Clarifying the preferential occupation of Ga3+ ions in YAG:Ce,Ga nanocrystals with various Ga3+-doping concentrations by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mater Chem C 4:10691–10700. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC02763F
Wako AH, Dejene FB, Swart HC (2016) Effect of Ga3+ and Gd3+ ions substitution on the structural and optical properties of Ce3+-doped yttrium aluminium garnet phosphor nanopowders. Luminescence 31(7):1313–1320. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3108
Zhu Q, Ding S, Xiahou J, Li S, Sun X, Li J (2020) A groundbreaking strategy for fabricating YAG:Ce3+ transparent ceramic film via sintering LRH nanosheets on sapphire. Chem Commun 56:12761–12764. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CC05244B
Ling J, Xu W, Yang J, Mu T, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Hong M (2021) The effect of Lu3+ doping upon YAG:Ce phosphor ceramics for high-power white LEDs. J Eur Ceram Soc 41(12):5967–5976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.05.005
Shen CY, Li K, Hou QL, Feng HJ, Dong XY (2010) White LED based on YAG:Ce,Gd phosphor and CdSe–ZnS core/shell quantum dots. IEEE Photonic Technol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2010.2046724
Ţucureanu V, Munteanu D (2019) Enhanced optical properties of YAG:Ce yellow phosphor by modification with gold nanoparticles. Ceram Int 45:7641–7648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.061
Kong DS, Kim MJ, Song HJ, Cho IS, Jeong S, Shin H, Lee S, Jung HS (2016) Fine tuning of emission property of white light-emitting diodes by quantum-dot-coating on YAG:Ce nanophosphors. Appl Surf Sci 379:467–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.04.116
Asakura R, Isobe T, Kurokawa K, Aizawa H, Ohkubo M (2006) Tagging of avidin immobilized beads with biotinylated YAG:Ce3+ nanocrystal phosphor. Anal Bioanal Chem 386(6):1641–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0814-6
Tsukamoto A, Isobe T (2009) Characterization and biological application of YAG:Ce3+ nanophosphor modified with mercaptopropyl trimethoxy silane. J Mater Sci 44(5):1344–1350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3012-4
Asakura R, Isobe T (2013) Surface modification of YAG:Ce3+ nanoparticles by poly(acrylic acid) and their biological application. J Mater Sci 48:8228–8234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7634-9
Hussain T, Zhong L, Danesh M, Ye H, Liang Z, Xiao D, Qiu CW, Lou C, Chi L, Jiang L (2015) Enable low-amount YAG:Ce3+ to convert into white light with plasmonic Au nanoparticles. Nanoscale 7(23):10350–10356. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR01038A
Chao WH, Wu RJ, Tsai CS, Wu TB (2010) Surface plasmon-enhanced emission from Ag-coated Ce doped Y3Al5O12 thin films phosphor capped with a dielectric layer of SiO2. J Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3277015
Chung EJ, Masaki T, Song YH, Senthil K, Jung MK, Yoon DH (2013) Enhancement of thermal quenching properties of a yellow-emitting SiO2-coated Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ phosphor for white light-emitting diode applications. Phys Scr T157:014012. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/2013/T157/014012
Kiani Khouzani M, Bahrami A, Yazdan Mehr M, van Driel WD, Zhang G (2020) Towards multi-functional SiO2@YAG:Ce core–shell optical nanoparticles for solid state lighting applications. Nanomaterials 10:153. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010153
Ţucureanu V, Matei A, Avram A, Popescu MC, Mihalache I, Avram M, Mãrculescu CV, Ţîncu BC, Volmer M, Munteanu D (2017) Structural and luminescence properties of yellow phosphors prepared by a modified sol–gel method. MRS Commun 7(3):721–727. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.84
That PT, Le PX (2022) The qualities of dyed YAG:Ce3+@SiO2 for WLEDs via energy conversion. Bull Electr Eng Inform 11(5):2587–2594. https://doi.org/10.11591/eei.v11i5.4064
Tang Y, He X, Zhang Y, Yuan H, Xin Y, Ren X, Chen Q, Yin H (2022) Anchoring of red perovskite nanocrystals on YAG:Ce phosphor for high color rendering index WLEDs. J Alloys Compd 899:163347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.163347
Shi Y, Su X, Zhu H, Fu R, He Q, Zhu M, Ren H (2022) Simulation of optical behavior of YAG:Ce3+@SiO2 phosphor used for chip scale packages WLED. J Lumin 244:118699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2021.118699
Marius M, Popovici EJ, Barbu-Tudoran L, Indrea E, Mesaros A (2014) Cerium-doped yttrium aluminate-based phosphors prepared by wet-chemical synthesis route: Modulation of the luminescence color by changing the host-lattice composition. Ceram Int 40:6233–6239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.11.079
Ţucureanu V, Matei A, Avram A, Popescu MC, Dănila M, Avram M, Mărculescu C, Ţîncu B, Burinaru T, Munteanu D (2017) Influence of sintering temperature on the structure of yttrium based phosphor nanoparticles. Ann “Dunarea De Jos” Univ Galati. Fascicle Ix. Metallurgy Mater Sci 1:31–36
Matei A, Ţucureanu V, Ţîncu B, Popescu M, Romaniţan C, Cernica I, Dumitrescu L (2017) Experimental aspects for CeO2 nanoparticles synthesis and characterization. Ann “Dunarea De Jos” Univ Galati Fascicle Ix Metallurgy Mater Sci 1:31–36
Ţucureanu V, Matei A, Avram A (2020) The effect of the polymeric matrix on the emission properties of YAG-based phosphors. J Alloys Compd 844:15613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156136
Xu J, Liu B, Liu Z, Gong Y, Hu B, Wang J, Li H, Wang X, Du B (2018) Design of laser-driven SiO2-YAG:Ce composite thick film: Facile synthesis, robust thermal performance, and application in solid-state laser lighting. Opt Mater 75:508–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2017.10.049
Ogi T, Nandiyanto ABD, Okino K, Iskandar F, Wang WN, Tanabe E, Okuyama K (2013) Towards better phosphor design: effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on photoluminescence enhancement of YAG:Ce. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 2(5):R91. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.021305jss
Pan GH, Wu H, He S, Zhang L, Hao Z, Zhanga X, Zhang J (2018) Dye-embedded YAG:Ce3+@SiO2 composite phosphors toward warm wLEDs through radiative energy transfer: preparation, characterization and luminescence properties. Nanoscale 10:22237–22251. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR07360K
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant of the Ministry of National Education and Scientific Research, RDI Program for Space Technology and Advanced Research—STAR, project number 639/2017 and MICRO-NANO-SIS PLUS—Project No. PN1916. This work was also supported by UEFISCDI in the Partnership Framework: PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2019-3141, C382PED/2020. The authors would like to acknowledge to researchers: C. Ţucureanu for technical support in samples characterization and M. Paznicu, M. Brătan, T. Dobre for cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Conflict of interest for Vasilica Ţucureanu—None; Cosmin Romaniţan—None; Alina Matei—None.
Ethical approval
We confirm that: This manuscript is the authors' original work; this manuscript does not contain any studies involving animals or human subjects performed by any of the authors; This manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Andrea de Camargo.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ţucureanu, V., Romaniţan, C. & Matei, A. Improving the emissive properties of yttrium-based phosphor through internal and external modifications. J Mater Sci 58, 7272–7286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08488-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08488-2