Abstract
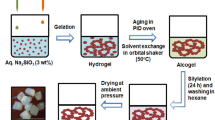
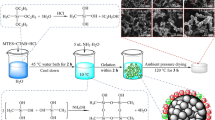
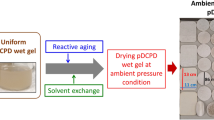
In this paper, an eco-friendly method of producing hybrid silica aerogels by freeze-drying method (FD) is proposed. In the freeze-drying system, deionized water was the only solvent, hybrid aerogels were prepared by acid–base catalysis and sol–gel method using methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) and water–glass as co-precursors. The microstructure, specific surface area, pore size distribution and thermal properties of the hybrid aerogels were characterized and analyzed. It was found that all samples exhibited the dual-mesoporous structures, and the molar ratio of co-precursors had a significant effect on the performance of aerogels. The tap density decreased and the porosity increased with the increase in the molar ratio of MTMS, while the thermal diffusion coefficient and thermal conductivity of aerogel decreased first and then increased. Especially when the molar ratio is 2.0, the hybrid aerogels exhibited excellent insulation performance, such as thermal diffusion coefficient of 0.0183 mm s−1, thermal conductivity of 0.0460 W(m k)−1 and great thermal stability up to 540 °C. It illustrates that hybrid aerogels have broad application prospects as insulation materials.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thapliyal PC, Singh K (2014) Aerogels as promising thermal insulating materials: an overview. J Mater 2014:127049. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/127049
Kim H, Kim K, Kim H et al (2020) Eco-friendly synthesis of water-glass-based silica aerogels via catechol-based modifier. Nanomaterials 10(12):2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122406
Fricke JG (1992) Ultrasonic velocity measurements in silica, carbon and organic aerogels. J Non-Cryst Solids. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(05)80459-4
Adebajo MO, Frost RL, Kloprogge JT et al (2003) Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: a review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J Porous Mater 10(3):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027484117065
Buratti C, Merli F, Moretti E (2017) Aerogel-based materials for building applications: influence of granule size on thermal and acoustic performance. Energy Build 152:472–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.07.071
Shimizu T, Kanamori K, Nakanishi K (2017) Silicone-based organic-inorganic hybrid aerogels and xerogels. Chem-A European J 23(22):5176. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201603680
Sanli D, Erkey C (2013) Monolithic composites of silica aerogels by reactive supercritical deposition of hydroxy-terminated poly(dimethylsiloxane). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:11708–11717. https://doi.org/10.1021/am403200d
Li M, Jiang H, Xu D et al (2016) Low density and hydrophobic silica aerogels dried under ambient pressure using a new co-precursor method. J Non-Cryst Solids 452:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.09.001
Cheng X, Li C, Shi X et al (2017) Rapid synthesis of ambient pressure dried monolithic silica aerogels using water as the only solvent. Mater Lett 204:157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.05.107
Li Z, Cheng X, He S et al (2016) Tailoring thermal properties of ambient pressure dried MTMS/TEOS co-precursor aerogels. Mater Lett 171(may15):91–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.02.025
Zhang Y, Xiang L, Shen Q et al (2020) Rapid synthesis of dual-mesoporous silica aerogel with excellent adsorption capacity and ultra-low thermal conductivity. J Non-Cryst Solids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120547
Wang J, Zhang Y, Wei Y, Zhang X (2015) Fast and one-pot synthesis of silica aerogels via a quasi-solvent-exchange-free ambient pressure drying process. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 218:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.07.019
Ok SS, Gizli N (2020) Hydrophobic silica aerogels synthesized in ambient conditions by preserving the pore structure via two-step silylation-ScienceDirect. Ceram Int 46(17):27789–27799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.278
Freytag A, Sanchez-Paradinas S, Naskar S, N. et al (2016) Versatile aerogel fabrication by freezing and subsequent freeze-drying of colloidal nanoparticle solutions. Angew Chem Int Ed 55(3):1200–1203. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201508972
Pan Y, He S, Gong L et al (2017) Low thermal-conductivity and high thermal stable silica aerogel based on MTMS/Water-glass co-precursor prepared by freeze drying. Mater Design 113:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.083
Zhou T, Cheng X, Pan Y et al (2017) Mechanical performance and thermal stability of glass fiber reinforced silica aerogel composites based on co-precursor method by freeze drying. Appl Surf Sci 437:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.146
He F, Zhao H, Qu X et al (2009) Modified aging process for silica aerogel. J Mater Process Technol 209(3):1621–1626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.04.009
Jiang Y, Feng J, Feng J (2017) Synthesis and characterization of ambient-dried microglass fibers/silica aerogel nanocomposites with low thermal conductivity. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83(1):64–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4383-2
Dorcheh AS, Abbasi MH (2008) Silica aerogel; synthesis, properties and characterization. J Mater Process Technol 199(1–3):10–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.10.060
Gurav JL, Rao AV, Nadargi DY, Park HH (2010) Ambient pressure dried TEOS-based silica aerogels: good absorbents of organic liquids. J Mater Sci 45(2):503–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3968-8
He J, Li XL, Su D, Ji HM, Wang XJ (2016) Ultra-low thermal conductivity and high strength of aerogels/fibrous ceramic composites. J Eur Ceram Soc 36:1487–1493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.11.021
Song H, Dongmei H, Haijiang B, Zhi L, Hui Y, Xudong C (2015) Synthesis and characterization of silica aerogels dried under ambient pressure bed on water glass. J Non-Cryst Solids 410:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.12.011
Sing KSW, Williams RT (2004) Physisorption hysteresis loops and the characterization of nanoporous materials. Adsorpt Sci Technol 22(10):773–782. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263617053499032
Sarawade PB, Kim JK, Hilonga A et al (2011) Synthesis of hydrophilic and hydrophobic xerogels with superior properties using sodium silicate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 139(1–3):138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2010.10.030
Rojas F, Kornhauser I, Felipe C, Esparza JM, Cordero S, Domínguez A, Riccardo JL (2002) Capillary condensation in heterogeneous mesoporous networks consisting of variable connectivity and pore-size correlation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 4:2346–2355. https://doi.org/10.1039/b108785a
Stojanovic A, Comesaña SP, Rentsch D, Koebel MM, Malfait WJ (2019) Ambient pressure drying of silica aerogels after hydrophobization with mono-, di- and tri-functional silanes and mixtures thereof. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 284:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.04.038
Mahadik SA, Pedraza F, Parale VG, Park H-H (2016) Organically modified silica aerogel with different functional silylating agents and effect on their physico-chemical properties. J Non-Cryst Solids 453:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.08.035
Zong S, Wei W, Jiang Z, Yan Z, Zhu J, Xie J (2015) Characterization and comparison of uniform hydrophilic/hydrophobic transparent silica aerogel beads: skeleton strength and surface modification. RSC Adv 5:55579–55587. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra08714g
Yu H, Liang X, Wang J, Wang M, Yang S (2015) Preparation and characterization of hydrophobic silica aerogel sphere products by co-precursor method. Solid State Sci 48:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2015.08.005
Hung WC, Horng RS, Shia RE (2021) Investigation of thermal insulation performance of glass/carbon fiber-reinforced silica aerogel composites. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 97:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05444-3
Chen YX, Sepahvand S, Gauvin F, Schollbach K, Yu Q (2021) One-pot synthesis of monolithic silica-cellulose aerogel applying a sustainable sodium silicate precursor. Constr Build Mater 293(11):123289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123289
Huijuan L, Wei S, Cooper AT, Maohong F (2009) Preparation and characterization of a novel silica aerogel as adsorbent for toxic organic compounds. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 347(1–3):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.11.033
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Nation Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB0309100), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No.2019T120390); Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral research funds (No. 2018K018A) ; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No.31470509] and the Key Laboratory of Eco-textiles, Ministry of Education— (supported by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities NO. JUSRP52007A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Chris Cornelius.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, S., Yu, K., Meng, C. et al. Eco-friendly approach for preparation of hybrid silica aerogel via freeze drying method. J Mater Sci 57, 7491–7502 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06835-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06835-9