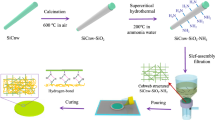
Abstract
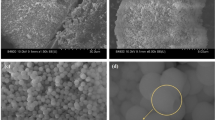
The field of microelectronic devices and 5G communication has an increasing demand for polymer composites with low dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, and good hydrophobicity. However, traditional polymer composites cannot simultaneously satisfy them, which severely hinders their application. In this work, a liquid crystal epoxy resin (LCE4) consisted of a flexible chain and rigid mesogenic unit was prepared and cured with methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride (MHHPA). And the mechanism of the curing reaction and the phase structure of the liquid crystal epoxy resins were investigated. In addition, dielectric hydrophobic liquid crystal epoxy nanometer composite materials were successfully prepared with functionalized mesoporous silica (SBA-15) as a filler. The results showed that pure LCE4 exhibited excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability. Compared with pure LCE4, the composite material for SBA-15 modified with KH560 displayed lower dielectric constant, lower dielectric loss, higher glass transition temperature, and better hydrophobicity. For example, with a 0.5 wt% SBA-15, the dielectric constant and dielectric loss of the composite material were as low as (2.35, 0.025) compared with pure LCE4 (3.25, 0.036) that was reduced by 24.7% and 31%. In addition, the glass transition temperature and water contact angle are increased by 16 °C and 14°, respectively. Composites also showed good thermal stability and mechanical properties. The reasons may mainly be derived from the internal structure of LCE4, the effective modification of mesoporous SBA-15 by KH560, and the excellent dispersion of organic and inorganic phases.
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
Feng CP, Chen L, Wei F, Ni HY, Chen J, Yang W (2016) Highly thermally conductive UHMWPE/graphite composites with segregated structures. RSC Adv 6(70):65709–65713
Kim K, Kim M, Kim J (2014) Thermal and mechanical properties of epoxy composites with a binary particle filler system consisting of aggregated and whisker type boron nitride particles. Compos Sci Technol 103:72–77
Luo T, Lloyd JR (2012) Enhancement of thermal energy transport across graphene/graphite and polymer interfaces: a molecular dynamics study. Adv Func Mater 22(12):2495–2502
Hopkins PE, Baraket M, Barnat EV, Beechem TE, Kearney SP, Duda JC, Robinson JT, Walton SG (2012) Manipulating thermal conductance at metal-graphene contacts via chemical functionalization. Nano Lett 12(2):590–595
Taha-Tijerina J, Narayanan TN, Gao G, Rohde M, Tsentalovich DA, Pasquali M, Ajayan PM (2012) Electrically insulating thermal nano-oils using 2D fillers. ACS Nano 6(2):1214–1220
Liu Y, Qian C, Qu L, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Wu X, Zou B, Chen W, Chen Z, Chi Z, Liu S, Chen X, Xu J (2015) A bulk dielectric polymer film with intrinsic ultralow dielectric constant and outstanding comprehensive properties. Chem Mater 27(19):6543–6549
Huang X, Iizuka T, Jiang P, Ohki Y, Tanaka T (2012) Role of interface on the thermal conductivity of highly filled dielectric epoxy/AlN composites. J Phys Chem C 116(25):13629–13639
Jiang Q, Zhang W, Hao J, Wei Y, Mu J, Jiang Z (2015) A unique “cage-cage’’’ shaped hydrophobic fluoropolymer film derived from a novel double-decker structural POSS with a low dielectric constant.” J Mater Chem C 3(44):11729–11734
Tousignant MN, Rice NA, Niskanen J, Richard CM, Ritaine D, Adronov A, Lessard BH (2021) High performance organic electronic devices based on a green hybrid dielectric. Adv Electron Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.202100700
Wu B, Liu H, Fu R, Song X, Su X, Liu X (2021) Epoxy-matrix composite with low dielectric constant and high thermal conductivity fabricated by HGMs/Al2O3 co-continuous skeleton. J Alloys Compd 869:159332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159332
Xu X, Hu R, Chen M, Dong J, Xiao B, Wang Q, Wang H (2020) 3D boron nitride foam filled epoxy composites with significantly enhanced thermal conductivity by a facial and scalable approach. Chem Eng J 397:125447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125447
Zhang P, Zhao J, Zhang K, Bai R, Wang Y, Hua C, Wu Y, Liu X, Xu H, Li Y (2016) Fluorographene/polyimide composite films: Mechanical, electrical, hydrophobic, thermal and low dielectric properties. Compos Part a-Appl Sci Manuf 84:428–434
Wahab MA, Chaobin H, Altalhi T, Albaqami MD, Alothman ZA, Haque R (2021) Nanopore engineered tortuosity towards thermo-mechanically enhanced low-k polymer-mesoporous organosilica composite membranes. Compos Sci Technol 211:108854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108854
Wang L, Bai Z, Liu C, Wei R, Liu X (2021) Porous fluorinated polyarylene ether nitrile as ultralow permittivity dielectrics used under humid environment. J Mater Chem C 9(3):860–868
Liu X, Yue D, Yang C, Li N, Gao S, Liu Y, Mo G, Wu Z, Yin J, Su B, Li L (2019) Fluorinated carbon nanofiber/polyimide composites: Electrical, mechanical, and hydrophobic properties. Surf Coat Technol 361:206–211
Yu Z, Wu S, Li C, Xiao Y, Zheng L, Liu J, Zhang B (2021) Ultra-low dielectric constant fluorinated graphene/polybenzoxazole composite films with excellent thermal stabilities and mechanical properties. Compos Part a-Appl Sci Manuf 145:106387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106387
Chrusciel JJ, Lesniak E (2015) Modification of epoxy resins with functional silanes, polysiloxanes, silsesquioxanes, silica and silicates. Prog Polym Sci 41:67–121
Pan Y-T, Zhang L, Zhao X, Wang D-Y (2017) Interfacial engineering of renewable metal organic framework derived honeycomb-like nanoporous aluminum hydroxide with tunable porosity. Chem Sci 8(5):3399–3409
Jiang S-D, Tang G, Chen J, Huang Z-Q, Hu Y (2018) Biobased polyelectrolyte multilayer-coated hollow mesoporous silica as a green flame retardant for epoxy resin. J Hazard Mater 342:689–697
Xu Y-J, Wang J, Tan Y, Qi M, Chen L, Wang Y-Z (2018) A novel and feasible approach for one-pack flame-retardant epoxy resin with long pot life and fast curing. Chem Eng J 337:30–39
Guo H, Lu M, Liang L, Wu K, Ma D, Xue W (2017) Liquid crystalline epoxies with lateral substituents showing a low dielectric constant and high thermal conductivity. J Electron Mater 46(2):982–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5003-6
Carfagna C, Amendola E, Giamberini M (1994) Rigid-rod networks - liquid-crystalline epoxy-resins. Compos Struct 27(1–2):37–43
Li Y, Badrinarayanan P, Kessler MR (2013) Liquid crystalline epoxy resin based on biphenyl mesogen: Thermal characterization. Polymer 54(12):3017–3025
Zhang X, Gu A, Liang G, Zhuo D, Yuan L (2011) Liquid crystalline epoxy resin modified cyanate ester for high performance electronic packaging. J Polym Res 18(6):1441–1450
Liu Z, Yuan L, Liang G, Gu A (2015) Tough epoxy/cyanate ester resins with improved thermal stability, lower dielectric constant and loss based on unique hyperbranched polysiloxane liquid crystalline. Polym Adv Technol 26(12):1608–1618
Y Li, V Ambrogi, P Cerruti, M Goswami, Z Yang, MR Kessler, O Rios (2021) Functional liquid crystalline epoxy networks and composites: from materials design to applications, Int Mater Rev
Yang X, Zhong X, Zhang J, Gu J (2021) Intrinsic high thermal conductive liquid crystal epoxy film simultaneously combining with excellent intrinsic self-healing performance. J Mater Sci Technol 68:209–215
Hong Y, Goh M (2021) Advances in liquid crystalline epoxy resins for high thermal conductivity. Polymers 13(8):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081302
Tian K, Yang S, Niu J, Wang H (2021) Enhanced thermal conductivity and mechanical toughness of the epoxy resin by incorporation of mesogens without nanofillers. Ieee Access 9:31575–31580
Kim Y, Yoo S, Lee HG, Won Y, Choi J, Kang K (2021) Structural analysis of silica aerogels for the interlayer dielectric in semiconductor devices. Ceram Int 47(21):29722–29729
Nam J-Y, Kim H-K, Song Y-S (2021) Fabrication and analysis of sepiolite/glass microcapsules/liquid crystal polymer composites. Molecules 26(9):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092522.
Shwaykani H, El-Hajj A, Costantine J, Al-Husseini M (2021) A calibration-free method for the dielectric constant calculation of low-loss materials. Ieee Trans Instrum Meas 70:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2020.3011765
Zhang J, Xu R, Yu D (2007) A novel poly-benzoxazinyl functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane and its nanocomposite with polybenzoxazine. Eur Polymer J 43(3):743–752
Du W, Shan J, Wu Y, Xu R, Yu D (2010) Preparation and characterization of polybenzoxazine/trisilanol polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes composites. Mater Des 31(4):1720–1725
Yang PD, Zhao DY, Margolese DI, Chmelka BF, Stucky GD (1998) Generalized syntheses of large-pore mesoporous metal oxides with semicrystalline frameworks. Nature 396(6707):152–155
Park I, Peng HG, Gidley DW, Xue SQ, Pinnavaia TJ (2006) Epoxy-silica mesocomposites with enhanced tensile properties and oxygen permeability. Chem Mater 18(3):650–656
Lin J, Wang X (2008) Preparation, microstructure, and properties of novel low-kappa brominated epoxy/mesoporous silica composites. Eur Polymer J 44(5):1414–1427
Purushothaman R (2015) Amine functionalized SBA-15/terpolyimide composites with low dielectric constant. J Porous Mater 22(3):585–594
Hukkamaki J, Suvanto S, Suvanto M, Pakkanen TT (2004) Influence of the pore structure of MCM-41 and SBA-15 silica fibers on atomic layer chemical vapor deposition of Cobalt carbonyl. Langmuir 20(23):10288–10295
Yao J, Sheng M, Bai S, Su H, Shang H, Deng H, Sun J (2021) Ionic Liquids grafted mesoporous silica for chemical fixation of CO2 to cyclic carbonate: morphology effect. Catal Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-021-03667-9
Lu Y, Lin Q, Ren W, Zhang Y (2015) Investigation on the preparation and properties of low-dielectric ethylene-vinyl acetate rubber/mesoporous silica composites. J Polym Res 22(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0694-6
Lasmi S, Zoukrami F, Antonio Marcos-Fernandez A, Guerba H (2020) Influence of modified mesoporous silica SBA-15 and compatibilizer on the properties and structure of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer-based nanocomposites. Polym-Plast Technol Mater 59(18):2003–2017
Jahromi S, Kuipers WAG, Norder B, Mijs WJ (1995) Liquid-crystalline epoxide thermosets - dynamic-mechanical and thermal-properties. Macromolecules 28(7):2201–2211
Mormann W, Broche M, Schwarz P (1997) Mesogenic azomethine based diepoxides - monomers for the synthesis of “liquid crystal” thermoset networks. Macromol Chem Phys 198(11):3615–3626
Lee JY, Jang JS (1998) Effect of substituents on the curing of liquid crystalline epoxy resin. J Polym Sci Part a-Polym Chem 36(6):911–917
Ortiz C, Wagner M, Bhargava N, Ober CK, Kramer EJ (1998) Deformation of a polydomain, smectic liquid crystalline elastomer. Macromolecules 31(24):8531–8539
Shiota A, Ober CK (1998) Smectic networks obtained from twin LC epoxy monomers - Mechanical deformation of the smectic networks. J Polym Sci Part B-Polym Phys 36(1):31–38
Ribera D, Mantecon A, Serra A (2001) Synthesis and crosslinking of a series of dimeric liquid crystalline epoxy resins containing imine mesogens. Macromol Chem Phys 202(9):1658–1671
Zhang Q, Chen G, Wu K, Shi J, Liang L, Lu M (2020) Biphenyl liquid crystal epoxy containing flexible chain: Synthesis and thermal properties. J Appl Polym Sci 137(38):49143. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49143
Luo T, Wei X, Luo S, Li H, Li W (2013) Study of Surface Modification of Al2O3 Nanoparticles with KH-560. Asian J Chem 25(12):6777–6779
Zheng W, Tang C, Xie J, Gui Y (2019) Micro-scale effects of nano-SiO2 modification with silane coupling agents on the cellulose/nano-SiO2 interface. Nanotechnology 30(44):445701. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab3546
Kruk M, Jaroniec M (2001) Gas adsorption characterization of ordered organic-inorganic nanocomposite materials. Chem Mater 13(10):3169–3183
Ma J, Liu Q, Chen D, Wen S, Wang T (2015) Synthesis and characterisation of pore-expanded mesoporous silica materials. Micro Nano Letters 10(2):140–144
Luo P, Xu M, Wang S, Xu Y (2017) Structural Dynamic Mechanical and Dielectric Properties of Mesoporous Silica/Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites. Ieee Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 24(3):1685–1697
Jin C, Lin S, Wetzel JT (2001) Evaluation of ultra-low-k dielectric materials for advanced interconnects. J Electron Mater 30(4):284–289
Zhao X-Y, Liu H-J (2010) Review of polymer materials with low dielectric constant. Polym Int 59(5):597–606
Lin J, Wang X (2008) New type of low-dielectric composites based on o-cresol novolac epoxy resin and mesoporous silicas: fabrication and performances. J Mater Sci 43(13):4455–4465. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954008313511347
Prabunathan P, Sethuraman K, Alagar M (2014) Development of bio-based F-SBA-15 reinforced epoxy nanocomposites for low-k dielectric applications. High Perform Polym 26(3):283–289
Guo H, Zheng J, Gan J, Liang L, Wu K, Lu M (2015) Relationship between crosslinking structure and low dielectric constant of hydrophobic epoxies based on substituted biphenyl mesogenic units. RSC Adv 5(107):88014–88020
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Guangzhou Science and Technology Program Key Projects (No. 201904010244). The authors would like to thank Huang Zhenyun from shiyanjia laboratory for support of DSC and BET analysis (www.Shiyanjia.com).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Maude Jimenez.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, W. et al. Functionalized mesoporous silica liquid crystal epoxy resin composite: an ideal low-dielectric hydrophobic material. J Mater Sci 57, 1156–1173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06672-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06672-w