Abstract
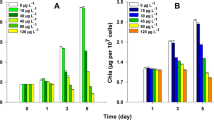
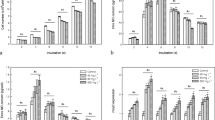
The allelochemical 5,4′-dihydroxyflavone (DHF) exerts a strong inhibitory effect against Microcystis aeruginosa TY001. In this study, the effects of DHF on growth, full photosynthetic performance, gene expression, and the antioxidant system of M. aeruginosa were examined to explore the possible damage mechanism. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed downregulated expression of prx and fabZ, two photosynthesis-related genes (psaB and psbA), and a DNA repair gene (recA) on days 3 and 5. The levels of antioxidant enzymes also decreased, including superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase. Additionally, DHF significantly increased malondialdehyde and reactive oxygen species levels in cells. In conclusion, inhibited photosynthesis and oxidative damage were the main mechanisms by which DHF inhibited M. aeruginosa TY001. This study provides evidence that polyphenolic compounds, such as DHF, may be effective components of aquatic management strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Alexova R, Fujii M, Birch D, Cheng J, Waite TD, Ferrari BC, Neilan BA (2011) Iron uptake and toxin synthesis in the bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa under iron limitation. Environ Microbiol 13:1064–1077
Bauer N, Blaschke U, Beutler E, Gross EM, Jenett-Siems K, Siems K, Hilta S (2009) Seasonal and interannual dynamics of polyphenols in Myriophyllum verticillatum and their allelopathic activity on Anabaena variabilis. Aquat Bot 91:110–116
Bi XD, Zhang SL, Dai W, Xing KZ, Pang Y, Zhang DJ (2014) Analysis of effects of berberine on the photosynthesis of Microcystis aeruginosa at gene transcriptional level. Clean- Soil Air Water 43:44–50
Blackhall ML, Coombes JS, Fasset R (2004) The relationship between antioxidant supplements and oxidative stress in renal transplant recipients: a review. ASAIO J 50:451–457
Cushnie T, Lamb AJ (2005) Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int J Antimicrob Ag 26:343–356
Dodds WK, Bouska WW, Eitzmann JL, Pilger TJ, Pitts KL, Riley AJ, Schloesser JT, Thornbrugh DJ (2009) Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environ Sci Technol 43:12–19
Eullaffroy P, Vernet G (2003) The F684/F735 chlorophyll fluorescence ratio: a potential tool for rapid detection and determination of herbicide phytotoxicity in algae. Water Res 37:1983–1990
Fuente ADL, Muro-Pastor AM, Merchán F, Madrid F, Pérez-Martínez JI, Undabeytia T (2019) Electrocoagulation/flocculation of cyanobacteria from surface waters. J Clean Prod 238:117964
Giliberti G, Baccigalupi L, Cordone A, Ricca E, De Felice M (2006) Transcriptional analysis of the recA gene of Streptococcus thermophiles. Microb Cell Fact 5:1–8
Goiris K, Muylaert K, Voorspoels S, Noten B, De Paepe D, Baart E, GJ, De Cooman L, (2014) Detection of flavonoids in microalgae from different evolutionary lineages. J Phycol 50:483–492
Gross EM, Gene EL (2009) Allelochemical reactions. In: Likens GE (ed) Encyclopedia of Inland Waters. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 715–726
Honda T, Takahashi H, Sako Y, Yoshida T (2014) Gene expression of Microcystis aeruginosa during infection of cyanomyovirus Ma-LMM01. Fisheries Sci 80:83–91
Horling F, Lamkemeyer P, König J, Finkemeier I, Kandlbinder A, Baier M, Dietz K (2003) Divergent light-, ascorbate-, and oxidative stress- dependent regulation of expression of the peroxiredoxin gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 131:317–325
Huang HM, Xiao X, Ghadouani A, Wu JP, Nie ZY, Peng C, Xu XH, Shi JY (2015) Effects of natural flavonoids on photosynthetic activity and cell integrity in Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins 7:66–80
Im SJ, Shon HK, Kim IS, Jang A (2019) The effects of naturally occurring operation factors on the removal mechanism of major algae metabolized materials in forward osmosis process. J Clean Prod 239:118009
Kaebernick M, Neilan BA, Börner T, Dittmann E (2000) Light and the transcriptional response of the microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster. Appl Environ Microb 66:3387–3392
Kasai F, Kawachi M, Erata M, Watanabe MM (2004) NIES-Collection, List of Strains, Seventh ed. National Institute for Environmental Studies Japan, Tsukuba, pp 257
Kurmayer R, Kutzenberger T (2003) Application of real-time PCR for quantification of microcystin genotypes in a population of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Appl Environ Microb 69:6723–6730
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Liu Y, Zhang J, Gao BY (2015) Cellular and transcriptional responses in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to two antibiotic contaminants. Microb Ecol 69:535–543
Liu GC, Zheng H, Zhai XW, Wang ZY (2018) Characteristics and mechanisms of microcystin-LR adsorption by giant reed-derived biochars: role of minerals, pores, and functional groups. J Clean Prod 176:463–473
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lu YP, Wang J, Yu Y, Shi LM, Kong FX (2014a) Changes in the physiology and gene expression of Microcystis aeruginosa under EGCG stress. Chemosphere 117:164–169
Lu ZY, Liu BY, He Y, Chen ZL, Zhou QH, Wu ZB (2014b) Effects of daily exposure of cyanobacterium and chlorophyte to low-doses of pyrogallol. Allelopathy J 34:195–206
Ma HY, Wu YL, Gan NQ, Zheng LL, Li TL, Song LR (2015) Growth inhibitory effect of Microcystis on Aphanizomenon flos-aquae isolated from cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Dianchi, China. Harmful Algae 42:43–51
Ni LX, Jie XT, Wang PF, Li SY, Wang GX, Li Y, Li YP, Acharya K (2015) Effect of linoleic acid sustained-release microspheres on Microcystis aeruginosa antioxidant enzymes activity and microcystins production and release. Chemosphere 121:110–116
Paerl HW, Otten TG (2013) Blooms bite the hand that feeds them. Science 342:433–434
Qian HF, Xu XY, Chen W (2009) Allelochemical stress causes oxidative damage and inhibition of photosynthesis in Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere 75:368–375
Ribau Teixeira M, Camacho FP, Sousa VS, Bergamasco R (2017) Green technologies for cyanobacteria and natural organic matter water treatment using natural based products. J Clean Prod 162:484–490
Sahu GK, Sabat SC (2011) Changes in growth, pigment content and antioxidants in the root and leaf tissues of wheat plants under the influence of exogenous salicylic acid. Braz J Plant Physiol 23:209–218
Salas MP, Céliz G, Geronazzo H, Daz M, Resnik SL (2011) Antifungal activity of natural and enzymatically-modified flavonoids isolated from citrus species. Food Chem 124:1411–1415
Selvaraj K, Chowdhury R, Bhattacharjee C (2014) Optimization of the solvent extraction of bioactive polyphenolic compounds from aquatic fern Azolla microphylla using response surface methodology. Int Food Res J 21:1559–1567
Shao JH, Wu ZX, Yu GL, Peng X, Li RH (2009) Allelopathic mechanism of pyrogallol to Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 (Cyanobacteria): from views of gene expression and antioxidant system. Chemosphere 75:924–928
Shao JH, Liu DM, Gong DX, Zeng QR, Yan ZY, Gu JD (2013) Inhibitory effects of sanguinarine against the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843 and possible mechanisms of action. Aquat Toxicol 142–143:257–263
Strasser RJ, Srivastava A, Govindjee, (1995) Polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transient in plant and cyanobacteria. Photochem Photobiol 61:32–42
Vidigal P, Martin-Hernandez AM, Guiu-Aragonés S, Amâncio S, Carvalho L (2015) Selective silencing of 2Cys and type-IIB peroxiredoxins discloses their roles in cell redox state and stress signaling. J Integr Plant Biol 7:591–601
Wan JJ, Guo PY, Peng XF, Wen KQ (2015) Effect of erythromycin exposure on the growth, antioxidant system and photosynthesis of Microcystis flos-aquae. J Hazard Mater 283:778–786
Wang J, Zhu JY, Liu SP (2011) Generation of reactive oxygen species in cyanobacteria and green algae induced by allelochemicals of submerged macrophytes. Chemosphere 85:977–982
Wang SZ, Zhang DY, Pan XL (2012) Effects of arsenic on growth and photosystem II (PS II) activity of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotox Environ Safe 84:104–111
Wang SZ, Chen FL, Mu SY, Zhang DY, Pan XL, Lee DJ (2013) Simultaneous analysis of photosystem responses of Microcystis aeruginosa under chromium stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 88:163–168
Wang J, Liu Q, Feng J, Lv JP, Xie SL (2016a) Effect of high-doses pyrogallol on oxidative damage, transcriptional responses and microcystins synthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa TY001. Ecotox Environ Safe 134:273–279
Wang J, Liu Q, Feng J, Lv JP, Xie SL (2016b) Photosynthesis inhibition of pyrogallol against the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa TY001. Pol J Environ Stud 25: 2601–2608
Wu ZX, Shi JQ, Yang SQ (2013) The effect of pyrogallic acid on growth, oxidative stress, and gene expression in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). Ecotoxicology 22:271–278
Wu X, Wu H, Wang SJ, Wang YM, Zhang RF, Hu XB, Ye JY (2018) Effect of propionamide on the growth of, Microcystis flos-aquae, colonies and the underlying physiological mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 630:526–535
Xiao X, Huang HM, Ge ZW, Rounge TB, Shi JY, Xu XH, Li RB, Chen YX (2014) A pair of chiral flavonolignans as novel anti—cyanobacterial allelochemicals derived from barley straw (Hordeum vulgare): Characterization and comparison of their anti-cyanobacterial activities. Environ Microbiol 16:1238–1251
Zhang C, Ling F, Yi YL, Zhang HY, Wang GX (2014) Algicidal activity and potential mechanisms of ginkgolic acids isolated from Ginkgo biloba exocarp on Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 26:323–332
Zhang SZ, Fu WY, Li N, Zhang F, Liu TX (2015) Antioxidant responses of Propylaea japonica (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) exposed to high temperature stress. J Insect Physiol 73:47–52
Zhao Y, Liu WS, Li Q, Yang Q, Chai WB, Zeng MJ, Li RH, Peng YY (2015) Multiparameter-based bioassay of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl) quinazoline, a newly-synthesized quinazoline derivative, toward Microcystis aeruginosa HAB5100 (Cyanobacteria). Bull Environ Contam Tox 94:376–381
Zhao W, Zheng Z, Zhang JL, Roger SF, Luo XZ (2019) Allelopathically inhibitory effects of Eucalyptus extracts on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere 225:424–433
Funding
This study was supported by the Fund for Shanxi “1331 Project” Key Innovative Research Team (grant no. TD201718), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 51709197), the Applied Basic Research Program of Shanxi (grant no. 201801D221282), the Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (grant no. 201802102), and the Key Research and Development Projects of Shanxi Province (grant no. 201803D31054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Shi, Y., Zhang, M. et al. Allelopathically inhibitory effects of 5,4′-dihydroxyflavone on the growth, antioxidant system and photosynthesis of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 33, 3843–3852 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02576-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02576-z