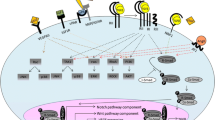
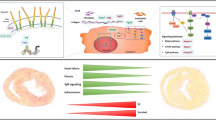
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a group of disorders affecting the heart and blood vessels and a leading cause of death worldwide. Thus, there is a need to identify new cardiokines that may protect the heart from damage as reported in GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators (2018) (The Lancet 392:1736–1788). Follistatin-like 1 (FSTL1) is a cardiokine that is highly expressed in the heart and released to the serum after cardiac injury where it is associated with CVD and predicts poor outcome. The action of FSTL1 likely depends not only on the tissue source but also post-translation modifications that are target tissue- and cell-specific. Animal studies examining the effect of FSTL1 in various models of heart disease have exploded over the past 15 years and primarily report a protective effect spanning from inhibiting inflammation via transforming growth factor, preventing remodeling and fibrosis to promoting angiogenesis and hypertrophy. A better understanding of FSTL1 and its homologs is needed to determine whether this protein could be a useful novel biomarker to predict poor outcome and death and whether it has therapeutic potential. The aim of this review is to provide a comprehensive description of the literature for this family of proteins in order to better understand their role in normal physiology and CVD.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Amino acid
- ACS:
-
Acute coronary syndrome
- ACVR2B:
-
Activin A receptor type 2B
- ATP1A1:
-
ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 1
- BMP:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein
- CAA:
-
Coronary artery aneurysms
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- DIP2A:
-
Disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A
- FS:
-
Follistatin
- FST:
-
Follistatin
- FSTL:
-
Follistatin-like
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association studies
- HFpEF:
-
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- I/R:
-
Ischemia/reperfusion
- LAD:
-
Left anterior descending
- LoF:
-
Loss-of-function
- LV:
-
Left ventricular
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- ncRNAs:
-
Non-coding RNAs
- PCI:
-
Percutaneous coronary intervention
- SPARC:
-
Secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich
- SPIG1:
-
SPARC-related protein containing immunoglobulin domain 1
- TAC:
-
Transverse aortic constriction
- TGF:
-
Transforming growth factor
References
Oshima Y, Ouchi N, Sato K et al (2008) Follistatin-like 1 is an Akt-regulated cardioprotective factor that is secreted by the heart. Circulation 117:3099–3108. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.767673
Shibanuma M, Mashimo J, Mita A et al (1993) Cloning from a mouse osteoblastic cell line of a set of transforming-growth-factor-beta 1-regulated genes, one of which seems to encode a follistatin-related polypeptide. Eur J Biochem FEBS 217:13–19
Zwijsen A, Blockx H, Van Arnhem W et al (1994) Characterization of a rat C6 glioma-secreted follistatin-related protein (FRP). Cloning and sequence of the human homologue. Eur J Biochem 225:937–946
Sylva M, Moorman AFM, van den Hoff MJB (2013) Follistatin-like 1 in vertebrate development: follistatin-like 1 in vertebrate development. Birth Defects Res Part C Embryo Today Rev 99:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdrc.21030
Mattiotti A, Prakash S, Barnett P, van den Hoff MJB (2018) Follistatin-like 1 in development and human diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 75:2339–2354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2805-0
Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J (2006) AceView: a comprehensive cDNA-supported gene and transcripts annotation. Genome Biol 7 Suppl 1:S12.1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2006-7-s1-s12
Takehara-Kasamatsu Y, Tsuchida K, Nakatani M et al (2007) Characterization of follistatin-related gene as a negative regulatory factor for activin family members during mouse heart development. J Med Investig JMI 54:276–288
Lara-Pezzi E, Felkin LE, Birks EJ et al (2008) Expression of follistatin-related genes is altered in heart failure. Endocrinology 149:5822–5827. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2008-0151
Oshima Y, Ouchi N, Shimano M et al (2009) Activin A and follistatin-like 3 determine the susceptibility of heart to ischemic injury. Circulation 120:1606–1615. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.872200
Shimano M, Ouchi N, Nakamura K et al (2011) Cardiac myocyte-specific ablation of follistatin-like 3 attenuates stress-induced myocardial hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 286:9840–9848. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.197079
Panse KD, Felkin LE, López-Olañeta MM et al (2012) Follistatin-like 3 mediates paracrine fibroblast activation by cardiomyocytes. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 5:814–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-012-9400-9
Namdari M, Negahdari B, Cheraghi M et al (2017) Cardiac failure detection in 30 minutes: new approach based on gold nanoparticles. J Microencapsul 34:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652048.2017.1296900
Shintani T, Kato A, Yuasa-Kawada J et al (2004) Large-scale identification and characterization of genes with asymmetric expression patterns in the developing chick retina. J Neurobiol 59:34–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.10338
Yonehara K, Shintani T, Suzuki R et al (2008) Expression of SPIG1 reveals development of a retinal ganglion cell subtype projecting to the medial terminal nucleus in the mouse. PLoS ONE 3:e1533. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001533
Masuda T, Kai N, Sakuma C et al (2009) Laser capture microdissection and cDNA array analysis for identification of mouse KIAA/FLJ genes differentially expressed in the embryonic dorsal spinal cord. Brain Res 1249:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.10.028
GBD (2017) Causes of Death Collaborators (2018) Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Lond Engl 392:1736–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7
Ling C, Cao S, Kong X (2022) Changes of FSTL1 and MMP-9 levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction and its relationship with hemorrhagic transformation. J Clin Neurosci Off J Neurosurg Soc Australas 99:164–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2021.10.041
Uematsu M, Nakamura K, Nakamura T et al (2020) Persistent myocardial production of follistatin-like 1 is associated with left ventricular adverse remodeling in patients with myocardial infarction: myocardial production of FSTL1 in AMI patients. J Card Fail 26:733–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.05.015
Gorelik M, Wilson DC, Cloonan YK et al (2012) Plasma follistatin-like protein 1 is elevated in Kawasaki disease and may predict coronary artery aneurysm formation. J Pediatr 161:116–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.01.011
El-Armouche A, Ouchi N, Tanaka K et al (2011) Follistatin-like 1 in chronic systolic heart failure: a marker of left ventricular remodeling. Circ Heart Fail 4:621–627. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.110.960625
Li B, An J, Feng S, Ge W (2016) Change in serum follistatin-like protein 1 and its clinical significance in children with chronic heart failure. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi
Cunningham F, Achuthan P, Akanni W et al (2018) Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1113
Stelzer G, Rosen N, Plaschkes I et al (2016) The GeneCards Suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinforma 54:1.30.1–1.30.33. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.5
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. cell 116:281–297
Sundaram GM, Common JEA, Gopal FE et al (2013) “See-saw” expression of microRNA-198 and FSTL1 from a single transcript in wound healing. Nature 495:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11890
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
The UniProt Consortium (2017) UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D158–D169. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1099
Hambrock HO, Kaufmann B, Müller S et al (2004) Structural characterization of TSC-36/Flik: analysis of two charge isoforms. J Biol Chem 279:11727–11735. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M309318200
Tanaka M, Ozaki S, Osakada F et al (1998) Cloning of follistatin-related protein as a novel autoantigen in systemic rheumatic diseases. Int Immunol 10:1305–1314
Liu T, Qian W-J, Gritsenko MA et al (2005) Human plasma N-glycoproteome analysis by immunoaffinity subtraction, hydrazide chemistry, and mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 4:2070–2080. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr0502065
Sayers EW, Agarwala R, Bolton EE et al (2019) Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D23–D28. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1069
Finn RD, Attwood TK, Babbitt PC et al (2017) InterPro in 2017-beyond protein family and domain annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D190–D199. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1107
Keutmann HT, Schneyer AL, Sidis Y (2004) The role of follistatin domains in follistatin biological action. Mol Endocrinol 18:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2003-0112
Letunic I, Bork P (2018) 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D493–D496. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx922
Schmidt T, Samaras P, Frejno M et al (2018) ProteomicsDB. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D1271–D1281. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1029
Bradshaw AD (2012) Diverse biological functions of the SPARC family of proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:480–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2011.12.021
Yates B, Braschi B, Gray KA et al (2017) Genenames.org: the HGNC and VGNC resources in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D619–D625. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1033
Wu Y, Zhou S, Smas CM (2010) Downregulated expression of the secreted glycoprotein follistatin-like 1 (Fstl1) is a robust hallmark of preadipocyte to adipocyte conversion. Mech Dev 127:183–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mod.2009.12.003
Cheng S, Huang Y, Lou C et al (2018) FSTL1 enhances chemoresistance and maintains stemness in breast cancer cells via integrin β3/Wnt signaling under miR-137 regulation. Cancer Biol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1529101
Galimov A, Hartung A, Trepp R et al (2015) Growth hormone replacement therapy regulates microRNA-29a and targets involved in insulin resistance. J Mol Med Berl Ger 93:1369–1379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1322-y
Rosenberg MI, Georges SA, Asawachaicharn A et al (2006) MyoD inhibits Fstl1 and Utrn expression by inducing transcription of miR-206. J Cell Biol 175:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200603039
Shi D-L, Shi G-R, Xie J et al (2016) MicroRNA-27a inhibits cell migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting follistatin-like protein 1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Cells 39:611–618. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2016.0103
Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Chen Y et al (2018) Inhibition of microRNA-9-5p protects against cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction in mice. Hum Gene Ther. https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2018.059
Zhang Z-M, Zhang A-R, Xu M et al (2017) TLR-4/miRNA-32-5p/FSTL1 signaling regulates mycobacterial survival and inflammatory responses in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages. Exp Cell Res 352:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.02.025
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam J-W, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 4:. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Chou C-H, Chang N-W, Shrestha S et al (2016) miRTarBase 2016: updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D239–D247. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1258
Mouillet J-F, Mishima T, Paffaro AMDA et al (2015) The expression and post-transcriptional regulation of FSTL1 transcripts in placental trophoblasts. Placenta 36:1231–1238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2015.09.005
Doroudgar S, Glembotski CC (2011) The cardiokine story unfolds: ischemic stress-induced protein secretion in the heart. Trends Mol Med 17:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2010.12.003
Ouchi N, Oshima Y, Ohashi K et al (2008) Follistatin-like 1, a secreted muscle protein, promotes endothelial cell function and revascularization in ischemic tissue through a nitric-oxide synthase-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 283:32802–32811. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M803440200
Widera C, Horn-Wichmann R, Kempf T et al (2009) Circulating concentrations of follistatin-like 1 in healthy individuals and patients with acute coronary syndrome as assessed by an immunoluminometric sandwich assay. Clin Chem 55:1794–1800. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2009.129411
Thul PJ, Åkesson L, Wiking M et al (2017) A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal3321
Chaly Y, Fu Y, Marinov A et al (2014) Follistatin-like protein 1 enhances NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated IL-1β secretion from monocytes and macrophages. Eur J Immunol 44:1467–1479. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201344063
Claros MG, Vincens P (1996) Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur J Biochem 241:779–786
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (2000) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol 300:1005–1016. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.3903
Wei K, Serpooshan V, Hurtado C et al (2015) Epicardial FSTL1 reconstitution regenerates the adult mammalian heart. Nature 525:479–485. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15372
Magadum A, Singh N, Kurian AA et al (2018) Ablation of a single N-glycosylation site in human FSTL 1 induces cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 13:133–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2018.08.021
Sidis Y (2001) Follistatin: essential role for the N-terminal domain in activin binding and neutralization. J Biol Chem 276:17718–17726. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M100736200
Li L, Li X, Liu X et al (2013) Expression, characterization, and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of recombinant murine follistatin-like 1 expressed in Drosophila S2 cells. Biosci Trends 7:93–100
Zhou J, Liao M, Hatta T et al (2006) Identification of a follistatin-related protein from the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis and its effect on tick oviposition. Gene 372:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2005.12.020
Tanaka M, Murakami K, Ozaki S et al (2010) DIP2 disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A (Drosophila) is a candidate receptor for follistatin-related protein/follistatin-like 1 - analysis of their binding with TGF-β superfamily proteins: DIP2A is a candidate receptor for FRP/FSTL1. FEBS J 277:4278–4289. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07816.x
Geng Y, Dong Y, Yu M et al (2011) Follistatin-like 1 (Fstl1) is a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 4 signaling antagonist in controlling mouse lung development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:7058–7063. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1007293108
Li K-C, Zhang F-X, Li C-L et al (2011) Follistatin-like 1 suppresses sensory afferent transmission by activating Na+, K+-ATPase. Neuron 69:974–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.022
Murakami K, Tanaka M, Usui T et al (2012) Follistatin-related protein/follistatin-like 1 evokes an innate immune response via CD14 and toll-like receptor 4. FEBS Lett 586:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.010
Prieto C, De Las RJ (2006) APID: agile protein interaction dataanalyzer. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W298–W302. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl128
Ouchi N, Asaumi Y, Ohashi K et al (2010) DIP2A functions as a FSTL1 receptor. J Biol Chem 285:7127–7134. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.069468
Ogura Y, Ouchi N, Ohashi K et al (2012) Therapeutic impact of follistatin-like 1 on myocardial ischemic injury in preclinical models. Circulation 126:1728–1738. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.115089
Miyabe M, Ohashi K, Shibata R et al (2014) Muscle-derived follistatin-like 1 functions to reduce neointimal formation after vascular injury. Cardiovasc Res 103:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvu105
Seki M, Powers JC, Maruyama S et al (2018) Acute and chronic increases of circulating FSTL1 normalize energy substrate metabolism in pacing-induced heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 11:e004486. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.004486
Shimano M, Ouchi N, Nakamura K et al (2011) Cardiac myocyte follistatin-like 1 functions to attenuate hypertrophy following pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:E899-906. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108559108
Ni S, Li C, Xu N et al (2018) Follistatin-like protein 1 induction of matrix metalloproteinase 1, 3 and 13 gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes requires MAPK, JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB pathways. J Cell Physiol 234:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26580
Sundaram GM, Ismail HM, Bashir M et al (2017) EGF hijacks miR-198/FSTL1 wound-healing switch and steers a two-pronged pathway toward metastasis. J Exp Med 214:2889–2900. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20170354
Zhang D, Ma X, Sun W et al (2015) Down-regulated FSTL5 promotes cell proliferation and survival by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:3386–3394
Miyamae T, Marinov AD, Sowders D et al (1950) (2006) Follistatin-like protein-1 is a novel proinflammatory molecule. J Immunol Baltim Md 177:4758–4762
Wilson DC, Marinov AD, Blair HC et al (2010) Follistatin-like protein 1 is a mesenchyme-derived inflammatory protein and may represent a biomarker for systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62:2510–2516. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27485
Masuda T, Sakuma C, Nagaoka A et al (2014) Follistatin-like 5 is expressed in restricted areas of the adult mouse brain: implications for its function in the olfactory system. Congenit Anom 54:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/cga.12022
Karczewski KJ, Weisburd B, Thomas B et al (2017) The ExAC browser: displaying reference data information from over 60 000 exomes. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D840–D845. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw971
Sylva M, Li VSW, Buffing AAA et al (2011) The BMP antagonist follistatin-like 1 is required for skeletal and lung organogenesis. PLoS ONE 6:e22616. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022616
Adams D, Larman B, Oxburgh L (2007) Developmental expression of mouse follistatin-like 1 (Fstl1): dynamic regulation during organogenesis of the kidney and lung. Gene Expr Patterns 7:491–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.modgep.2006.10.009
Dal-Pra S, Fürthauer M, Van-Celst J et al (2006) Noggin1 and follistatin-like2 function redundantly to chordin to antagonize BMP activity. Dev Biol 298:514–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.07.002
Liu S, Shen H, Xu M et al (2010) FRP inhibits ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell apoptosis through an Akt-NF-{kappa}B-Bcl-2 pathway and inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis in an apoE-knockout mouse model. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E351-363. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00005.2010
Okabayashi K, Shoji H, Onuma Y et al (1999) cDNA cloning and distribution of the Xenopus follistatin-related protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 254:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.9892
Suzuki R, Matsumoto M, Fujikawa A et al (2014) SPIG1 negatively regulates BDNF maturation. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 34:3429–3442. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1597-13.2014
Szabo L, Morey R, Palpant NJ et al (2015) Statistically based splicing detection reveals neural enrichment and tissue-specific induction of circular RNA during human fetal development. Genome Biol 16:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0690-5
Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2016) Cardiac extracellular vesicles in normal and infarcted heart. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010063
Li M, Ding W, Sun T et al (2018) Biogenesis of circular RNAs and their roles in cardiovascular development and pathology. FEBS J 285:220–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14191
van den Berg G, Somi S, Buffing AAM et al (2007) (2007) Patterns of expression of the follistatin and Follistatin-like1 genes during chicken heart development: a potential role in valvulogenesis and late heart muscle cell formation. Anat Rec Hoboken NJ 290:783–787. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.20559
Kretzschmar K, Post Y, Bannier-Hélaouët M et al (2018) Profiling proliferative cells and their progeny in damaged murine hearts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E12245–E12254. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1805829115
Wang M, Weiss M, Simonovic M et al (2012) PaxDb, a database of protein abundance averages across all three domains of life. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP 11:492–500. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.O111.014704
Wu C, Jin X, Tsueng G et al (2016) BioGPS: building your own mash-up of gene annotations and expression profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D313-316. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1104
Stylianidis V, Hermans KCM, Blankesteijn WM (2017) Wnt signaling in cardiac remodeling and heart failure. Handb Exp Pharmacol 243:371–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2016_56
Prakash S, Borreguero LJJ, Sylva M et al (2017) Deletion of Fstl1 (follistatin-Like 1) from the endocardial/endothelial lineage causes mitral valve disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37:e116–e130. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309089
Prakash S, Mattiotti A, Sylva M et al (2019) Identifying pathogenic variants in the follistatin-like 1 gene (FSTL1) in patients with skeletal and atrioventricular valve disorders. Mol Genet Genomic Med e567. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.567
Maruyama S, Nakamura K, Papanicolaou KN et al (2016) Follistatin-like 1 promotes cardiac fibroblast activation and protects the heart from rupture. EMBO Mol Med 8:949–966. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201506151
Tanaka K, Valero-Muñoz M, Wilson RM et al (2016) Follistatin like 1 regulates hypertrophy in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. JACC Basic Transl Sci 1:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacbts.2016.04.002
Widera C, Giannitsis E, Kempf T et al (2012) Identification of follistatin-like 1 by expression cloning as an activator of the growth differentiation factor 15 gene and a prognostic biomarker in acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chem 58:1233–1241. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2012.182816
Aikawa T, Shimada K, Miyauchi K et al (2019) Associations among circulating levels of follistatin-like 1, clinical parameters, and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents. PLoS ONE 14:e0216297. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216297
Lee S-Y, Kim D-Y, Kyung Kwak M et al (2019) High circulating follistatin-like protein 1 as a biomarker of a metabolically unhealthy state. Endocr J. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ18-0352
Xi Y, Gong D-W, Tian Z (2016) FSTL1 as a potential mediator of exercise-induced cardioprotection in post-myocardial infarction rats. Sci Rep 6:32424. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32424
Hayakawa S, Ohashi K, Shibata R et al (2015) Cardiac myocyte-derived follistatin-like 1 prevents renal injury in a subtotal nephrectomy model. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 26:636–646. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014020210
Philipp U, Vollmar A, Häggström J et al (2012) Multiple loci are associated with dilated cardiomyopathy in Irish wolfhounds. PLoS ONE 7:e36691. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036691
Stern JA, Hsue W, Song K-H et al (2015) Severity of mitral valve degeneration is associated with chromosome 15 loci in Whippet dogs. PLoS ONE 10:e0141234. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141234
Divers J, Palmer ND, Langefeld CD et al (2017) Genome-wide association study of coronary artery calcified atherosclerotic plaque in African Americans with type 2 diabetes. BMC Genet 18:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-017-0572-9
Guo Y, Tomlinson B, Chu T et al (2012) A genome-wide linkage and association scan reveals novel loci for hypertension and blood pressure traits. PLoS ONE 7:e31489. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031489
Schriml LM, Mitraka E, Munro J et al (2019) Human Disease Ontology 2018 update: classification, content and workflow expansion. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D955–D962. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1032
Maruyama S, Nakamura K, Papanicolaou KN et al (2016) Follistatin‐like 1 promotes cardiac fibroblast activation and protects the heart from rupture. EMBO Mol Med 8:949–966. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201506151
Tuunanen H, Ukkonen H, Knuuti J (2008) Myocardial fatty acid metabolism and cardiac performance in heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rep 10:142–148
Le Luduec JB, Condamine T, Louvet C et al (2008) An immunomodulatory role for follistatin-like 1 in heart allograft transplantation. Am J Transplant Off J Am Soc Transplant Am Soc Transpl Surg 8:2297–2306. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02398.x
Shen H, Cui G, Li Y et al (2019) Follistatin-like 1 protects mesenchymal stem cells from hypoxic damage and enhances their therapeutic efficacy in a mouse myocardial infarction model. Stem Cell Res Ther 10:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-1111-y
van Wijk B, Gunst QD, Moorman AFM, van den Hoff MJB (2012) Cardiac regeneration from activated epicardium. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0044692
Chen W, Xia J, Hu P et al (2016) Follistatin-like 1 protects cardiomyoblasts from injury induced by sodium nitroprusside through modulating Akt and Smad1/5/9 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 469:418–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.026
Yang W, Duan Q, Zhu X et al (2019) Follistatin-like 1 attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiomyocytes via regulation of autophagy. In: BioMed Res. Int. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2019/9537382/abs/. Accessed 22 May 2019
Li C, Dai L, Zhang J et al (2018) Follistatin-like protein 5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inducing caspase-dependent apoptosis and regulating Bcl-2 family proteins. J Cell Mol Med 22:6190–6201. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13906
Nakamura M, Sadoshima J (2018) Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Rev Cardiol 15:387–407. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-018-0007-y
Rubattu S, Forte M, Marchitti S, Volpe M (2019) Molecular implications of natriuretic peptides in the protection from hypertension and target organ damage development. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040798
Shiojima I, Sato K, Izumiya Y et al (2005) Disruption of coordinated cardiac hypertrophy and angiogenesis contributes to the transition to heart failure. J Clin Invest 115:2108–2118. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI24682
Talman V, Ruskoaho H (2016) Cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction-from repair and remodeling to regeneration. Cell Tissue Res 365:563–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2431-9
Frangogiannis NG (2015) Inflammation in cardiac injury, repair and regeneration. Curr Opin Cardiol 30:240–245. https://doi.org/10.1097/HCO.0000000000000158
Winbanks CE, Chen JL, Qian H et al (2013) The bone morphogenetic protein axis is a positive regulator of skeletal muscle mass. J Cell Biol 203:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211134
Bergmann O (2019) Clearing up the mist: cardiomyocyte renewal in human hearts. Eur Heart J 40:1037–1038. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz097
Bergmann O, Zdunek S, Felker A et al (2015) Dynamics of cell generation and turnover in the human heart. Cell 161:1566–1575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.026
DeLeon-Pennell KY, Meschiari CA, Jung M, Lindsey ML (2017) Matrix metalloproteinases in myocardial infarction and heart failure. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 147:75–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.02.001
Chan QKY, Ngan HYS, Ip PPC et al (2009) Tumor suppressor effect of follistatin-like 1 in ovarian and endometrial carcinogenesis: a differential expression and functional analysis. Carcinogenesis 30:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgn215
Fan D, Takawale A, Lee J, Kassiri Z (2012) Cardiac fibroblasts, fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodeling in heart disease. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-1536-5-15
Hu P-F, Ma C-Y, Sun F-F et al (2019) Follistatin-like protein 1 (FSTL1) promotes chondrocyte expression of matrix metalloproteinase and inflammatory factors via the NF-κB pathway. J Cell Mol Med 23:2230–2237. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14155
Kawabata D, Tanaka M, Fujii T et al (2004) Ameliorative effects of follistatin-related protein/TSC-36/FSTL1 on joint inflammation in a mouse model of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:660–668. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20023
Liu Y, Wei J, Zhao Y et al (2017) Follistatin-like protein 1 promotes inflammatory reactions in nucleus pulposus cells by interacting with the MAPK and NFκB signaling pathways. Oncotarget 8:43023–43034. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17400
Ni X, Cao X, Wu Y, Wu J (2018) FSTL1 suppresses tumor cell proliferation, invasion and survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep 39:13–20. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.6061
Tanaka M, Ozaki S, Kawabata D et al (2003) Potential preventive effects of follistatin-related protein/TSC-36 on joint destruction and antagonistic modulation of its autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunol 15:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxg005
Zabala W, Cruz R, Barreiro-de Acosta M et al (2013) New genetic associations in thiopurine-related bone marrow toxicity among inflammatory bowel disease patients. Pharmacogenomics 14:631–640. https://doi.org/10.2217/pgs.13.38
Rosano GM, Vitale C (2018) Metabolic modulation of cardiac metabolism in heart failure. Card Fail Rev 4:99–103. https://doi.org/10.15420/cfr.2018.18.2
Li F, Zhang K, Xu T et al (2019) Exosomal microRNA-29a mediates cardiac dysfunction and mitochondrial inactivity in obesity-related cardiomyopathy. Endocrine 63:480–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1753-7
Coronado MJ, Bruno KA, Blauwet LA et al (2019) Elevated Sera sST2 is associated with heart failure in men ≤50 years old with myocarditis. J Am Heart Assoc 8:e008968. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.118.008968
Li W, Alahdal M, Deng Z et al (2020) Molecular functions of FSTL1 in the osteoarthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 83:106465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106465
Funding
This work was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health grants R21 AI145356, R21 AI152318, and R21 AI154927 and the American Heart Association 20TPA35490415 to DF. This study has received support from RECETOX research infrastructure (Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic: LM2018121), Horizon 2020 Teaming 2 project (857560), and the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/17_04369/ 0009632 and CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/ 0000469). Moreover, the study was funded by grant no. NU22-02–00418 by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The whole team participated in the preparation of the manuscript, while Martin Horak conceived the idea and prepared the initial draft, Piia Kokkonen and David Bednar provided the database analyses and provided valuable insight into the functional aspects of FSTL1 and its paralogs. DeLisa Fairweather critically reviewed the manuscript and provided valuable insight into the practical implications of use of FSTLs as biomarkers in cardiology. Julie Bienertova-Vasku provided guidance for manuscript preparation by Martin Horak and critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horak, M., Fairweather, D., Kokkonen, P. et al. Follistatin-like 1 and its paralogs in heart development and cardiovascular disease. Heart Fail Rev 27, 2251–2265 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-022-10262-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-022-10262-6