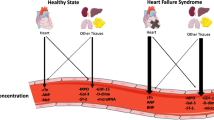
Abstract
With the advances of drug therapy, the prognosis of cancer patients has seen remarkable improvements, and cancer-related mortality has decreased significantly. However, the followed drug-related cardiotoxicity becomes a serious threat to patients’ living quality and survival rate. Cardiovascular toxicity associated with some chemotherapy drugs is reversible and dose-dependent. If early identification is possible, early cardiovascular protection measures or adjustment of chemotherapy regimens can be taken to improve the prognosis of patients. Therefore, early prevention and monitoring of chemotherapy-related cardiotoxicity are critical for cancer patients and survivors. Among them, biomarkers are an important method for the early identification of myocardial injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Truong J, Yan AT, Cramarossa G, Chan KK (2014) Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: detection, prevention, and management.[J]. Can J Cardiol 30(8):869–878
Mertens AC, Liu Q, Neglia JP, Wasilewski K, Leisenring W, Armstrong GT, Robison LL, Yasui Y (2008) Cause-specific late mortality among 5-year survivors of childhood cancer: the childhood cancer survivor study.[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(19):1368–1379
Plana JC, Galderisi M, Barac A, Ewer MS, Ky B, Scherrer-Crosbie M, Ganame J, Sebag IA, Agler DA, Badano LP, Banchs J, Cardinale D, Carver J, Cerqueira M, DeCara J, Edvardsen T, Flamm SD, Force T, Griffin BP, Jerusalem G, Liu JE, Magalhães A, Marwick T, Sanchez LY, Sicari R, Villarraga HR, Lancellotti P (2014) Expert consensus for multimodality imaging evaluation of adult patients during and after cancer therapy: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 15(10):1063–1093
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Lamantia G, Colombo N, Civelli M, de Giacomi G, Rubino M, Veglia F, Fiorentini C, Cipolla CM (2010) Anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy: clinical relevance and response to pharmacologic therapy[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(3):213–220
Bird BRJH, Swain SM (2008) Cardiac toxicity in breast cancer survivors: review of potential cardiac problems[J]. Clin Cancer Res 14(1):14–24
Jensen BV, Skovsgaard T, Nielsen SL (2002) Functional monitoring of anthracycline cardiotoxicity: a prospective, blinded, long-term observational study of outcome in 120 patients[J]. Ann Oncol 13(5):699–709
Ky B, Putt M, Sawaya H, French B, Januzzi JL Jr, Sebag IA, Plana JC, Cohen V, Banchs J, Carver JR, Wiegers SE, Martin RP, Picard MH, Gerszten RE, Halpern EF, Passeri J, Kuter I, Scherrer-Crosbie M (2014) Early increases in multiple biomarkers predict subsequent cardiotoxicity in patients with breast cancer treated with doxorubicin, taxanes, and trastuzumab[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol 63(8):809–816
Zardavas D, Suter TM, Van Veldhuisen DJ et al (2017) Role of troponins I and T and N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide in monitoring cardiac safety of patients with early-stage human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer receiving trastuzumab: a herceptin adjuvant study cardiac marker substudy[J]. J Clin Oncol 35(8):878–884
Simões R, Silva LM, Cruz ALVM, Fraga VG, de Paula Sabino A, Gomes KB (2018) Troponin as a cardiotoxicity marker in breast cancer patients receiving anthracycline-based chemotherapy: a narrative review[J]. Biomed Pharmacother 107:989–996
Ponde N, Bradbury I, Lambertini M et al (2017) Cardiac biomarkers for early detection and prediction of trastuzumab and/or lapatinib-induced cardiotoxicity in patients with HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer: a NeoALTTO sub-study (BIG 1–06).[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat:1–8
Armenian SH, Gelehrter SK, Vase T, Venkatramani R, Landier W, Wilson KD, Herrera C, Reichman L, Menteer JD, Mascarenhas L, Freyer DR, Venkataraman K, Bhatia S (2014) Screening for cardiac dysfunction in anthracycline-exposed childhood cancer survivors.[J]. Clin Cancer Res 20(24):6314–6323
Sherief LM, Kamal AG, Khalek EA et al (2012) Biomarkers and early detection of late onset anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in children[J]. Hematology 17(3):151–156
Sawaya H, Sebag IA, Plana JC, Januzzi JL, Ky B, Cohen V, Gosavi S, Carver JR, Wiegers SE, Martin RP, Picard MH, Gerszten RE, Halpern EF, Passeri J, Kuter I, Scherrer-Crosbie M (2011) Early detection and prediction of cardiotoxicity in chemotherapy-treated patients.[J]. Am J Cardiol 107(9):1375–1380
Kitayama H, Kondo T, Sugiyama J, Kurimoto K, Nishino Y, Kawada M, Hirayama M, Tsuji Y (2017) High-sensitive troponin T assay can predict anthracycline- and trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients.[J]. Breast Cancer 24(6):774–782
Mladosievicova B, Urbanova D, Radvanska E et al (2012) Role of NT-proBNP in detection of myocardial damage in childhood leukemia survivors treated with and without anthracyclines[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31(1):86
Lenihan DJ, Stevens PL, Massey M, Plana JC, Araujo DM, Fanale MA, Fayad LE, Fisch MJ, Yeh ET (2016) The utility of point-of-care biomarkers to detect cardiotoxicity during anthracycline chemotherapy: a feasibility study[J]. J Card Fail 22(6):433–438
Putt M, Hahn VS, Januzzi JL et al (2015) Longitudinal changes in multiple biomarkers are associated with cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin, taxanes, and trastuzumab[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol 65(10):1164–1172
Leger KJ, Leonard D, Nielson D et al (2017) Circulating microRNAs: potential markers of cardiotoxicity in children and young adults treated with anthracycline chemotherapy[J]. J Am Heart Assoc 6(4):e004653
Holmgren G, Synnergren J, Andersson CX et al (2016) MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Toxicol In Vitro 34(1):26–34
Ruggeri C, Gioffré S, Achilli F, Colombo GI, D'Alessandra Y (2018) Role of microRNAs in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: an overview of preclinical models and cancer patients[J]. Heart Fail Rev 23(1):109–122
Liang S, Xinyong C, Hongmin Z et al (2018) TLR2 and TLR3 expression as a biomarker for the risk of doxorubicin-induced heart failure[J]. Toxicol Lett
Frères P, Bouznad N, Servais L, Josse C, Wenric S, Poncin A, Thiry J, Moonen M, Oury C, Lancellotti P, Bours V, Jerusalem G (2018) Variations of circulating cardiac biomarkers during and after anthracycline-containing chemotherapy in breast cancer patients[J]. BMC Cancer 18(1):102
Sawaya H, Sebag IA, Plana JC et al (2012) Assessment of echocardiography and biomarkers for the extended prediction of cardiotoxicity in patients treated with anthracyclines, taxanes, and trastuzumab.[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 5(5):596
Finkelman BS, Putt M, Wang T et al (2017) Arginine-nitric oxide metabolites and cardiac dysfunction in patients with breast cancer[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol 70(2):152
Yarana C, Carroll D, Chen J, et al (2017) Extracellular vesicles released by cardiomyocytes in a doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury mouse model contain protein biomarkers of early cardiac injury.[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 112:clincanres.2046.2017
Scuric Z, Carroll JE, Bower JE et al (2017) Biomarkers of aging associated with past treatments in breast cancer survivors[J]. NPJ Breast Cancer 3(1):50
Balduzzi S, Mantarro S, Guarneri V, Tagliabue L, Pistotti V, Moja L, D’Amico R (2014) Trastuzumab-containing regimens for metastatic breast cancer. In: Moja L (ed) Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Chichester
Morris PG, Chen C, Steingart R et al (2011) Troponin I and C-reactive protein are commonly detected in patients with breast cancer treated with dose-dense chemotherapy incorporating trastuzumab and lapatinib[J]. Clin Cancer Res 17(10):3490–3499
Elghandour AH, Sorady ME, Sahar A et al (2009) Human heart-type fatty acid-binding protein as an early diagnostic marker of doxorubicin cardiac toxicity[J]. Hematol Rev 1(1):543–543
Horacek JM, Jebavy L, Vasatova M, Pudil R, Tichy M, Jakl M, Maly J (2013) Glycogen phosphorylase BB as a potential marker of cardiac toxicity in patients treated with anthracyclines for acute leukemia[J]. Bratisl Med J 114(12):708–710
Hamm CW, Goldmann BU, Heeschen C, Kreymann G, Berger J, Meinertz T (1997) Emergency room triage of patients with acute chest pain by means of rapid testing for cardiac troponin T or troponin I.[J]. N Engl J Med 337(23):1648–1653
Adriana A, Giuseppina P, Francesco D et al (2010) Cardiotoxicity of anticancer drugs: the need for cardio-oncology and cardio-oncological prevention[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(1):14–25
Kang Y, Xu X, Cheng L, Li L, Sun M, Chen H, Pan C, Shu X (2014) Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography combined with high-sensitive cardiac troponin T in early detection and prediction of cardiotoxicity during epirubicine-based chemotherapy[J]. Eur J Heart Fail 16(3):300–308
Weber M, Hamm C (2006) Role of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and NT-proBNP in clinical routine[J]. Heart 92(6):843–849
De IF, Salerno G, Taglieri L et al (2016) Serum biomarkers evaluation to predict chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients.[J]. Tumor Biol 37(3):3379–3387
Ruggiero A, De Rosa G, Rizzo D et al (2013) Myocardial performance index and biochemical markers for early detection of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia[J]. Int J Clin Oncol 18(5):927–933
Christenson ES, James T, Agrawal V, Park BH (2015) Use of biomarkers for the assessment of chemotherapy-induced cardiac toxicity[J]. Clin Biochem 48(4–5):223–235
Vejpongsa P, Yeh ET (2014) Prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: challenges and opportunities[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol 64(9):938–945
Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E (2008) Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing.[J]. Cell 132(1):9–14
Kapranov P, Cheng J, Dike S, Nix DA, Duttagupta R, Willingham AT, Stadler PF, Hertel J, Hackermüller J, Hofacker IL, Bell I, Cheung E, Drenkow J, Dumais E, Patel S, Helt G, Ganesh M, Ghosh S, Piccolboni A, Sementchenko V, Tammana H, Gingeras TR (2007) RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription.[J]. Science 316(5830):1484–1488
Yi X, Bekeredjian R, DeFilippis NJ, Siddiquee Z, Fernandez E, Shohet RV (2006) Transcriptional analysis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290(3):1098–1102
Riad A, Bien S, Gratz M et al (2014) Toll-like receptor-4 deficiency attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in mice.[J]. Eur J Heart Fail 10(3):233–243
Frantz S, Kelly RA, Bourcier T (2001) Role of TLR-2 in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB by oxidative stress in cardiac myocytes.[J]. J Biol Chem 276(7):5197–5203
Boxtel WV, Bulten BF, Mavinkurve-Groothuis AMC et al (2015) New biomarkers for early detection of cardiotoxicity after treatment with docetaxel, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide[J]. 20(2):143
Sharma A, Khatun Z, Shiras A (2016) Tumor exosomes: cellular postmen of cancer diagnosis and personalized therapy[J]. Nanomedicine 11(4):421–437
Jih-Kai Y, Chao-Yung W (2016) Telomeres and telomerase in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Genes 7(9):58
(2011) Telomere length in old age and cholesterol across the life course[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc 59(10):1979–1981
Beyer AM, Freed JK, Durand MJ, Riedel M, Ait-Aissa K, Green P, Hockenberry JC, Morgan RG, Donato AJ, Peleg R et al (2016) Critical role for telomerase in the mechanism of flow-mediated dilation in the human microcirculation. Circ Res 118:856–866
Shrivastava AK, Singh HV, Raizada A, Singh SK (2015) C-reactive protein, inflammation and coronary heart disease. Egypt Heart J 67:89–97
Christenson ES, James T, Agrawal V et al (2014) Use of biomarkers for the assessment of chemotherapy-induced cardiac toxicity[J]. Clin Biochem 48(4–5)
Xia Z (2018) Heart-type fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP) as a biomarker for acute myocardial injury and long-term post-ischemic prognosis[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39(7)
Keller T, Zeller T, Ojeda F et al (2011) Serial changes in highly sensitive troponin I assay and early diagnosis of myocardial infarction[J]. JAMA 306(24):2684–2693
Lillpopp L , Tzikas S , Ojeda F et al (2012) Prognostic information of glycogen phosphorylase isoenzyme BB in patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome[J]. Am J Cardiol 110(9):1225–1230
Funding
This study was funded by the basic applied research projects in Shanxi Province (grant number 201601D021156) and the Scientific Research Fund of Shanxi cardiovascular Hospital (grant number 20170203) and the Scientific Research Topics of Shanxi Health commission (grant number 2015070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gai, W., An, J., Wang, Z. et al. Research progress of biomarkers in early detection of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity. Heart Fail Rev 26, 1195–1201 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-020-09948-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-020-09948-6