Abstract
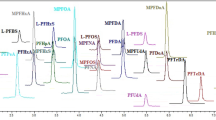
In this study, an analytical method for the routine determination of nine perfluorinated compounds (PFCs), using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer (UPLC-QTOF-MS), was developed, validated, and used for their assay in surface water and sediments. The method yielded good linearity with a correlation coefficient (R2) ranging between 0.991 and 0.999 for all the compounds investigated. Limits of detection (LOD) ranged between 0.02 and 0.08 ng/l, while the limit of quantification (LOQ) ranged from 0.065 to 0.261 ng/l. Recovery studies were carried out in replicate assays, and percentage recoveries ranged between 56 and 112% for the nine perfluorinated compounds investigated. The method was applied to determine levels of perflurooctanoic acid (PFOA) and PFOS in surface water and sediment samples collected along the Plankenburg River in Stellenbosch, South Africa. Samples were pre-treated, extracted, and cleaned up via offline solid-phase extraction (SPE) procedures, using hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) C-18 cartridges. Levels of PFOA and PFOS found in surface water ranged between (12.8 ± 4.24 and 62.62 ± 4.86 ng/l) and (<LOD and 3.8 ng/l), respectively, while levels measured in corresponding sediment samples ranged between 0.14–0.33 ng/g (PFOA) and <LOD and 0.7 ± 0.013 ng/g (PFOS). Concentrations of PFOA and PFOS were suspected to be associated with anthropogenic activities in the vicinity of the sampling areas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens, L., Norström, K., Viktor, T., Cousins, A. P., & Josefsson, S. (2015). Stockholm Arlanda Airport as a source of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances to water, sediment and fish. Chemosphere, 129, 33–38.
Bao, J., Jin, Y., Liu, W., Ran, X., & Zhang, Z. (2009). Perfluorinated compounds in sediments from the Daliao River system of northeast China. Chemosphere, 77(5), 652–657.
Barton, C. A., Kaiser, M. A., & Russell, M. H. (2007). Partitioning and removal of perfluorooctanoate during rain events: the importance of physical-chemical properties. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 9(8), 839–846.
Benford, D., de Boer, J., Carere, A., di Domenico, A., Johansson, N., Schrenk, D., Schoeters, G., de Voogt, P., Dellatte, E. (2008). Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and their salts. EFSA Journal, 653, 1–131.
Berger, U., & Haukås, M. (2005). Validation of a screening method based on liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry for analysis of perfluoroalkylated substances in biota. Journal of Chromatography A, 1081(2), 210–217.
Chen, H., Reinhard, M., Nguyen, V. T., & Gin, K. Y.-H. (2016). Reversible and irreversible sorption of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) by sediments of an urban reservoir. Chemosphere, 144, 1747–1753.
Daso, A. P., Fatoki, O. S., & Odendaal, J. P. (2013). Occurrence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and 2, 2′, 4, 4′, 5, 5′-hexabromobiphenyl (BB-153) in water samples from the Diep River, Cape Town, South Africa. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(8), 5168–5176.
EFSA, P. S. (2008). Perflurooctanoic acid (PFOA) and their salts. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain, The EFSA Journal, 653, 1–131.
Ericson, I., Domingo, J. L., Nadal, M., Bigas, E., Llebaria, X., van Bavel, B., & Lindström, G. (2009). Levels of perfluorinated chemicals in municipal drinking water from Catalonia, Spain: public health implications. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 57(4), 631–638.
Fiori, J., & Andrisano, V. (2014). LC–MS method for the simultaneous determination of six glucocorticoids in pharmaceutical formulations and counterfeit cosmetic products. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 91, 185–192.
Fromme, H., Midasch, O., Twardella, D., Angerer, J., Boehmer, S., & Liebl, B. (2007). Occurrence of perfluorinated substances in an adult German population in southern Bavaria. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 80(4), 313–319.
Giesy, J. P., & Kannan, K. (2002). Peer reviewed: perfluorochemical surfactants in the environment. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(7), 146A–152A.
Guo, R., Sim, W.-J., Lee, E.-S., Lee, J.-H., & Oh, J.-E. (2010). Evaluation of the fate of perfluoroalkyl compounds in wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 44(11), 3476–3486.
Higgins, C. P., & Luthy, R. G. (2006). Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(23), 7251–7256.
Higgins, C. P., Field, J. A., Criddle, C. S., & Luthy, R. G. (2005). Quantitative determination of perfluorochemicals in sediments and domestic sludge. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(11), 3946–3956.
Hu, J., & Yu, J. (2010). An LC-MS-MS method for the determination of perfluorinated surfactants in environmental matrices. Chromatographia, 72(5–6), 411–416.
Jahnke, A., & Berger, U. (2009). Trace analysis of per-and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in various matrices—how do current methods perform? Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(3), 410–421.
Jain, D., & Basniwal, P. K. (2013). ICH guideline practice: application of validated RP-HPLC-DAD method for determination of tapentadol hydrochloride in dosage form. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 4(1), 9.
Lein, N. P. H., Fujii, S., Tanaka, S., Nozoe, M., & Tanaka, H. (2008). Contamination of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in surface water of the Yodo River basin (Japan). Desalination, 226(1–3), 338–347.
Lim, T. C., Wang, B., Huang, J., Deng, S., & Yu, G. (2011). Emission inventory for PFOS in China: review of past methodologies and suggestions. The Scientific World Journal, 11, 1963–1980.
Lin, Y., Liu, R., Hu, F., Liu, R., Ruan, T., & Jiang, G. (2016). Simultaneous qualitative and quantitative analysis of fluoroalkyl sulfonates in riverine water by liquid chromatography coupled with Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A., 1435, 66–74.
Llorca, M., Farré, M., Picó, Y., & Barceló, D. (2009). Development and validation of a pressurized liquid extraction liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for perfluorinated compounds determination in fish. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(43), 7195–7204.
Loos, R., Gawlik, B. M., Locoro, G., Rimaviciute, E., Contini, S., & Bidoglio, G. (2009). EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environmental Pollution, 157(2), 561–568.
Martín, J., Rodríguez-Gómez, R., Zafra-Gómez, A., Alonso, E., Vílchez, J., & Navalón, A. (2016). Validated method for the determination of perfluorinated compounds in placental tissue samples based on a simple extraction procedure followed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Talanta, 150, 169–176.
Moody, C. A., Kwan, W. C., Martin, J. W., Muir, D. C., & Mabury, S. A. (2001). Determination of perfluorinated surfactants in surface water samples by two independent analytical techniques: liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry and 19F NMR. Analytical Chemistry, 73(10), 2200–2206.
Mudumbi, J., Ntwampe, S., Muganza, F., & Okonkwo, J. (2014). Perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctane sulfonate in South African river water. Water Science and Technology, 69(1), 185–194.
Naile, J. E., Garrison, A. W., Avants, J. K., & Washington, J. W. (2016). Isomers/enantiomers of perfluorocarboxylic acids: method development and detection in environmental samples. Chemosphere, 144, 1722–1728.
Noorlander, C. W., van Leeuwen, S. P., te Biesebeek, J. D., Mengelers, M. J., & Zeilmaker, M. J. (2011). Levels of perfluorinated compounds in food and dietary intake of PFOS and PFOA in the Netherlands. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(13), 7496–7505.
Olsen, G. W., Burris, J. M., Burlew, M. M., & Mandel, J. H. (2003). Epidemiologic assessment of worker serum perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) concentrations and medical surveillance examinations. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 45(3), 260–270.
Opeolu, B., Fatoki, O., & Odendaal, J. (2010). Development of a solid-phase extraction method followed by HPLC-UV detection for the determination of phenols in water. International Journal of the Physical Sciences, 5(5), 576–581.
Pan, G., & You, C. (2010). Sediment–water distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in Yangtze River Estuary. Environmental Pollution, 158(5), 1363–1367.
Paulse, A., Jackson, V., & Khan, W. (2009). Comparison of microbial contamination at various sites along the Plankenburg: and Diep Rivers, Western Cape, South Africa. Water SA, 35(4), 469–478.
Perra, G., Focardi, S. E., & Guerranti, C. (2013). Levels and spatial distribution of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in superficial sediments from the marine reserves of the Tuscan Archipelago National Park (Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1), 379–382.
Post, G. B., Cohn, P. D., & Cooper, K. R. (2012). Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), an emerging drinking water contaminant: a critical review of recent literature. Environmental Research, 116, 93–117.
Prevedouros, K., Cousins, I. T., Buck, R. C., & Korzeniowski, S. H. (2006). Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(1), 32–44.
Rand, A. A., & Mabury, S. A. (2017). Is there a human health risk associated with indirect exposure to perfluoroalkyl carboxylates (PFCAs)? Toxicology, 375, 28–36.
SAW (2015). State Administration of Work Safety (SAWS). Dangerous chemicals directory (2015 Edition) www.chinasafety.gov.cn (China).
Schwanz, T. G., Llorca, M., Farré, M., & Barceló, D. (2016). Perfluoroalkyl substances assessment in drinking waters from Brazil, France and Spain. Science of the Total Environment, 539, 143–152.
Shoeib, T., Hassan, Y., Rauert, C., & Harner, T. (2016). Poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in indoor dust and food packaging materials in Egypt: Trends in developed and developing countries. Chemosphere, 144, 1573–1581.
So, M., Miyake, Y., Yeung, W., Ho, Y., Taniyasu, S., Rostkowski, P., et al. (2007). Perfluorinated compounds in the Pearl river and Yangtze river of China. Chemosphere, 68(11), 2085–2095.
Swartz, M. E., &Krull, I. S. (1997). Analytical method development and validation: CRC Press.
Tarafdar, A., & Sinha, A. (2018). Public health risk assessment with bioaccessibility considerations for soil PAHs at oil refinery vicinity areas in India. Science of the Total Environment, 616-617, 1477–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.166.
Trudel, D., Horowitz, L., Wormuth, M., Scheringer, M., Cousins, I. T., & Hungerbühler, K. (2008). Estimating consumer exposure to PFOS and PFOA. Risk Analysis, 28(2), 251–269.
USEPA (2009). Provisional health advisories for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). http://water.epa.gov/action/advisories/drinking/upload/2009_01_15_criteria_drinking_pha-PFOA_PFOS.pdf (Date assessed: 15/Dec/2016).
Wang, T., Wang, Y., Liao, C., Cai, Y., & Jiang, G. (2009). Perspectives on the inclusion of perfluorooctane sulfonate into the Stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants1. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(14), 5171–5175.
Wang, X., Wang, S., & Cai, Z. (2013). The latest developments and applications of mass spectrometry in food-safety and quality analysis. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 52, 170–185.
Wang, T., Wang, P., Meng, J., Liu, S., Lu, Y., Khim, J. S., & Giesy, J. P. (2015). A review of sources, multimedia distribution and health risks of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in China. Chemosphere, 129, 87–99.
Wang, P., Lu, Y., Wang, T., Meng, J., Li, Q., Zhu, Z., Sun, Y., Wang, R., & Giesy, J. P. (2016). Shifts in production of perfluoroalkyl acids affect emissions and concentrations in the environment of the Xiaoqing River Basin, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 307, 55–63.
Wang, J., Zhang, X., Ling, W., Liu, R., Liu, J., Kang, F., & Gao, Y. (2017). Contamination and health risk assessment of PAHs in soils and crops in industrial areas of the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Chemosphere, 168, 976–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.113.
Weinberg, I., Dreyer, A., & Ebinghaus, R. (2011). Waste water treatment plants as sources of polyfluorinated compounds, polybrominated diphenyl ethers and musk fragrances to ambient air. Environmental Pollution, 159(1), 125–132.
Wilhelm, M., Bergmann, S., & Dieter, H. H. (2010). Occurrence of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in drinking water of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany and new approach to assess drinking water contamination by shorter-chained C4–C7 PFCs. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 213(3), 224–232.
Wille, K., Bussche, J. V., Noppe, H., De Wulf, E., Van Caeter, P., Janssen, C., et al. (2010a). A validated analytical method for the determination of perfluorinated compounds in surface-, sea-and sewagewater using liquid chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1217(43), 6616–6622.
Wille, K., Noppe, H., Verheyden, K., Bussche, J. V., De Wulf, E., Van Caeter, P., et al. (2010b). Validation and application of an LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of 13 pharmaceuticals in seawater. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 397(5), 1797–1808.
Zhang, T., Sun, H. W., Wu, Q., Zhang, X. Z., Yun, S. H., & Kannan, K. (2010). Perfluorochemicals in meat, eggs and indoor dust in China: assessment of sources and pathways of human exposure to perfluorochemicals. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(9), 3572–3579.
Funding
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of the National Research Foundation (NRF), South Africa, through the Thuthuka Research Grant No. 84185 awarded to Prof B. O. Opeolu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 475kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagbayigbo, B.O., Opeolu, B.O., Fatoki, O.S. et al. Validation and determination of nine PFCS in surface water and sediment samples using UPLC-QTOF-MS. Environ Monit Assess 190, 346 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6715-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6715-2