Abstract
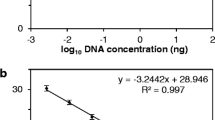
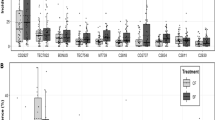
Corn stunt disease is a disease that extends from the southern United States to Argentina and is one of the most important diseases in warm subtropical areas of the continent, periodically causing yield reductions in maize. The aims of this study were to develop a severity scale, estimate the effect of corn stunt caused by Spiroplasma kunkelii in maize hybrids, and identify attributes related to yield loss that would be useful to evaluate germplasms. Under artificial inoculation conditions with infective and non-infective insects, symptoms were grouped to develop and validate a scale and a severity index. Disease severity, moment of appearance of the characteristic symptom, pathogen concentration, and effect on yield were correlated for eight temperate and temperate x tropical commercial and precommercial hybrid maize germplasms. We developed and validated a 7-score severity scale. The characteristic symptom of S. kunkelii infection occurs earlier in the temperate germplasm than in the tropical x temperate germplasm. The performance of two of the four temperate germplasms was remarkable compared to the hybrids. Severity and pathogen concentration were correlated with each other, and both correlated with yield and with yield reduction. The moment of appearance of the characteristic disease symptom did not correlate with the other attributes. The severity index and the pathogen concentration may be useful to evaluate germplasm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alivizatos, A. S., & Markham, P. G. (1986). Acquisition and transmission of corn stunt spiroplasma by its leafhopper vector Dalbulus maidis. Annals of Applied Biology, 108(3), 535–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1986.tb01992.x
Bajet, N. B. (1989). Occurrence of Corn Stunt Spiroplasma at different elevations in Mexico. Plant Disease, 73(11), 926. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-73-0926
Bradfute, O. E., Tsai, J. H., & Gordon, D. T. (1981). Corn Stunt Spiroplasma and viruses associated with a maize disease epidemic in Southern Florida. Plant Disease, 65(10), 837. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-65-837
Carloni, E., Carpane, P., Paradell, S., Laguna, I., & Giménez Pecci, M. P. (2013). Presence of Dalbulus maidis (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and of Spiroplasma kunkelii in the temperate region of Argentina. Journal of Economic Entomology, 106(4), 1574–1581. https://doi.org/10.1603/EC12323
Caro, L., Carpane, P., Carloni, E., Santa, M., Laguna, I. G., & Giménez Pecci, M. P. (2006). Relación entre síntomas y serología y plantas de Maíz (Zea mays L.) infectadas experimentalmente con Spiroplasma kunkelii Whitcomb (pp. 304–305). XII Jornadas Fitosanitarias Argentinas.
Caro, L., Laguna, I. G., & Giménez Pecci, M. P. (2008). Ajuste de la escala que asocia síntomas y serología en maíz experimentalmente infectado con Spiroplasma kunkelii (p. 327). 1o Congreso Argentino de Fitopatología.
Carpane, P., Laguna, I. G., Virla, E. G., Paradell, S., Murua, L., & Giménéz Pecci, M. P. (2006). Experimental transmission of corn stunt spiroplasma present in different regions of Argentina. Maydica, 51, 461–468.
Carpane, P., Melcher, U., Wayadande, A., Giménez Pecci, M. P., Laguna, G., Dolezal, W., & Fletcher, J. (2012). An Analysis of the Genomic Variability of the Phytopathogenic Mollicute <i>Spiroplasma kunkelii<i/>. Phytopathology, 103(2), 120926072324005. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-07-12-0158-R
Da Costa, R., Da Silva, D. D., Cota, L., Campos, L., Almeida, R., & Bernardes, F. (2019). Incidence of corn stunt disease in off-season corn hybrids in different sowing seasons. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 54. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1678-3921.pab2019.v54.00872
De Oliveira, C. M., Lopes, J. R. S., Camargo, L. E. A., Fungaro, M. H. P., & Nault, L. R. (2007). No TitlGenetic diversity in populations of Dalbulus maidis (DeLong and Wolcott) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) from distant localities in Brazil assessed by RAPD-PCR Markers. Environmental Entomology, 36, 204–212.
De Oliveira, E., De Oliveira, C. M., Souza, I. R. P., Magalhães, P. C., & Cruz, I. (2002). Corn stuns: expression of leaf symptoms, detection of mollicutes and interactions with genotypes. Revista Brasileira de Milho e Sorgo, 1, 53–62.
De Oliveira, E., Landau, E., Guimarães, P. E., & Guimarães, L. J. M. (2010). Resistance of corn to stunting caused by spiroplasm and to stunting caused by phytoplasma. Asociación Brasileña de Maíz y Sorgo, 226.
De Oliveira, E., Resende, R., Giménéz Pecci, M. P., Laguna, I. G., Herrera, P., & Cruz, I. (2003). Incidência de viroses e enfezamentos e estimativa de perdas causadas por molicutes em milho no Paraná. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 38(1), 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2003000100003
Di Renzo, M. A., Bonamico, N. C., Díaz, D. D., Salerno, J. C., Ibañez, M. M., & Gesumaria, J. J. (2002). Inheritance of resistance to Mal de Río Cuarto (MRC) disease in Zea mays (L.). The Journal of Agricultural Science, 139(1), 47–53. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859602002241
Di Rienzo, J. A., Casanoves, F., Balzarini, M. G., Gonzalez, L., Tablada, M., & Robledo, C. W. (2020). InfoStatversión 2020. Centro de Transferencia (No. 2020). Centro de Transferencia InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacioinal de Córdoba, Argentina. www.infostat.com.ar
Díaz, C. G., Virla, E. G., Carloni, E., Giménéz Pecci, M. P., & Laguna, I. G. (2005). Evaluación preliminar del efecto de la fecha de siembra sobre la incidencia del corn stunt spiroplasma (CSS) (pp. 277–288). VIII Congreso Nacional de Maíz.
Galvão, S. R., Sabato, E. O., & Bedendo, I. P. (2021). Occurrence and distribution of single or mixed infection of phytoplasma and spiroplasma causing corn stunting in Brazil. Tropical Plant Pathology, 46(2), 152–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-020-00381-6
Giménéz Pecci, M. P., Carpane, P., Carloni, E., Nome, C. F., Fiorona, M., & Laguna, I. G. (2009). Técnicas empleadas en la identificación y caracterización de Spiroplasma kunkelii Withcomb (Reino Eubacteria, Clase Mollicutes). In I. G. Laguna, V. Conci, P. Rodriguez Pardina, G. Truol, M. Fiorona, & L. Di Feo (Eds.), Procedimientos empleados en la identificación de organismos fitopatógenos (pp. 53–65). Ediciones INTA.
Gimenéz Pecci, M. P., García, A., Druetta, M., Cabral, J. B., Ramirez, E. H., Raspanti, J., Ferrer, M., Maurino, M. F., & Laguna, I. G. (2014). ePeriodicidad y distribución de dos enfermedades del maíz (Zea mays L.) en la década del 2000 en Argentina (pp. 46–47). Escuela de Matemática Aplicada a La Biología-BIOMAT.
Giménéz Pecci, M. P., Laguna, I. G., Avila, A. O., De Remes Lenicov, A. M. M., Virla, E. G., Borgogno, C., Nome, C. F., & Paradell, S. (2002). Difusión del Corn Stunt Spiroplasma del maíz (Spiroplasma kunkelii) y del vector (Dalbulus maidis) en la República Argentina. Revista de La Facultad de Agronomía de La Plata, 105(1), 1–8.
Gussie, J. S. (1995). Movement and multiplication of Spiroplasma kunkelii in Corn. Phytopathology, 85(10), 1093. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-85-1093
Hidalgo, H., Jeffers, D., Castañon, G., & Rodriguez, F. (1998). Resistencia al achaparramiento del maíz mediante infestaciones de Dalbulus maidis en maíz. Agronomía MEsoamericana, 9(2), 119–124.
Hogenboom, N. G. (1993). Economic importance of breeding for disease resistance. In T. Jacobs & J. E. Parlevliet (Eds.), Durability of disease resistance. Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture (pp. 5–9). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2004-3_1
Lee, I. M. (1993). Universal amplification and analysis of pathogen 16S rDNA for classification and identification of mycoplasmalike organisms. Phytopathology, 83(8), 834. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-83-834
Lenardon, S. L., Laguna, I. G., Gordon, D. L., Truol, G., Gómez, G., & Bratfute, O. E. (1993). Identification of Corn stunt spiroplasma in maize from Argentina. Plant Disease, 77(1), 100C. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-77-0100C
Márquez Sánchez, F. (1982). The genetic improvement of resistance to the corn disease stunt and downy mildew in Nicaragua. Chapingo, 27, 26–27.
Massola, N. S., Bebendo, I. P., Amorin, L., & Lopes, J. R. S. (1999a). Effects of the inoculation time on corn with Spiroplasma kunkelii on yield components. Fitopatologia Brasileira, 24, 571–573.
Massola, N. S., Bebendo, I. P., Amorin, L., & Lopes, J. R. S. (1999b). Quantificação de danos causados pelo enfezamento vermelho e enfezamento pálido do milho em condições de campo. Fitopatologia brasileira, 24(2), 136–142 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=10137411
Mendoza, M., López, A., Rodriguez, S. A., Oyervides García, A., De León, C., & Jeffers, D. (2002). Acción génica de la resistencia al Achaparramiento del maíz causado por espiroplasma, fitoplasmas y virus. Revista Mexicana de Fitopatología, 20, 13–17.
Nault, L. R. (1980). Maize Bushy Stunt and Corn Stunt: a comparison of disease symptoms, pathogen host ranges, and vectors. Phytopathology, 70(7), 659. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-70-659
Oleszczuk, J. D., Catalano, M. I., Dalaisón, L., Di Rienzo, J. A., Giménez Pecci, M. P., & Carpane, P. (2020). Characterization of components of resistance to Corn Stunt disease. PLOS ONE, 15(10), e0234454. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0234454
Pérez López, E., Olivier, C. Y., Luna Rodríguez, M., Rodríguez, Y., Iglesias, L. G., Castro Luna, A., Adame García, J., & Dumonceaux, T. J. (2016). Maize bushy stunt phytoplasma affects native corn at high elevations in Southeast Mexico. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 145(4), 963–971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0883-0
Ritchie, S. W., & Hanway, J. J. (1982). How a corn plant develops. Iowa State University of Science and Technology. Cooperative Extension Service Ames, Iowa. Special Report N° 48.
Sabato, E. O., Landau, E. C., Barros, B. A., & Oliveira, C. M. (2020). Differential transmission of phytoplasma and spiroplasma to maize caused by variation in the environmental temperature in Brazil. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 157(1), 163–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-020-01997-9
Scott, G. E., Rosenkranz, E. E., & Nelson, L. R. (1977). Yield loss of corn due to corn stunt disease complex 1. Agronomy Journal, 69(1), 92–94. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1977.00021962006900010024x
Sierra Macías, M., Becerra Leor, E., Palafox Caballero, A., Rodriguez Montalvo, F., Espinosa Calderón, A., & Valdivia Bernal, R. (2010). Tropical corn (Zea mays L.) genotypes with high yield and tolerance to corn stunt disease in the gulf of Mexico region. Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, 12, 485–493.
Silva, R. G., Galvão, J. C., Miranda, G. V., & De Oliveira, E. (2003). Controle genético da resistência aos enfezamentos do milho. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 38(8), 921–928. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2003000800004
Sutula, C. L. (1986). Interpreting ELISA data and establishing the positive-negative threshold. Plant Disease, 70(8), 722. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-70-722
Teixeira, F. F., Costa, F. M., Sabato, E. O., Leite, C. E., Meirelles, W., Guimarães, C., & Belicuas, S. (2013). Pré-melhoramento de milho quanto à resistência a enfezamentos. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 48(1), 51–58. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2013000100007
Virla, E. G., Díaz, C. G., Carpane, P., Laguna, I. G., Ramallo, J., Gerónimo Gómez, L., & Giménez Pecci, M. P. (2004). Evaluación preliminar de la disminución en la producción de maíz causada por el " Corn stunt spiroplasma " ( CSS ) en Tucumán. Argentina. Boletín de Sanidad Vegetal. Plagas, 30, 403–413.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Sergio Uhart (Corteva Agriscience Argentina) and Irma Graciela Laguna (Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas – CONICET - INTA) for critical reading of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from PD-E4-I090-001 (INTA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that there are no competing economic interests or known personal relationships that may have interfered with the work reported in this document. All authors are informed and agree on the publication of the manuscript.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable, the research does not involve humans or animals.
Informed consent
Not applicable, the research does not involve human participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barontini, J.M., Malavera, A.P., Ferrer, M. et al. Infection with Spiroplasma kunkelii on temperate and tropical x temperate maize in Argentina and development of a tool to evaluate germplasm. Eur J Plant Pathol 162, 455–463 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02415-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02415-4